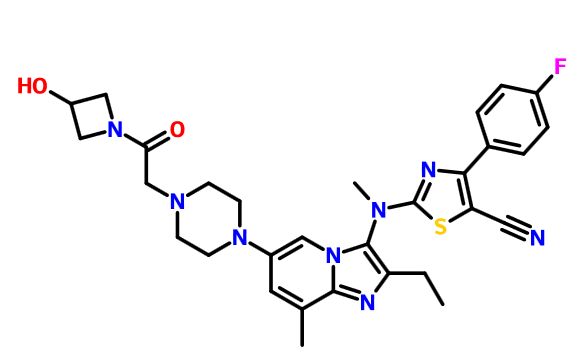
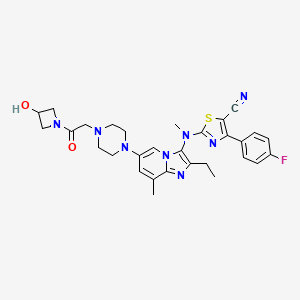
LY 2922470
as per WO2013025424A1

LY 2922470
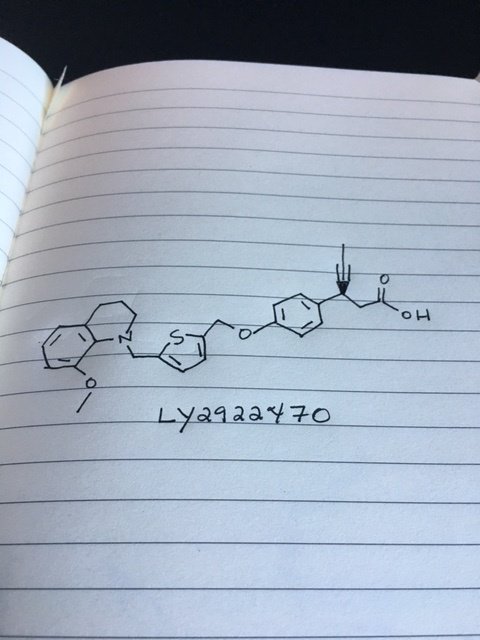
Picture credit....Bethany Halford
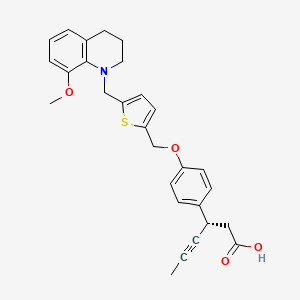
(3S)-3-[4-[[5-[(8-methoxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl)methyl]thiophen-2-yl]methoxy]phenyl]hex-4-ynoic acid
Benzenepropanoic acid, 4-[[5-[(3,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-1(2H)-quinolinyl)methyl]-2-thienyl]methoxy]-β-1-propyn-1-yl-, (βS)-
Glucose Lowering Agents, Signal Transduction Modulators
| CAS | 1423018-12-5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula: | C28H29NO4S |
| Molecular Weight: | 475.59916 g/mol |
|---|
- Phase I Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Eli Lilly And Company
Antihyperglycaemics
- 28 Jan 2014 Eli Lilly completes a phase I trial in Type-2 diabetes mellitus in USA (NCT01867216)
- 30 Jun 2013 Phase-I clinical trials in Type-2 diabetes mellitus in USA (PO)
- 14 Jun 2013 Eli Lilly plans a phase I trial for Type-2 diabetes mellitus in USA (NCT01867216)
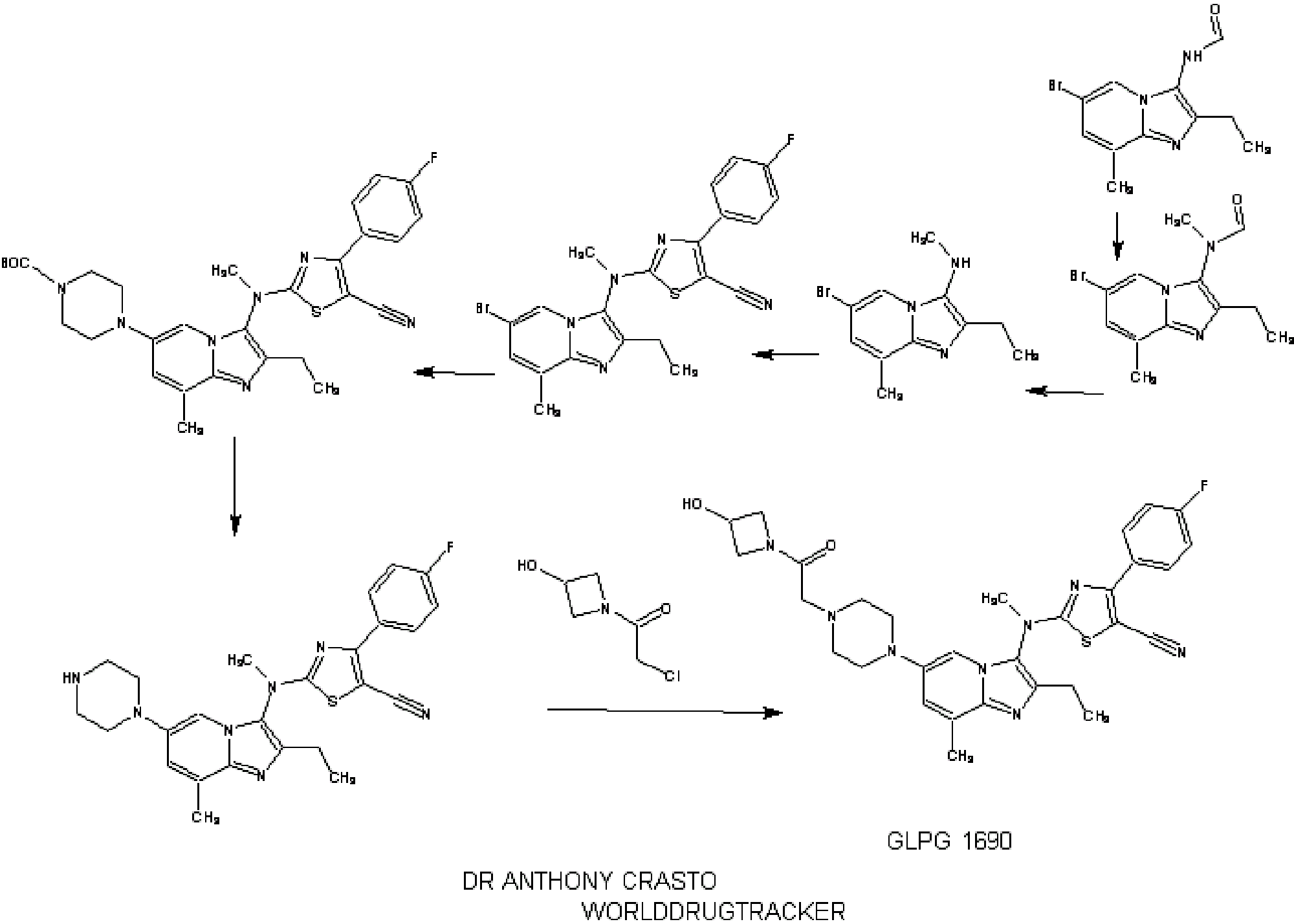
WO 2013025424
https://www.google.com/patents/US20130045990?cl=de
| Also published as | CA2843474A1, CA2843474C, CN103687856A, CN103687856B, EP2744806A1, US8431706, WO2013025424A1, Less « |
| Inventors | Chafiq Hamdouchi |
| Original Assignee | Eli Lilly And Company |



Preparation 18-Methoxyquinoline
Add potassium hydroxide (435 g, 7.76 mol) to a solution of 8-hydroxy quinoline (250 g, 1.724 mol) in THF (10 L) at ambient temperature and stir. Add methyl iodide (435 g, 2.58 mol) dropwise and stir overnight. Filter the reaction mixture and wash the solid with THF (2 L). Concentrate the solution to dryness; add water; extract with dichloromethane (2×3 L); combine the organic layers; and wash with brine. Collect the organic layers and dry over sodium sulfate. Remove the solids by filtration. Collect the filtrate and concentrate under reduced pressure to give a red oil, which solidifies on standing, to give the title compound (281 g, 102%), which can be used without further purification. ESI (m/z) 160(M+H).
Preparation 2
8-Methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline
Add sodium cyanoborohydride (505 g, 8.11 mol) in EtOH (1 L) to a solution of 8-methoxy quinoline (425 g, 2.673 mol) in EtOH (9 L), and stir. Cool the reaction mixture to an internal temperature of 0° C. and add HCl (35%, 1.12 L, 10.962 mol) dropwise over 60 min so that the internal temperature did not rise above 20° C. Allow the reaction mixture to warm to ambient temperature and then heat to reflux for 2.5 hours. Cool to ambient temperature and stir overnight. Add ammonium hydroxide (25%, 1 L); dilute with water (15 L); and extract the mixture with dichloromethane (3×10 L). Combine the organic layers and dry over sodium sulfate. Remove the solids by filtration. Collect the filtrate and concentrate under reduced pressure to give a residue. Purify the residue by silica gel flash chromatography, eluting with ethyl acetate: hexane (1:10) to give the title compound (357 g, 82%). ESI (m/z) 164(M+H).
Preparation 3
Methyl-5-methylthiophene-2-carboxylate
Add thionyl chloride (153 ml, 2.1 mol) dropwise over 20 min to a solution of 5-methylthiophene-2-carboxylic acid (100 g, 0.703 mol) in MeOH (1 L) at 0° C. and stir. After the addition is complete, heat the reaction mixture to reflux for 3.5 hours. Cool and concentrate in vacuo to give a thick oil. Dilute the oil with EtOAc (500 ml) and sequentially wash with water (300 ml) then brine (300 ml). Dry the organic layer over sodium sulfate. Remove the solids by filtration. Collect the filtrate and concentrate under reduced pressure to give the title compound (106 g, 97%), which is used without further purification. ESI (m/z) 156(M+H).
Preparation 4
Methyl 5-(bromomethyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate
Add freshly recrystallised NBS (323.8 g, 1.81 mol) to a solution of methyl-5-methylthiophene-2-carboxylate (258 g, 1.65 mol) in chloroform (2.6 L) at room temperature, and stir. Add benzoyl peroxide (3.99 g, 0.016 mol) and heat the reaction mixture to reflux for 7 hours. Cool the reaction mixture to ambient temperature and filter through diatomaceous earth. Wash the filter cake with chloroform (250 ml). Collect the organic layers and remove the solvent to give the title compound (388 g, 100%), which is used without further purification. ESI (m/z) 236(M+H).
Preparation 5
Methyl-5-[8-methoxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl)methyl]thiophene-2-carboxylate
Add methyl-5-(bromoethyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate (432.5 g, 1.84 mol) in EtOH (500 ml) to a solution of 8-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline (300 g 1.84 mol) in EtOH (1 L) and stir. Add DIPEA (641 ml, 3.67 mol) dropwise and stir at room temperature overnight. After completion of the reaction, remove the EtOH in vacuo, and add water (5 L). Extract the aqueous with EtOAc (3×3 L); combine the organic layers; and dry over sodium sulfate. Filter the solution and concentrate under reduced pressure to give a residue. Purify the residue by silica gel flash chromatography eluting with ethyl acetate: hexane (6:94) to give the title compound (325 g, 56%). ESI (m/z) 318(M+H).
Preparation 6
[5-[(8-Methoxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl)methyl]-2-thienyl]methanol
Add DIBAL-H (1 M in toluene 2.7 L, 2.66 mol) slowly via a cannula over a period of 1.5 h to a stirred solution of methyl-5-(8-methoxy-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1(2H)-yl)methyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate (281 g, 0.886 mol) in THF (4 L) at −70° C. Monitor the reaction via thin layer chromatography (TLC) for completion. After completion of the reaction, allow the reaction mixture to warm to 20° C. and add a saturated solution of ammonium chloride. Add a solution of sodium potassium tartrate (1.3 Kg in 5 L of water), and stir overnight. Separate the organic layer; extract the aqueous phase with EtOAc (2×5 L); then combine the organic layers; and dry the combined organic layers over sodium sulfate. Remove the solids by filtration. Remove the solvent from the filtrate under reduced pressure to give the title compound as a white solid (252 g, 98%). ESI (m/z) 290(M+H).
Preparation 7
Ethyl(3S)-3-[4-[[5-[(8-methoxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl)methyl]-2-thienyl]methoxy]phenyl]hex-4-ynoate
Add tributylphosphine (50% solution in EtOAc, 543 ml, 1.34 mol) to a solution of ADDP (282.5 g, 1.5 eq) in THF (3 L) and cool the mixture to an internal temperature of 0° C., then stir for 15 minutes. Add (S)-ethyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hex-4-ynoate (173.5 g, 0.747 mol) in THF (3 L) dropwise over 15 min; then add 5-((8-methoxy-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1(2H)-yl)methyl)thiophene-2-yl)methanol (216 g, 0747 mol) in THF (5 L) dropwise. Allow the reaction mixture to warm to ambient temperature and stir overnight. Filter the reaction mixture through diatomaceous earth and wash the filter cake with ethyl acetate (2 L). Concentrate the organic filtrate to dryness. Add water (4 L); extract with ethyl acetate (3×5 L); combine the organic layers; and dry the combined organic layers over sodium sulfate. Remove the solids by filtration and concentrate under reduced pressure to give an oil. Purify the residue by silica gel flash chromatography by eluting with ethyl acetate: hexane (6:94) to give the title compound (167 g, 44%). ESI (m/z) 504(M+H).
Example 1
(3S)-3-[4-[[5-[(8-Methoxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl)methyl]-2-thienyl]methoxy]phenyl]hex-4-ynoic acid

Add a solution of potassium hydroxide (49.76 g, 0.88 mol) in water (372 ml) to a solution of (S)-ethyl-3-(4-((5-8-methoxy-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1(2H)-yl)methyl)thiophen-2-yl)methoxy) phenyl)hex-4-ynoate (149 g, 0.296 mol) in EtOH (1.49 L) at room temperature and stir overnight. Concentrate the reaction mixture to dryness and add water (1.3 L). Extract the resulting solution with EtOAc (2×300 ml) and separate. Adjust the pH of the aqueous layer to pH=6 with 2 N HCl. Collect the resulting solids. Recrystallise the solids from hot MeOH (298 ml, 2 vol) to give the title compound (91 g, 65%). ESI (m/z) 476(M+H).
Abstract
GPR40 agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: From the laboratory to the patient
251st Am Chem Soc (ACS) Natl Meet (March 13-17, San Diego) 2016, Abst MEDI 260


Presenter

Chafiq Hamdouchi
Senior Research Advisor at Eli Lilly and Company
Summary
Dr. Hamdouchi earned his bachelor’s degree and doctorate in organic chemistry from Louis Pasteur University, Strasbourg-France.
Following two postdoctoral fellowships, sponsored by the National Science Foundation-USA and Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia-Spain, he joined Eli Lilly and Company in 1995.
Throughout his 20 years of career at Lilly, he has contributed to a sustainable drug discovery portfolio from preclinical hypothesis to clinical proof-of-concept that spans the oncology, neuroscience and endocrinology therapeutic areas. He has led multidisciplinary (chemistry, pharmacology, ADMET, PK, medical) scientific teams in USA, Europe and Asia to deliver a number of compounds that achieved first human dose.
He is a co-inventor of six innovative molecules being pursued in clinical development for the treatment of Diabetes, Cancer and Neurodegenerative Diseases.
He has an extensive patent and publication record and deep experience in conducting drug discovery and development in Asia through effective partnership and mentorship.
Following two postdoctoral fellowships, sponsored by the National Science Foundation-USA and Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia-Spain, he joined Eli Lilly and Company in 1995.
Throughout his 20 years of career at Lilly, he has contributed to a sustainable drug discovery portfolio from preclinical hypothesis to clinical proof-of-concept that spans the oncology, neuroscience and endocrinology therapeutic areas. He has led multidisciplinary (chemistry, pharmacology, ADMET, PK, medical) scientific teams in USA, Europe and Asia to deliver a number of compounds that achieved first human dose.
He is a co-inventor of six innovative molecules being pursued in clinical development for the treatment of Diabetes, Cancer and Neurodegenerative Diseases.
He has an extensive patent and publication record and deep experience in conducting drug discovery and development in Asia through effective partnership and mentorship.
SEE AT............ONE ORGANIC CHEMIST ONE DAY BLOG
| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8431706 | 2013-04-30 | 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroqinoline derivative useful for the treatment of diabetes |
GPR40 agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: From the laboratory to the patient
251st Am Chem Soc (ACS) Natl Meet (March 13-17, San Diego) 2016, Abst MEDI 260
//////Phase 1, LY2922470, LY 2922470, Eli Lilly, Type 2 diabetes mellitus, 1423018-12-5, Chafiq Hamdouchi
CC#CC(CC(=O)O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)OCC2=CC=C(S2)CN3CCCC4=C3C(=CC=C4)OC
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
 amcrasto@gmail.com
amcrasto@gmail.com
P.STHE VIEWS EXPRESSED ARE MY PERSONAL AND IN NO-WAY SUGGEST THE VIEWS OF THE PROFESSIONAL BODY OR THE COMPANY THAT I REPRESENT, amcrasto@gmail.com, +91 9323115463 India.
I , Dr A.M.Crasto is writing this blog to share the knowledge/views, after reading Scientific Journals/Articles/News Articles/Wikipedia. My views/comments are based on the results /conclusions by the authors(researchers). I do mention either the link or reference of the article(s) in my blog and hope those interested can read for details. I am briefly summarising the remarks or conclusions of the authors (researchers). If one believe that their intellectual property right /copyright is infringed by any content on this blog, please contact or leave message at below email address amcrasto@gmail.com. It will be removed ASAP









 .
.