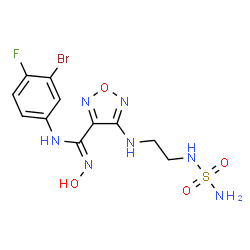
Epacadostat
(Z)-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-4-[2-(sulfamoylamino)ethylamino]-1,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboxamidine
1,2,5-Oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide, 4-[[2-[(aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl]amino]-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-
1204669-58-8
INCB024360
N-(3-Brom-4-fluorphenyl)-N'-hydroxy-4-{[2-(sulfamoylamino)ethyl]amino}-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-carboximidamid
UNII 71596A9R13
(Z)-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-4-(2-(sulfamoylamino)ethylamino)-1,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
1,2,5-Oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide, 4-[[2-[(aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl]amino]-N'-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N-hydroxy-
Molecular Formula, C11H13BrFN7O4S
Average mass438.233 Da
cas 1204669-58-8 (or 1204669-37-3)
| Synonym: | IDO1 inhibitor INCB024360
indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor INCB024360 |
| Code name: | INCB 024360
INCB024360 |
| Chemical structure: | 1,2,5-Oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide, 4-((2-((Aminosulfonyl)amino)ethyl)amino)-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-, (C(Z))- |
| Company | Incyte Corp. |
| Description | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitor |
| Molecular Target | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) |
| Mechanism of Action | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (INDO) inhibitor |
| Therapeutic Modality | Small molecule |


- OriginatorIncyte Corporation
- DeveloperFred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center; Incyte Corporation; Merck AG
- ClassAmides; Antineoplastics; Imides; Oxadiazoles; Small molecules
- Phase IIFallopian tube cancer; Malignant melanoma; Non-small cell lung cancer; Ovarian cancer; Peritoneal cancer; Solid tumours
Most Recent Events
- 15 Jan 2016Phase-II clinical trials in Solid tumours (Combination therapy, Late-stage disease, Second-line therapy or greater) in USA (PO)
- 11 Jan 2016Phase-II
clinical trials in Non-small cell lung cancer (Combination therapy,
Late-stage disease, Second-line therapy or greater) in USA (PO)
- 11 Jan 2016The
US FDA and Health Canada approve IND application and Clinical Trial
Application, respectively, for a phase Ib trial in Ovarian cancer
(Combination therapy, Recurrent, Second-line therapy or greater)
In 2016, orphan drug designation was assigned to the compound in the US. for the treatment of stage IIB-IV melanoma
EpacadostatAn
orally available hydroxyamidine and inhibitor of indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1), with potential immunomodulating and
antineoplastic activities. epacadostat targets and binds to IDO1, an
enzyme responsible for the oxidation of tryptophan into kynurenine. By
inhibiting IDO1 and decreasing kynurenine in tumor cells, epacadostat
increases and restores the proliferation and activation of various
immune cells, including dendritic cells (DCs), NK cells, and
T-lymphocytes, as well as interferon (IFN) production, and a reduction
in tumor-associated regulatory T cells (Tregs). Activation of the immune
system, which is suppressed in many cancers, may inhibit the growth of
IDO1-expressing tumor cells. IDO1 is overexpressed by a variety of tumor
cell types and DCsINCB24360 (epacadostat), An Agent For Cancer
Immunotherapy
Incyte and Merck Expand Clinical Collaboration to
Include Phase 3 Study Investigating the Combination of Epacadostat with
Keytruda® (pembrolizumab) as First-line Treatment for Advanced Melanoma
Pivotal
study to evaluate Incyte’s IDO1 inhibitor in combination with Merck’s
anti-PD-1 therapy in patients with advanced or metastatic melanoma
WILMINGTON,
Del. and KENILWORTH, N.J. -- October 13, 2015 -- Incyte Corporation
(Nasdaq: INCY) and Merck (NYSE:MRK), known as MSD outside the United
States and Canada, today announced the expansion of the companies’
ongoing clinical collaboration to include a Phase 3 study evaluating the
combination of epacadostat, Incyte’s investigational selective IDO1
inhibitor, with Keytruda® (pembrolizumab), Merck’s anti-PD-1 therapy, as
first-line treatment for patients with advanced or metastatic melanoma.
The Phase 3 study, which is expected to begin in the first half of
2016, will be co-funded by Incyte and Merck.
“We are very pleased
to expand our collaboration with Merck and to move the clinical
development program for epacadostat in combination with Keytruda into
Phase 3,” said Hervé Hoppenot, President and Chief Executive Officer of
Incyte. “We believe the combination of these two immunotherapies shows
promise and, if successfully developed, may help to improve clinical
outcomes for patients with metastatic melanoma.”
“The initiation
of this large Phase 3 study with Incyte in the first-line advanced
melanoma treatment setting is an important addition to our robust
immunotherapy clinical development program for Keytruda,” said Dr. Roger
Dansey, senior vice president and therapeutic area head, oncology
late-stage development, Merck Research Laboratories. “We continue to
explore the benefit that Keytruda brings to patients suffering from
advanced melanoma when used alone, and we are pleased to be able to add
this important combination study with epacadostat to our Keytruda
development program.”
Under the terms of the agreement Incyte and
Merck have also agreed, for a period of two years, not to initiate new
pivotal studies of an IDO1 inhibitor in combination with a PD-1/PD-L1
antagonist as first-line therapy in advanced or metastatic melanoma with
any third party. During this time, the companies will each offer the
other the opportunity to collaborate on any new pivotal study involving
an IDO1 inhibitor in combination with a PD-1/PD-L1 antagonist for types
of melanoma and lines of therapy outside of the current collaboration
agreement.
The agreement is between Incyte and certain subsidiaries and Merck through its subsidiaries.
Epacadostat
and Keytruda are part of a class of cancer treatments known as
immunotherapies that are designed to enhance the body’s own defenses in
fighting cancer; the two therapies target distinct regulatory components
of the immune system. IDO1 is an immunosuppressive enzyme that has been
shown to induce regulatory T cell generation and activation, and allow
tumors to escape immune surveillance. Keytruda is a humanized monoclonal
antibody that blocks the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands,
PD-L1 and PD-L2. Preclinical evidence suggests that the combination of
these two agents may lead to an enhanced anti-tumor immune response
compared with either agent alone.
Safety and efficacy data from
the ongoing Phase 1/2 study evaluating the combination of epacadostat
with Keytruda in patients with advanced malignancies is scheduled to be
highlighted as a late-breaking oral presentation (Abstract #142) at the
upcoming Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer 30th Anniversary Annual
Meeting & Associated Programs, November 4–8, 2015 at the Gaylord
National Resort & Convention Center in National Harbor, MD.
Metastatic Melanoma
Melanoma,
the most serious form of skin cancer, strikes adults of all ages and
accounts for approximately five percent of all new cases of cancer in
the United States each year. The number of new cases of melanoma
continues to rise by almost three percent each year which translates to
76,000 new cases yearly in the U.S. alone.[i] The 5-year survival rate
for late-stage or metastatic disease is 15 percent.[ii]
About Epacadostat (INCB024360)
Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is an immunosuppressive enzyme that has been
shown to induce regulatory T cell generation and activation, and allow
tumors to escape immune surveillance. Epacadostat is an orally
bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of IDO1 that has nanomolar potency
in both biochemical and cellular assays and has demonstrated potent
activity in enhancing T lymphocyte, dendritic cell and natural killer
cell responses in vitro, with a high degree of selectivity. Epacadostat
has shown proof-of-concept clinical data in patients with unresectable
or metastatic melanoma in combination with the CTLA-4 inhibitor
ipilimumab, and is currently in four proof-of-concept clinical trials
with PD-1 and PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in a variety of cancer
histologies.

PATENT
WO 2014066834
https://www.google.com/patents/WO2014066834A1?cl=en
EXAMPLE 1
4-({2-[(Aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl}amino)- V-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)- V -hydroxy- l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
Step 1: 4-Amino-N'-hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
[00184]
Malononitrile (320.5 g, 5 mol) was added to water (7 L) preheated to 45
°C and stirred for 5 min. The resulting solution was cooled in an ice
bath and sodium nitrite (380 g, 5.5 mol) was added. When the temperature
reached 10 °C, 6 N hydrochloric acid (55 mL) was added. A mild
exothermic reaction ensued with the temperature reaching 16 °C. After 15
min the cold bath was removed and the reaction mixture was stirred for
1.5 hrs at 16-18 °C. The reaction mixture was cooled to 13 °C and 50%
aqueous hydroxylamine (990 g, 15 mol) was added all at once. The
temperature rose to 26 °C. When the exothermic reaction subsided the
cold bath was removed and stirring was continued for 1 hr at 26-27 °C,
then it was slowly brought to reflux. Reflux was maintained for 2 hrs
and then the reaction mixture was allowed to cool overnight. The
reaction mixture was stirred in an ice bath and 6 N hydrochloric acid
(800 mL) was added in portions over 40 min to pH 7.0. Stirring was
continued in the ice bath at 5 °C. The precipitate was collected by
filtration, washed well with water and dried in a vacuum oven (50 °C) to
give the desired product (644 g, 90%). LCMS for C3H6N5O2
(M+H)+: m/z = 144.0.
13C
MR (75 MHz, CD3OD): δ 156.0, 145.9, 141.3. Step 2:
4-Amino-N-hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl chloride [00185]
4-Amino-N
,-hydroxy-l ,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide (422
g, 2.95 mol) was added to a mixture of water (5.9 L), acetic acid (3 L)
and 6 Ν hydrochloric acid (1.475 L, 3 eq.) and this suspension was
stirred at 42 - 45 °C until complete solution was achieved. Sodium
chloride (518 g, 3 eq.) was added and this solution was stirred in an
ice/water/methanol bath. A solution of sodium nitrite (199.5 g, 0.98
eq.) in water (700 mL) was added over 3.5 hrs while maintaining the
temperature below 0 °C. After complete addition stirring was continued
in the ice bath for 1.5 hrs and then the reaction mixture was allowed to
warm to 15 °C. The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed well
with water, taken in ethyl acetate (3.4 L), treated with anhydrous
sodium sulfate (500 g) and stirred for 1 hr. This suspension was
filtered through sodium sulfate (200 g) and the filtrate was
concentrated on a rotary evaporator. The residue was dissolved in methyl
i-butyl ether (5.5 L), treated with charcoal (40 g), stirred for 40 min
and filtered through Celite. The solvent was removed in a rotary
evaporator and the resulting product was dried in a vacuum oven (45 °C)
to give the desired product (256 g, 53.4%). LCMS for C3H4CIN4O2 (M+H)+:
m/z = 162.9.
13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD): 5 155.8, 143.4, 129.7.
Step
3:
4-Amino-N'-hydroxy-N-(2-methoxyethyl)-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
[00186] 4-Amino-N-hydroxy-l ,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl chloride
(200.0 g, 1.23 mol) was mixed with ethyl acetate (1.2 L). At 0-5 °C
2-methoxyethylamine [Aldrich, product # 143693] (119.0 mL, 1.35 mol) was
added in one portion while stirring. The reaction temperature rose to
41 °C. The reaction was cooled to 0 - 5 °C. Triethylamine (258 mL, 1.84
mol) was added. After stirring 5 min, LCMS indicated reaction
completion. The reaction solution was washed with water (500 mL) and
brine (500 mL), dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated to give the
desired product (294 g, 1 19%) as a crude dark oil.
LCMS for C
6Hi
2 50
3 (M+H)
+:
m/z = 202.3. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- ): δ 10.65 (s, 1 H), 6.27 (s, 2 H),
6.10 (t, J = 6.5 Hz, 1 H), 3.50 (m, 2 H), 3.35 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 2 H),
3.08 (s, 3 H).
Step 4: N'-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
[00187]
4-Amino-N-hydroxy-N-(2-methoxyethyl)-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-
carboximidamide (248.0 g, 1.23 mol) was mixed with water (1 L).
Potassium hydroxide (210 g, 3.7 mol) was added. The reaction was
refluxed at 100 °C overnight (15 hours). TLC with 50% ethyl acetate
(containing 1% ammonium hydroxide) in hexane indicated reaction
completed (product Rf = 0.6, starting material Rf = 0.5). LCMS also
indicated reaction completion. The reaction was cooled to room
temperature and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 x 1 L). The combined
ethyl acetate solution was dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated to
give the desired product (201 g, 81%) as a crude off-white solid. LCMS
for C6H12N5O3 (M+H)
+: m/z = 202.3
LH NMR (400 MHz, OMSO-d
6):
δ 10.54 (s, 1 H), 6.22 (s, 2 H), 6.15 (t, J = 5.8 Hz, 1 H), 3.45 (t, J=
5.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.35 (m, 2 H), 3.22 (s, 3 H). Step 5:
N-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl
chloride
[00188] At room temperature
N'-hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]- 1 ,2,5-
oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide (50.0 g, 0.226 mol) was dissolved in 6.0 M
hydrochloric acid aqueous solution (250 mL, 1.5 mol). Sodium chloride
(39.5 g, 0.676 mol) was added followed by water (250 mL) and ethyl
acetate (250 mL). At 3-5 °C a previously prepared aqueous solution (100
mL) of sodium nitrite (15.0 g, 0.217 mol) was added slowly over 1 hr.
The reaction was stirred at 3 - 8 °C for 2 hours and then room
temperature over the weekend. LCMS indicated reaction completed. The
reaction solution was extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 200 mL). The
combined ethyl acetate solution was dried over sodium sulfate and
concentrated to give the desired product (49.9 g, 126%) as a crude white
solid. LCMS for
C
6HioClN
403 (M+H)
+: m/z = 221.0.
!H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d
6): δ 13.43 (s, 1 H), 5.85 (t, J= 5.6 Hz, 1 H), 3.50 (t, J= 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.37(dd, J= 10.8, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.25 (s, 3 H).
Step
6 : N-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-4- [(2-methoxyethyl)amino] - 1
,2,5- oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide [00189]
N-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]- 1 ,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl
chloride (46.0 g, 0.208 mol) was mixed with water (300 mL). The mixture
was heated to 60 °C. 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline [Oakwood products, product #
013091] (43.6 g, 0.229 mol) was added and stirred for 10 min. A warm
sodium bicarbonate (26.3 g, 0.313 mol) solution (300 mL water) was added
over 15 min. The reaction was stirred at 60 °C for 20 min. LCMS
indicated reaction completion. The reaction solution was cooled to room
temperature and extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 300 mL). The combined
ethyl acetate solution was dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated to
give the desired product (76.7 g, 98%) as a crude brown solid. LCMS for
Ci
2Hi
4BrF
50
3 (M+H)
+: m/z = 374.0, 376.0. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- t
f):
δ 11.55 (s, 1 H), 8.85 (s, 1 H), 7.16 (t, J= 8.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.08 (dd, J=
6.1, 2.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.75 (m, 1 H), 6.14 (t, J= 5.8 Hz, 1 H), 3.48 (t, J =
5.2 Hz, 2 H), 3.35 (dd, J= 10.8, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.22 (s, 3 H).
Step 7: 4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-3-{4- [(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3- yl}-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one
[00190]
A mixture of N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-4-[(2-
methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide (76.5 g, 0.204
mol), 1,1 '- carbonyldiimidazole (49.7 g, 0.307 mol), and ethyl acetate
(720 mL) was heated to 60 °C and stirred for 20 min. LCMS indicated
reaction completed. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, washed
with 1 N HC1 (2 x 750 mL), dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated
to give the desired product (80.4 g, 98%) as a crude brown solid. LCMS
for
(M+H)
+:
m/z = 400.0, 402.0. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-c½): δ 7.94 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1
H), 7.72 (dd, J = 9.1, 2.3 Hz, 1 H), 7.42 (m, 1 H), 6.42 (t, J= 5.7 Hz,
1 H), 3.46 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 2 H), 3.36 (t, J= 5.8 Hz, 2 H), 3.26 (s, 3
H).
Step 8: 4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3- yl}-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one
[00191]
4-(3-Bromo-4-fluoroplienyl)-3-{4-[(2-metlioxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-
3-yl}-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one (78.4 g, 0.196 mol) was dissolved in
dichloromethane (600 mL). At -67 °C boron tribromide (37 mL, 0.392 mol)
was added over 15 min. The reaction was warmed up to -10 °C in 30 min.
LCMS indicated reaction completed. The reaction was stirred at room
temperature for 1 hour. At 0 - 5 °C the reaction was slowly quenched
with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (1.5 L) over 30 min. The
reaction temperature rose to 25 °C. The reaction was extracted with
ethyl acetate (2 x 500 mL, first extraction organic layer is on the
bottom and second extraction organic lager is on the top). The combined
organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated to give
the desired product (75 g, 99%) as a crude brown solid. LCMS for Ci
2HioBrFN
50
4 (M+H)
+: m/z = 386.0, 388.0.
1H
NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^): δ 8.08 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.70 (m, 1
H), 7.68 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.33 (t, J = 5.6 Hz, 1 H), 4.85 (t, J=
5.0 Hz, 1 H), 3.56 (dd, J= 10.6, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.29 (dd, J= 11.5, 5.9
Hz, 2 H).
Step 9 : 2-({4-
[4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro- 1 ,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl] -
l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl methanesulfonate
[00192] To a
solution of 4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-
l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one (1.5 kg, 3.9 mol,
containing also some of the corresponding bromo-compound) in ethyl
acetate (12 L) was added methanesulfonyl chloride (185 mL, 2.4 mol)
dropwise over 1 h at room temperature. Triethylamine (325 mL, 2.3 mol)
was added dropwise over 45 min, during which time the reaction
temperature increased to 35 °C. After 2 h, the reaction mixture was
washed with water (5 L), brine (1 L), dried over sodium sulfate,
combined with 3 more reactions of the same size, and the solvents
removed in vacuo to afford the desired product (7600 g, quantitative
yield) as a tan solid. LCMS for C HnBrFNsOeS a (M+Na)
+: m/z = 485.9, 487.9.
!H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- d
6):
δ 8.08 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (m, 1 H), 7.58 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 1
H), 6.75 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1 H), 4.36 (t, J = 5.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.58 (dd, J =
11.2, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.18 (s, 3 H).
Step 10: 3-{4-[(2-Azidoethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}-4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)- l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one
To
a solution of 2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-f uorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l
,2,4- oxadiazol-3-yl]-l ,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl methanesulfonate
(2.13 kg, 4.6 mol, containing also some of the corresponding
bromo-compound) in dimethylformamide (4 L) stirring in a 22 L flask was
added sodium azide (380 g, 5.84 mol). The reaction was heated at 50 °C
for 6 h, poured into ice/water (8 L), and extracted with 1 : 1 ethyl
acetate:heptane (20 L). The organic layer was washed with water (5 L)
and brine (5 L), and the solvents removed in vacuo to afford the desired
product (1464 g, 77%) as a tan solid. LCMS for CnHgBrFNsOs a
(M+Na)
+: m/z = 433.0, 435.0.
!H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J
6):
δ 8.08 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (m, 1 H), 7.58 (t, J= 8.7 Hz, 1
H), 6.75 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 1 H), 3.54 (t, J = 5.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.45 (dd, J= 1
1.1 , 5.2 Hz, 2 H).
Step 11: 3-{4-[(2-Aminoethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}-4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-
1.2.4- oxadiazol-5(4H)-one hydrochloride
[00194] Sodium iodide (1080 g, 7.2 mol) was added to 3-{4-[(2-azidoethyl)amino]-
1.2.5-
oxadiazol-3-yl}-4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-l ,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one
(500 g, 1.22 mol) in methanol (6 L). The mixture was allowed to stir for
30 min during which time a mild exotherm was observed.
Chlorotrimethylsilane (930 mL, 7.33 mol) was added as a solution in
methanol (1 L) dropwise at a rate so that the temperature did not exceed
35 °C, and the reaction was allowed to stir for 3.5 h at ambient
temperature. The reaction was neutralized with 33 wt% solution of sodium
thiosulfate pentahydrate in water (-1.5 L), diluted with water (4 L),
and the pH adjusted to 9 carefully with solid potassium carbonate (250 g
- added in small portions: watch foaming). Di-ieri-butyl dicarbonate
(318 g, 1.45 mol) was added and the reaction was allowed to stir at room
temperature. Additional potassium carbonate (200 g) was added in 50 g
portions over 4 h to ensure that the pH was still at or above 9. After
stirring at room temperature overnight, the solid was filtered,
triturated with water (2 L), and then MTBE (1.5 L). A total of 11 runs
were performed (5.5 kg, 13.38 mol). The combined solids were triturated
with 1 : 1 THF:dichloromethane (24 L, 4 runs in a 20 L rotary evaporator
flask, 50 °C, 1 h), filtered, and washed with dichloromethane (3 L each
run) to afford an off- white solid. The crude material was dissolved at
55 °C tetrahydrofuran (5 mL/g), treated with decolorizing carbon (2
wt%) and silica gel (2 wt%), and filtered hot through celite to afford
the product as an off-white solid (5122 g). The combined MTBE, THF, and
dichloromethane filtrates were concentrated in vacuo and chromatographed
(2 kg silica gel, heptane with a 0-100% ethyl acetate gradient, 30 L)
to afford more product (262 g). The combined solids were dried to a
constant weight in a convection oven (5385 g, 83%).
In a 22 L
flask was charged hydrogen chloride (4 N solution in 1 ,4-dioxane, 4 L,
16 mol). tert-Butyl
[2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l ,2,4-
oxadiazol-3-yl]-l ,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]carbamate (2315 g,
4.77 mol) was added as a solid in portions over 10 min. The slurry was
stirred at room temperature and gradually became a thick paste that
could not be stirred. After sitting overnight at room temperature, the
paste was slurried in ethyl acetate (10 L), filtered, re-slurried in
ethyl acetate (5 L), filtered, and dried to a constant weight to afford
the desired product as a white solid (combined with other runs, 5 kg
starting material charged, 41 13 g, 95%). LCMS for
Ci
2H
nBrFN
60
3 (M+H)
+:
m/z = 384.9, 386.9. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^): δ 8.12 (m, 4 H), 7.76 (m,
1 H), 7.58 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.78 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1 H), 3.51 (dd, J
= 1 1.8, 6.1 Hz, 2 H), 3.02 (m, 2 H).
Step 12: tert-Butyl
({[2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-nuorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l,2,4-
oxadiazol-3-yl]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]amino}sulfonyl)carbamate
A
5 L round bottom flask was charged with chlorosulfonyl isocyanate
[Aldrich, product # 142662] (149 mL, 1.72 mol) and dichloromethane (1.5
L) and cooled using an ice bath to 2 °C. teri-Butanol (162 mL, 1.73 mol)
in dichloromethane (200 mL) was added dropwise at a rate so that the
temperature did not exceed 10 °C. The resulting solution was stirred at
room temperature for 30-60 min to provide tert-bvAy\
[chlorosulfonyl]carbamate.
A 22 L flask was charged with 3-
{4-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]- 1 ,2,5-oxadiazol-3-
yl}-4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one hydrochloride
(661 g, 1.57 mol) and 8.5 L dichloromethane. After cooling to -15 °C
with an ice/salt bath, the solution oi tert- Vmtvl i Vi 1
r>rosulfonyl]carbamate (prepared as above) was added at a rate so
that the temperature did not exceed -10 °C (addition time 7 min). After
stirring for 10 min, triethylamine (1085 mL, 7.78 mol) was added at a
rate so that the temperature did not exceed -5 °C (addition time 10
min). The cold bath was removed, the reaction was allowed to warm to 10
°C, split into two portions, and neutralized with 10% cone HC1 (4.5 L
each portion). Each portion was transferred to a 50 L separatory funnel
and diluted with ethyl acetate to completely dissolve the white solid
(-25 L). The layers were separated, and the organic layer was washed
with water (5 L), brine (5 L), and the solvents removed in vacuo to
afford an off- white solid. The solid was triturated with MTBE (2 x 1.5
L) and dried to a constant weight to afford a white solid. A total of
4113 g starting material was processed in this manner (5409 g, 98%). 1H
NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^): δ 10.90 (s, 1 H), 8.08 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1
H), 7.72 (m, 1 H), 7.59 (t, J = 8.6 Hz, 1 H), 6.58 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 1 H),
3.38 (dd, J= 12.7, 6.2 Hz, 2 H), 3.10 (dd, J= 12.1 , 5.9 Hz, 2 H), 1.41
(s, 9 H).
Step 13:
N-[2-({4-[4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-
l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]sulfamide
[00198] To a 22 L
flask containing 98:2 trifluoroacetic acid:water (8.9 L) was added
tert-bvXyl
({[2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-
l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]amino}sulfonyl)carbamate (1931 g, 3.42
mol) in portions over 10 minutes. The resulting mixture was stirred at
room temperature for 1.5 h, the solvents removed in vacuo, and chased
with dichloromethane (2 L). The resulting solid was treated a second
time with fresh 98:2 trifluoroacetic acid:water (8.9 L), heated for 1 h
at 40- 50 °C, the solvents removed in vacuo, and chased with
dichloromethane (3 x 2 L). The resulting white solid was dried in a
vacuum drying oven at 50 °C overnight. A total of 5409 g was processed
in this manner (4990 g, quant, yield). LCMS for C
12H
12BrFN
70
5S (M+H)
+:
m/z = 463.9, 465.9. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- ): δ 8.08 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.5
Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (m, 1 H), 7.59 (t, J= 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.67 (t, J = 5.9 Hz,
1H), 6.52 (t, J= 6.0 Hz, 1 H), 3.38 (dd, J = 12.7, 6.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.11
(dd, J = 12.3, 6.3 Hz). Step 14:
4-({2-[(Aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl}amino)-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-
hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
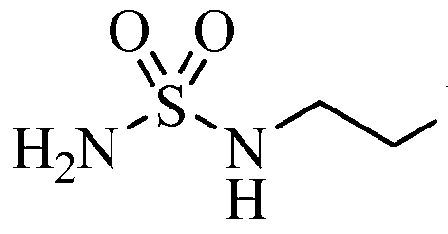
[00199]
To a crude mixture of N-[2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-
dihydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]sulfamide
(2.4 mol) containing residual amounts of trifluoroacetic acid stirring
in a 22 L flask was added THF (5 L). The resulting solution was cooled
to 0 °C using an ice bath and 2 N NaOH (4 L) was added at a rate so that
the temperature did not exceed 10 °C. After stirring at ambient
temperature for 3 h (LCMS indicated no starting material remained), the
pH was adjusted to 3-4 with concentrated HC1 (-500 mL). The THF was
removed in vacuo, and the resulting mixture was extracted with ethyl
acetate (15 L). The organic layer was washed with water (5 L), brine (5
L), and the solvents removed in vacuo to afford a solid. The solid was
triturated with MTBE (2 x 2 L), combined with three other reactions of
the same size, and dried overnight in a convection oven to afford a
white solid (3535 g). The solid was recrystallized (3 x 22 L flasks, 2:1
watenethanol, 14.1 L each flask) and dried in a 50 °C convection oven
to a constant weight to furnish the title compound as an off-white solid
(3290 g, 78%). LCMS for CnHnBrF yC S (M+H)
+: m/z = 437.9,
439.9. i NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J^): δ 11.51 (s, 1 H), 8.90 (s, 1 H), 7.17
(t, J= 8.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.11 (dd, J= 6.1, 2.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.76 (m, 1 H), 6.71
(t, J = 6.0 Hz, 1 H), 6.59 (s, 2 H), 6.23 (t, J= 6.1 Hz, 1 H), 3.35
(dd, J= 10.9, 7.0 Hz, 2 H), 3.10 (dd, J= 12.1, 6.2 Hz, 2 H).
PATENT
WO 2010005958
https://www.google.com/patents/WO2010005958A2?cl=en
EXAMPLES Example 1
4-({2-[(Aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl}amino)-7V-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-iV'-hydroxy- l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
Step A: 4-Amino-N'-hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
Malononitrile [Aldrich, product # M1407] (320.5 g, 5 mol) was added to water (7 L) preheated to 45
0C
and stirred for 5 min. The resulting solution was cooled in an ice bath
and sodium nitrite (380 g, 5.5 mol) was added. When the temperature
reached 10
0C, 6 N hydrochloric acid (55 mL) was added. A mild exothermic reaction ensued with the temperature reaching 16
0C. After 15 min the cold bath was removed and the reaction mixture was stirred for 1.5 hrs at 16-18
0C. The reaction mixture was cooled to 13
0C and 50% aqueous hydroxylamine (990 g, 15 mol) was added all at once. The temperature rose to 26
0C. When the exothermic reaction subsided the cold bath was removed and stirring was continued for 1 hr at 26-27
0C,
then it was slowly brought to reflux. Reflux was maintained for 2 hrs
and then the reaction mixture was allowed to cool overnight. The
reaction mixture was stirred in an ice bath and 6 N hydrochloric acid
(800 mL) was added in portions over 40 min to pH 7.0. Stirring was
continued in the ice bath at 5
0C. The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed well with water and dried in a vacuum oven (50
0C) to give the desired product (644 g, 90%). LCMS for C
3H
6N
5O
2 (M+H)+: m/z = 144.0.
13C NMR (75 MHz, CD
3OD): δ 156.0, 145.9, 141.3. Step B: 4-Amino-N-hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl chloride
4-Amino-N'-hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
(422 g, 2.95 mol) was added to a mixture of water (5.9 L), acetic acid
(3 L) and 6 Ν hydrochloric acid (1.475 L, 3 eq.) and this suspension was
stirred at 42 - 45
0C until complete solution was achieved.
Sodium chloride (518 g, 3 eq.) was added and this solution was stirred
in an ice/water/methanol bath. A solution of sodium nitrite (199.5 g,
0.98 eq.) in water (700 mL) was added over 3.5 hrs while maintaining the
temperature below 0
0C. After complete addition stirring was
continued in the ice bath for 1.5 hrs and then the reaction mixture was
allowed to warm to 15
0C. The precipitate was collected by
filtration, washed well with water, taken in ethyl acetate (3.4 L),
treated with anhydrous sodium sulfate (500 g) and stirred for 1 hr. This
suspension was filtered through sodium sulfate (200 g) and the filtrate
was concentrated on a rotary evaporator. The residue was dissolved in
methyl f-butyl ether (5.5 L), treated with charcoal (40 g), stirred for
40 min and filtered through Celite. The solvent was removed in a rotary
evaporator and the resulting product was dried in a vacuum oven (45
0C) to give the desired product (256 g, 53.4%). LCMS for C
3H
4ClN
4O
2(M+H)+: m/z = 162.9. 13c NMR (100 MHz, CD
3OD): δ 155.8, 143.4, 129.7.
Step C: 4-Amino-N'-hydroxy-N-(2-methoxyethyl)- 1 ,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
4-Amino-N-hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl chloride (200.0 g, 1.23 mol) was mixed with ethyl acetate (1.2 L). At 0-5
0C
2-methoxyethylamine [Aldrich, product # 143693] (119.0 mL, 1.35 mol)
was added in one portion while stirring. The reaction temperature rose
to 41
0C. The reaction was cooled to 0 - 5 °C. Triethylamine
(258 mL, 1.84 mol) was added. After stirring 5 min, LCMS indicated
reaction completion. The reaction solution was washed with water (500
mL) and brine (500 mL), dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated to
give the desired product (294 g, 119%) as a crude dark oil. LCMS for C
6Hi
2N
5O
3 (M+H)
+: m/z = 202.3.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J
6): δ 10.65 (s, 1 H), 6.27 (s, 2 H), 6.10 (t, J= 6.5 Hz, 1 H), 3.50 (m, 2 H), 3.35 (d, J= 5.8 Hz, 2 H), 3.08 (s, 3 H).
Step D: N'-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l ,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
4-Amino-N'-hydroxy-N-(2-methoxyethyl)-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidaniide
(248.0 g, 1.23 mol) was mixed with water (1 L). Potassium hydroxide
(210 g, 3.7 mol) was added. The reaction was refluxed at 100
0C
overnight (15 hours). TLC with 50% ethyl acetate (containing 1%
ammonium hydroxide) in hexane indicated reaction completed (product Rf=
0.6, starting material Rf = 0.5). LCMS also indicated reaction
completion. The reaction was cooled to room temperature and extracted
with ethyl acetate (3 x 1 L). The combined ethyl acetate solution was
dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated to give the desired product
(201 g, 81%) as a crude off-white solid. LCMS for C
6H
12N
5O
3 (M+H)
+: m/z = 202.3
1H
NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-Gk): δ 10.54 (s, 1 H), 6.22 (s, 2 H), 6.15 (t, J=
5.8 Hz, 1 H), 3.45 (t, J= 5.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.35 (m, 2 H), 3.22 (s, 3 H).
Step E: N-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl chloride
Ν. ,Ν O
At
room temperature
N'-hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3- carboximidamide
(50.0 g, 0.226 mol) was dissolved in 6.0 M hydrochloric acid aqueous
solution (250 mL, 1.5 mol). Sodium chloride (39.5 g, 0.676 mol) was
added followed by water (250 mL) and ethyl acetate (250 mL). At 3-5
0C
a previously prepared aqueous solution (100 mL) of sodium nitrite (15.0
g, 0.217 mol) was added slowly over 1 hr. The reaction was stirred at 3
- 8
0C for 2 hours and then room temperature over the
weekend. LCMS indicated reaction completed. The reaction solution was
extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 200 mL). The combined ethyl acetate
solution was dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated to give the
desired product (49.9 g, 126%) as a crude white solid. LCMS for C
6Hi
0ClN
4O
3 (M+H)
+: m/z = 221.0.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J
6): δ 13.43 (s, 1 H), 5.85 (t, J= 5.6 Hz, 1 H), 3.50 (t, J= 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.37(dd, J= 10.8, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.25 (s, 3 H).
Step F: N-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]- 1 ,2,5- oxadiazole-3 -carboximidamide
N-Hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidoyl
chloride (46.0 g, 0.208 mol) was mixed with water (300 mL). The mixture
was heated to 60 °C. 3-Bromo-4- fluoroaniline [Oakwood products,
product # 013091] (43.6 g, 0.229 mol) was added and stirred for 10 nrn
'n. A warm sodium bicarbonate (26.3 g, 0.313 mol) solution (300 mL water) was added over 15 min. The reaction was stirred at 60
0C
for 20 min. LCMS indicated reaction completion. The reaction solution
was cooled to room temperature and extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 300
mL). The combined ethyl acetate solution was dried over sodium sulfate
and concentrated to give the desired product (76.7 g, 98%) as a crude
brown solid. LCMS for Ci
2Hi
4BrFN
5O
3 (M+H)
+: m/z = 374.0, 376.0.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J
6):
δ 11.55 (s, 1 H), 8.85 (s, 1 H), 7.16 (t, J= 8.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.08 (dd, J=
6.1, 2.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.75 (m, 1 H), 6.14 (t, J= 5.8 Hz, 1 H), 3.48 (t, J=
5.2 Hz, 2 H), 3.35 (dd, J= 10.8, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.22 (s, 3 H).
Step G: 4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}- 1 ,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one
A
mixture of
N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N'-hydroxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-
oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide (76.5 g, 0.204 mol),
l,r-carbonyldiimidazole (49.7 g, 0.307 mol), and ethyl acetate (720 mL)
was heated to 60
0C and stirred for 20 min. LCMS indicated
reaction completed. The reaction was cooled to room temperature, washed
with 1 Ν HCl (2 x 750 mL), dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated
to give the desired product (80.4 g, 98%) as a crude brown solid. LCMS
for C
13H
12BrFN
5O
4 (M+H)
+: m/z = 400.0, 402.0.
1H NMR (400 MHz, OMSO-d
6):
δ 7.94 (t, J= 8.2 Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (dd, J= 9.1, 2.3 Hz, 1 H), 7.42 (m, 1
H), 6.42 (t, J= 5.7 Hz, 1 H), 3.46 (t, J= 5.4 Hz, 2 H), 3.36 (t, J= 5.8
Hz, 2 H), 3.26 (s, 3 H).
Step H: 4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-liydroxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}- 1 ,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one
4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-methoxyetliyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}-l,2,4-
oxadiazol-5(4H)-one (78.4 g, 0.196 mol) was dissolved in
dichloromethane (600 mL). At -67
0C boron tribromide (37 mL, 0.392 mol) was added over 15 min. The reaction was warmed up to -10
0C in 30 min. LCMS indicated reaction completed. The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. At 0 - 5
0C
the reaction was slowly quenched with saturated sodium bicarbonate
solution (1.5 L) over 30 min. The reaction temperature rose to 25
0C.
The reaction was extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 500 mL, first
extraction organic layer is on the bottom and second extraction organic
lager is on the top). The combined organic layers were dried over sodium
sulfate and concentrated to give the desired product (75 g, 99%) as a
crude brown solid. LCMS for C
12H
10BrFN
5O
4 (M+H)
+: m/z = 386.0, 388.0.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-^
6):
δ 8.08 (dd, J= 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.70 (m, 1 H), 7.68 (t, J= 8.7 Hz, 1
H), 6.33 (t, J= 5.6 Hz, 1 H), 4.85 (t, J= 5.0 Hz, 1 H), 3.56 (dd, J=
10.6, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.29 (dd, J= 11.5, 5.9 Hz, 2 H).
Step I:
2-({4-[4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-l,2,5-
oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl methanesulfonate
To
a solution of
4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-
3-yl}-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one (1.5 kg, 3.9 mol, containing also some
of the corresponding bromo-compound) in ethyl acetate (12 L) was added
methanesulfonyl chloride (185 mL, 2.4 mol) dropwise over 1 h at room
temperature. Triethylamine (325 mL, 2.3 mol) was added dropwise over 45
min, during which time the reaction temperature increased to 35
0C.
After 2 h, the reaction mixture was washed with water (5 L), brine (I
L), dried over sodium sulfate, combined with 3 more reactions of the
same size, and the solvents removed in vacuo to afford the desired
product (7600 g, quantitative yield) as a tan solid. LCMS for
Ci
3HnBrFN
5O
6SNa (M+Na)
+: m/z = 485.9, 487.9.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSCW
6):
δ 8.08 (dd, J= 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (m, 1 H), 7.58 (t, J= 8.7 Hz, 1
H), 6.75 (t, J- 5.9 Hz, 1 H), 4.36 (t, J= 5.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.58 (dd, J=
11.2, 5.6 Hz, 2 H), 3.18 (s, 3 H).
Step J: 3-{4-[(2-Azidoethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}-4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)- 1 ,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one
To
a solution of
2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-
l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl methanesulfonate (2.13 kg, 4.6 mol,
containing also some of the corresponding bromo-compound) in
dimethylformamide (4 L) stirring in a 22 L flask was added sodium azide
(380 g, 5.84 mol). The reaction was heated at 50
0C for 6 h,
poured into ice/water (8 L), and extracted with 1 : 1 ethyl
acetate:heptane (20 L). The organic layer was washed with water (5 L)
and brine (5 L), and the solvents removed in vacuo to afford the desired
product (1464 g, 77%) as a tan solid. LCMS for C
12H
8BrFN
8O
3Na (M+Na)
+: m/z =
433.0, 435.0.
1H
NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-*/*): δ 8.08 (dd, J= 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (m, 1
H), 7.58 (t, J= 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.75 (t, J= 5.7 Hz, 1 H), 3.54 (t, J= 5.3
Hz, 2 H), 3.45 (dd, J= 11.1, 5.2 Hz, 2 H).
Step K: 3-{4-[(2-Aminoethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}-4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)- 1 ,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one hydrochloride
Sodium
iodide (1080 g, 7.2 mol) was added to
3-{4-[(2-azidoethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-
yl}-4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one (500 g, 1.22
mol) in methanol (6 L). The mixture was allowed to stir for 30 min
during which time a mild exotherm was observed. Chlorotrimethylsilane
(930 mL, 7.33 mol) was added as a solution in methanol (1 L) dropwise at
a rate so that the temperature did not exceed 35
0C, and the
reaction was allowed to stir for 3.5 h at ambient temperature. The
reaction was neutralized with 33 wt% solution of sodium thiosulfate
pentahydrate in water (~1.5 L), diluted with water (4 L), and the pΗ
adjusted to 9 carefully with solid potassium carbonate (250 g - added in
small portions: watch foaming). Di-fe/t-butyl dicarbonate (318 g, 1.45
mol) was added and the reaction was allowed to stir at room temperature.
Additional potassium carbonate (200 g) was added in 50 g portions over 4
h to ensure that the pΗ was still at or above 9. After stirring at room
temperature overnight, the solid was filtered, triturated with water (2
L), and then MTBE (1.5 L). A total of 11 runs were performed (5.5 kg,
13.38 mol). The combined solids were triturated with 1 : 1
TΗF:dichloromethane (24 L, 4 runs in a 20 L rotary evaporator flask, 50
0C,
1 h), filtered, and washed with dichloromethane (3 L each run) to
afford an off- white solid. The crude material was dissolved at 55
0C
tetrahydrofuran (5 mL/g), treated with decolorizing carbon (2 wt%) and
silica gel (2 wt%), and filtered hot through celite to afford the
product as an off-white solid (5122 g). The combined MTBE, THF, and
dichloromethane filtrates were concentrated in vacuo and chromatographed
(2 kg silica gel, heptane with a 0-100% ethyl acetate gradient, 30 L)
to afford more product (262 g). The combined solids were dried to a
constant weight in a convection oven (5385 g, 83%).
In a 22 L
flask was charged hydrogen chloride (4 N solution in 1,4-dioxane, 4 L,
16 mol). fert-Butyl
[2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-
l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]carbamate (2315 g, 4.77 mol) was added
as a solid in portions over 10 min. The slurry was stirred at room
temperature and gradually became a thick paste that could not be
stirred. After sitting overnight at room temperature, the paste was
slurried in ethyl acetate (10 L), filtered, re-slurried in ethyl acetate
(5 L), filtered, and dried to a constant weight to afford the desired
product as a white solid (combined with other runs, 5 kg starting
material charged, 4113 g, 95%). LCMS for C
12H
nBrFN
6O
3 (M+H)
+: m/z
= 384.9, 386.9.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J
6):
δ 8.12 (m, 4 H), 7.76 (m, 1 H), 7.58 (t, J= 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.78 (t, J=
6.1 Hz, 1 H), 3.51 (dd, J= 11.8, 6.1 Hz, 2 H), 3.02 (m, 2 H).
Step
L: tert-Butyl
({[2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-diliydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-
3-yl]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]amino}sulfonyl)carbamate
A 5 L round bottom flask was charged with chlorosulfonyl isocyanate [Aldrich, product #
142662] (149 mL, 1.72 mol) and dichloromethane (1.5 L) and cooled using an ice bath to 2
0C.
tert-Butanol (162 mL, 1.73 mol) in dichloromethane (200 mL) was added
dropwise at a rate so that the temperature did not exceed 10
0C. The resulting solution was stirred at room temperature for 30-60 min to provide tert-butyl [chlorosulfonyljcarbamate.
A
22 L flask was charged with
3-{4-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}-4-(3-
bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-l,2,4-oxadiazol-5(4H)-one hydrochloride (661 g,
1.57 mol) and 8.5 L dichloromethane. After cooling to -15
0C
with an ice/salt bath, the solution of tert-butyl
[chlorosulfonyl]carbamate (prepared as above) was added at a rate so
that the temperature did not exceed -10
0C (addition time 7
min). After stirring for 10 min, triethylamine (1085 mL, 7.78 mol) was
added at a rate so that the temperature did not exceed -5
0C (addition time 10 min). The cold bath was removed, the reaction was allowed to warm to 10
0C,
split into two portions, and neutralized with 10% cone HCl (4.5 L each
portion). Each portion was transferred to a 50 L separatory funnel and
diluted with ethyl acetate to completely dissolve the white solid (~25
L). The layers were separated, and the organic layer was washed with
water (5 L), brine (5 L), and the solvents removed in vacuo to afford an
off-white solid. The solid was triturated with MTBE (2 x 1.5 L) and
dried to a constant weight to afford a white solid. A total of 4113 g
starting material was processed in this manner (5409 g, 98%). *Η NMR
(400 MHz, OMSO-d
6): δ 10.90 (s, 1 H), 8.08 (dd, J= 6.2, 2.5
Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (m, 1 H), 7.59 (t, J= 8.6 Hz, 1 H), 6.58 (t, J= 5.7 Hz, 1
H), 3.38 (dd, J= 12.7, 6.2 Hz, 2 H), 3.10 (dd, J = 12.1, 5.9 Hz, 2 H),
1.41 (s, 9 H). Step M:
N-[2-({4-[4-(3-Bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dmydro-l
,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]- l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]sulfamide
To
a 22 L flask containing 98:2 trifluoroacetic acid:water (8.9 L) was
added tert-butyl ({[2-
({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-diliydro-l,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-
yl}amino)ethyl]amino}sulfonyl)carbamate (1931 g, 3.42 mol) in portions
over 10 minutes. The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature
for 1.5 h, the solvents removed in vacuo, and chased with
dichloromethane (2 L). The resulting solid was treated a second time
with fresh 98:2 trifluoroacetic acid:water (8.9 L), heated for 1 h at
40-50
0C, the solvents removed in vacuo, and chased with
dichloromethane (3 x 2 L). The resulting white solid was dried in a
vacuum drying oven at 50
0C overnight. A total of 5409 g was processed in this manner (4990 g, quant, yield). LCMS for C]
2H
12BrFN
7O
5S (M+H)
+: m/z = 463.9, 465.9.
1H NMR (400 MHz, OM$>O-d
6):
δ 8.08 (dd, J= 6.2, 2.5 Hz, 1 H), 7.72 (m, 1 H), 7.59 (t, J= 8.7 Hz, 1
H), 6.67 (t, J= 5.9 Hz, IH), 6.52 (t, J= 6.0 Hz, 1 H), 3.38 (dd, J=
12.7, 6.3 Hz, 2 H), 3.11 (dd, J= 12.3, 6.3 Hz).
Step N: 4-( {2-[(Aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl} amino)-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N- hydroxy-l,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide
To
a crude mixture of
N-[2-({4-[4-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-l,2,4-
oxadiazol-3-yl]-l,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl}amino)ethyl]sulfamide (2.4 mol)
containing residual amounts of trifluoroacetic acid stirring in a 22 L
flask was added THF (5 L). The resulting solution was cooled to 0 °C
using an ice bath and 2 Ν NaOH (4 L) was added at a rate so that the
temperature did not exceed 10
0C. After stirring at ambient
temperature for 3 h (LCMS indicated no starting material remained), the
pH was adjusted to 3-4 with concentrated HCl (-500 mL). The THF was
removed in vacuo, and the resulting mixture was extracted with ethyl
acetate (15 L). The organic layer was washed with water (5 L), brine (5
L), and the solvents removed in vacuo to afford a solid. The solid was
triturated with MTBE (2 x 2 L), combined with three other reactions of
the same size, and dried overnight in a convection oven to afford a
white solid (3535 g). The solid was recrystallized (3 x 22 L flasks, 2: 1
water: ethanol, 14.1 L each flask) and dried in a 50
0C convection oven to a constant weight to furnish the title compound as an off-white solid (3290 g, 78%). LCMS for C
nH
14BrFN
7O
4S (M+H)
+: m/z = 437.9, 439.9.
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J
6):
δ 11.51 (s, 1 H), 8.90 (s, 1 H), 7.17 (t, J= 8.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.11 (dd, J=
6.1, 2.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.76 (m, 1 H), 6.71 (t, J= 6.0 Hz, 1 H), 6.59 (s, 2
H), 6.23 (t, J= 6.1 Hz, 1 H), 3.35 (dd, J= 10.9, 7.0 Hz, 2 H), 3.10 (dd,
J= 12.1, 6.2 Hz, 2 H).
The final product was an anhydrous
crystalline solid. The water content was determined to be less than 0.1%
by Karl Fischer titration.
CLIP
Incyte’s
Andrew P. Combs presented the company’s clinical candidate for cancer
immunotherapy. The basic tenet of this burgeoning field is that the
human body’s immune system is a tremendous resource for fighting
disease; scientists just need to figure out how to unleash it. One
target that’s proven to be particularly attractive for this purpose in
recent years is indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-1, or IDO1 (C&EN, April
6, page 10).
IDO1 plays
a role in signaling the immune system to stand down from attacking
foreign bodies it might otherwise go after, such as fetuses. Tumors also
produce IDO1 to evade the immune system, so molecules that can inhibit
this enzyme could bring the full force of the body’s defenses to bear on
these deadly invaders.
Incyte’s
search for an IDO1 inhibitor began with a high-throughput screen, which
led to a proof-of-concept compound. But the compound had poor oral
bioavailability. What’s more, the molecule and its analogs underwent
glucuronidation during its metabolism: Enzymes tacked on a glucuronic
acid group to the structure’s amidoxime, which was key to its activity.
The
chemists reasoned they could block this metabolism by sterically
hindering that position. Making such molecules proved to be more
difficult than they expected. But then they unearthed a Latvian paper
from 1993 that gave them the synthetic method they needed to make the
series of compounds that would lead to their clinical candidate
INCB24360 (epacadostat).
With
its furazan core, as well as its amidoxime, bromide, and sulfuric
diamide functional groups, INCB24360 is something of an odd duck, Combs
acknowledged. “Some of you in the audience may be looking at this and
saying, ‘That molecule does not look like something I would bring
forward or maybe even make,’ ” he said, noting that the structure breaks
many medicinal chemistry rules. “We’re a data-centric company, and we
followed the data, not the rules,” Combs told C&EN.
The
compound has completed Phase I clinical trials and is now being used in
collaborative studies with several other pharmaceutical companies that
combine INCB24360 with other cancer immunotherapy agents.
TEAMWORK
Incyte’s
team (from left): Andrew Combs, Dilip Modi, Joe Glenn, Brent Douty,
Padmaja Polam, Brian Wayland, Rick Sparks, Wenyu Zhu, and Eddy Yue.
Credit: Incyte
| WO2007113648A2 * | Mar 26, 2007 | Oct 11, 2007 | Pfizer Products Inc. | Ctla4 antibody combination therapy |
| US20070185165 * | Dec 19, 2006 | Aug 9, 2007 | Combs Andrew P | N-hydroxyamidinoheterocycles as modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| US20100055111 * | Feb 14, 2008 | Mar 4, 2010 | Med. College Of Georgia Research Institute, Inc. | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, pd-1/pd-l pathways, and ctla4 pathways in the activation of regulatory t cells |
| US20120058079 * | Nov 11, 2011 | Mar 8, 2012 | Incyte Corporation, A Delaware Corporation | 1,2,5-Oxadiazoles as Inhibitors of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase |
REFERENCES
1:
Vacchelli E, Aranda F, Eggermont A, Sautès-Fridman C, Tartour E,
Kennedy EP, Platten M, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Trial watch:
IDO inhibitors in cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology. 2014 Dec
15;3(10):e957994. eCollection 2014 Nov. Review. PubMed PMID: 25941578;
PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4292223.
2: Liu X, Shin N, Koblish HK,
Yang G, Wang Q, Wang K, Leffet L, Hansbury MJ, Thomas B, Rupar M, Waeltz
P, Bowman KJ, Polam P, Sparks RB, Yue EW, Li Y, Wynn R, Fridman JS,
Burn TC, Combs AP, Newton RC, Scherle PA. Selective inhibition of IDO1
effectively regulates mediators of antitumor immunity. Blood. 2010 Apr
29;115(17):3520-30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-246124. Epub 2010 Mar 2.
PubMed PMID: 20197554.
3: Koblish HK, Hansbury MJ, Bowman KJ, Yang
G, Neilan CL, Haley PJ, Burn TC, Waeltz P, Sparks RB, Yue EW, Combs AP,
Scherle PA, Vaddi K, Fridman JS. Hydroxyamidine inhibitors of
indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase potently suppress systemic tryptophan
catabolism and the growth of IDO-expressing tumors. Mol Cancer Ther.
2010 Feb;9(2):489-98. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0628. Epub 2010 Feb
2. PubMed PMID: 20124451.
//////////1204669-58-8 , INCB024360, INCB24360, epacadostat, PHASE 2, CANCER, orphan drug designation
Fc1ccc(cc1Br)N/C(=N\O)c2nonc2NCCNS(N)(=O)=O