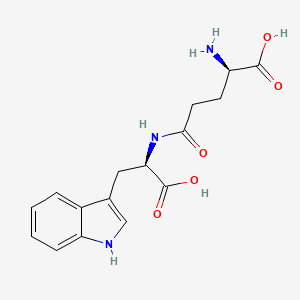
Orilotimod
(2R)-2-amino-5-{[(1R)-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino}-5-oxopentanoic acid
Apo805,UNII-Q66Z43C5XM; Thymodepressin; Orilotimod [USAN]; AC1OIBUF;
- C16H19N3O5
- MW 333.339
Orilotimod potassium,
-
APO805K1
D-Tryptophan, D-gamma-glutamyl-, potassium salt (1:1), CAS 960155-19-5
The drug, orilotimod, was originally developed and launched by Immunotech Developments; however, ApoPharma (a subsidiary of Apotex) is developing orilotimod, presumably a topical formulation, for the treatment of psoriasis. In August 2015, the ApoPharma’s drug was reported to be in phase 2 clinical development.
Thymodepressin is the free diacid having Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) Registry Number@ of 186087-26-3. U.S. Pat. No. 5,736,519 discloses H-D-iGlu-D-Trp-OH and a process for its preparation wherein it is purified by ion exchange chromatography. It is an immunosuppressant and selectively inhibits proliferation of hemopoietic precursor cells and stimulates granulocyte and lymphocyte apoptosis (Sapuntsova, S. G., et al. (May 2002), Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 133(5), 488-490).Thymodepressin is currently being sold in Russia as the disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan in liquid formulation for injection and intranasal administration for the treatment of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. The solid form of the disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan is an amorphous powder which is hygroscopic and very difficult to handle. The disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan has the molecular formula C16H17N3Na2O5 and is reported in Kashirin, D. M., et al. (2000), Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 34(11), 619-622.
PAPENT
BEAWARE EXAMPLE WITH AN ESTER GP
http://www.google.im/patents/WO2012129671A1?cl=en
Preparation of H-D-Glu( -Trp-OH)-0-Et hydrochloride salt (Apo836.HCI)
A. Preparation of Boc-D-Glu(D-Trp-0-Bzl)-0-Et
Proceeding in a similar manner as described under Example 3A, Boc-D- Glu(D-Trp-0-Bzl)-0-Et was prepared in 87% yield.1H NMR ( DMSO-D6l 400 MHz) δ ppm: 10.87, (s, 1 H), 8.35 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1 H), 7.48 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.35 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1 H), 7.29-7.33 (m, 3H), 7.23 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.09-7.22 (m, 3H), 7.08 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.98 (t, J = 7,7 Hz, 1 H), 4.98 – 5.06 (m, 2H), 4.55 (apparent q, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H), 4.04 – 4.11 (m, 2H), 3.90 – 3.95 (m, 1 H), 3.04 – 3.19 (m, 2H), 2.18 – 2.23 (m, 2H), 1.84 – 1.89 (m, 1 H), 1.70 – 1.77 (m, 1 H), 1.38 (s, 9H), 1.16 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); MS-ESI (m/z): 552 [ +1]+.
B. Preparation of Boc-D-Glu(D-Trp-OH)-0-Et
Proceeding in a similar manner as described under Example 3B, Boc-D-
Glu(D-Trp-OH)-0-Et was prepared in quantitative yield. 1H NMR ( DMSO-D6, 400 MHz) δ ppm: 12.62 (br. 1H), 10.82, (s, 1 H), 8.10 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.23 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.12 (s, 1 H), 7.06 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H), 6.98 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1 H)„ 4.45 (apparent q, J = 7.7 Hz, 1 H), 4.03 – 4.11 (m, 2H), 3.87 – 3.92 (m, 1 H), 3.13 – 3.18 (m, 1H), 2.96 – 3.03 (m,
1 H), 2.13 – 2.20 (m, 2H), 1.82 – 1.88 (m, 1H), 1.69-1.75 (m, 1 H), 1.38 (s, 9H>, 1.17 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); MS-ESI (m/z): 462 [M+1]+.
C. Preparation of H-D-Glu(D-Trp-OH)-0-Et.HCI (Apo836 HCI)
To an ice-cooled solution of Boc-D-Glu(D-Trp-OH)-0-Et (4.55 g, 9.8 mmol) obtained in Section B above in dichloromethane (100 mL) was bubbled HCI gas for 15 min. The reaction mixture was concentrated under vacuum by rotary evaporation to give H-D-Glu(D-Trp-OH)-0-Et hydrochloride (Apo836.HCI, 4.0 g) as a foamy solid. 1 H NMR ( DMSO-D6, 400 MHz) δ ppm: 12.68 (br. s, 1 H), 10.90, (s, 1H), 8.66 (br, s, 3H), 8.33 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.52 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.12 (d, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.06 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1 H), 6.98 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1 H), 4.47 (apparent q, J = 4.8 Hz, 1 H), 4.13 – 4.19 (m, 2H), 3.90 (br, 1 H), 3.16 – 3.20 (m, 1H), 2.98 – 3.04 (m, 1 H), 2.29 – 2.33 (m, 2H), 1.94 – 1.98
(m, 2H), 1.20 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); MS-ESI (m/z): 362 [M+1]+ (free base).
……………………..
US 20150225341
file:///H:/ORILOTIMODUS20150225341A1.pdf
Novel crystalline and amorphous salts of thymodepressin (orilotimod), particularly potassium salt, useful for treating psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Also claims salt exchange method for preparing thymodepressin salts.
hymodepressin is the free diacid having Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) Registry Number@ of 186087-26-3. U.S. Pat. No. 5,736,519 discloses H-D-iGlu-D-Trp-OH and a process for its preparation wherein it is purified by ion exchange chromatography. It is an immunosuppressant and selectively inhibits proliferation of hemopoietic precursor cells and stimulates granulocyte and lymphocyte apoptosis (Sapuntsova, S. G., et al. (May 2002), Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 133(5), 488-490).
Thymodepressin is currently being sold in Russia as the disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan in liquid formulation for injection and intranasal administration for the treatment of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. The solid form of the disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan is an amorphous powder which is hygroscopic and very difficult to handle. The disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan has the molecular formula C16H17N3Na2O5 and which is reported in Kashirin, D. M., et al. (2000), Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 34(11), 619-622.
Through investigations in our laboratory, we have determined that the freeze-dried disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan is extremely hygroscopic turning into a gel in a matter of minutes in air and cannot easily be handled.
A powdery or amorphous form of a compound, intended for pharmaceutical use may give rise to manufacturing problems due to bulk density issues, hygroscopicity and variable water content that cannot be corrected by vacuum drying. D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan is a dipeptide and the drying of an amorphous form at elevated temperature, for example, 80-100° C. under vacuum is not recommended. Thus, there are serious difficulties experienced during the purification of the disodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan and obtaining the pure disodium salt on a manufacturing scale. Further, there is no published procedure for its preparation.
The monosodium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan is identified by the CAS Registry System and is listed in the CAS REGISTRYSM File with a CAS Registry Number@ of 863988-88-9. However, there are no references citing the substance and thus no publication of its identity, its physical and/or chemical properties, its characterization or a procedure for its preparation. Freeze-dried powders of mono sodium and disodium salts of peptide drugs may not have controllable powder bulk density ranges for formulation. They may require significant investment in freeze-dried dispersion technology.
EXAMPLES
Example 1
Preparation of potassium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan (1:1) from D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan and potassium hydroxide
In a 100-mL round bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stir bar was placed 5 mL of potassium hydroxide solution (0.5 N). The solution was cooled to 0° C. in an ice-water bath, and solid H-D-iGlu-D-Trp-OH (1.00 g, 3 mmol) was added. The mixture was stirred while the pH of the solution was adjusted to ca. 6.0 by adding a few drops of potassium hydroxide solution (0.5 N). The solution was filtered to remove any solid particulates. The filtrate was evaporated to dryness at a bath temperature of about 30° C. to afford a solid. After drying under vacuum at room temperature for overnight, the salt was obtained in quantitative yield, with a HPLC purity (peak area percent) of 98.3%. HPLC method; Column: XTerra MS C18; 5 μm, 4.6×250 mm; Mobile phase: A=the aqueous phase: 4 mM Tris, 2 mM EDTA, pH 7.4; B=the organic phase: CH3CN; gradient: B %: 0 min. 5%, 15 min. 55%, 30 min. 55%, 32 min. 5%, 35 min. 5%; Flow rate: 1 mL/min; injection volume: 5 μL; λ: 222, 254, 282, 450 nm; retention time of the product: 6.41 min. The XRPD pattern of this crystalline material is shown in FIG. 1A; the water content by Karl-Fischer test is 0.7%; UV (water, c=23.8 ρM, λmax nm): 221 (ε 33270), 280 (ε 5417); MS (m/z): 372.0 [M]+, 334.2 [C16H20N3O5]+, 187.9 (100%). The FT-IR (KBr) spectrum is shown in FIG. 1B.Example 2
A. Preparation of mono potassium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan (1:1) from the mono ammonium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan (1:1)
A solution of H-D-iGlu-D-Trp-OH, mono ammonium salt (1:1), (1.66 g, 4.05 mmol) and potassium hydroxide (253 mg, 4.50 mmol) in water (20 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 15 min. The pH of the solution was about 9. The reaction mixture was evaporated under reduced pressure to a volume of about 1 mL. After cooling to room temperature, isopropanol was added until a solid precipitated out. The resulting suspension was stirred at room temperature for 15 min, then filtered. The solid was washed with isopropanol (2×20 mL) and ethyl acetate (20 mL), then dried under vacuum in an oven at 42° C. overnight. An off white solid was obtained (1.49 g, 99% yield). The water content by Karl-Fischer test is 2.5%. Analytical data (XRPD pattern, FT-IR and MS spectra) are similar to those described in Example 1.B. Preparation of amorphous form of potassium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan (1:1) from the mono ammonium salt of D-isoglutamyl-D-tryptophan (1:1)
A solution of H-D-iGlu-D-Trp-OH, mono ammonium salt (1:1), (517 mg, 1.40 mmol) and potassium hydroxide (82 mg, 1.46 mmol) in water (10 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. The resulting mixture was freeze-dried overnight. An off white solid was obtained in quantitative yield. The XRPD pattern spectrum confirmed that this material is amorphous.1H NMR (D2O) δ: 7.69 (d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (d, J=8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.23 (t, J=7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 7.16 (t, J=7.4 Hz, 1H), 4.59 (dd, J=8.7, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 3.51 (dd, J=6.8, 5.8 Hz, 1H), 3.38 (dd, J=14.8, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 3.11 (dd, J=14.8, 8.8 Hz, 1H), 2.20-2.49 (m, 2H) and 1.85-1.94 (m, 2H);
13C NMR (D2O) δ: 181.4, 177.0, 176.6, 138.8, 129.9, 126.9, 124.5, 121.9, 121.4, 114.5, 113.2, 58.6, 57.0, 34.6 (CH2), 30.2 (CH2) and 29.3 (CH2);
the water content by Karl-Fischer test is 5.4%;
the FT-IR (KBr) spectrum is shown in FIG. 1C;
MS (m/z): 371.7 [M]+, 334.2 [C16H20N3O5]+, 187.9 (100%);
HPLC purity (peak area percent): 99.8%, Retention time: 5.04 min; HPLC conditions: Column Waters Symmetry C18, 3.9×150 mm, 5 μm; Mobile phase: 0.035% HClO4, pH 2/CH3CN, 85/15, isocratic, Flow rate: 1 mL/min; λ: 220, 254, 280 nm.
| Patent | Submitted | Granted |
|---|---|---|
| GAMMA-GLUTAMYL AND BETA-ASPARTYL CONTAINING IMMUNOMODULATOR COMPOUNDS AND METHODS THEREWITH [EP1042286] | 2000-10-11 | 2010-08-25 |
| CRYSTALLINE D-ISOGLUTAMYL-D-TRYPTOPHAN AND THE MONO AMMONIUM SALT OF D-ISOGLUTAMYL-D-TRYPTOPHAN [US8119606] | 2010-01-21 | 2012-02-21 |
| Pharmaceutically Acceptable Salts of Thymodepressin and Processes for their Manufacture [US8138221] | 2010-03-04 | 2012-03-20 |
| CRYSTALLINE FORMS OF THE MONO-SODIUM SALT OF D-ISOGLUTAMYL-D-TRYPTOPHAN [US8207217] | 2010-02-04 | 2012-06-26 |
सुकून उतना ही देना प्रभू, जितने से जिंदगी चल जाये। औकात बस इतनी देना, कि औरों का भला हो जाये।
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE LIONEL MY SON
LIONEL MY SON
He was only in first standard in school when I was hit by a deadly one in a million spine stroke called acute transverse mylitis, it made me 90% paralysed and bound to a wheel chair, Now I keep him as my source of inspiration and helping millions, thanks to millions of my readers who keep me going and help me to keep my son happy

जिंदगी चल जाये।
औकात बस इतनी देना,
कि औरों का भला हो जाये।
Read all about Organic Spectroscopy on ORGANIC SPECTROSCOPY INTERNATIONAL

////////Orilotimod, PHASE 2, thymodepressin, APO 805K1
C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=CN2)CC(C(=O)O)NC(=O)CCC(C(=O)O)N




No comments:
Post a Comment