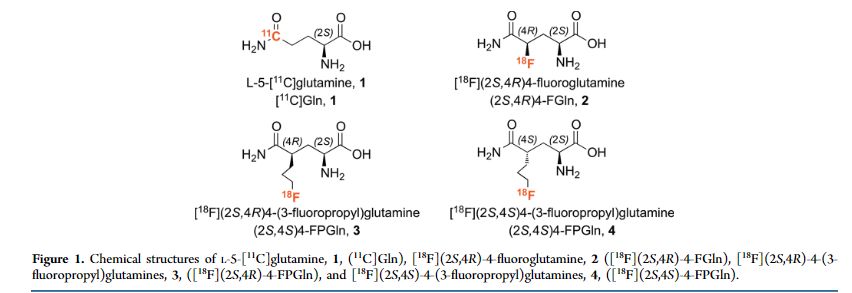
[F-18](2S,4S)-4-(3-Fluoropropyl)glutamine
CAS 1196963-79-7
MF C8 H15 F N2 O3
Heptanoic acid, 2-amino-4-(aminocarbonyl)-7-(fluoro-18F)-, (2S,4S)-
| [18F](2S,4S)-4-FPGln |
[18F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4
|
The early diagnosis of malignant tumors plays a very important role in the survival prognosis of cancer patients. In this non-invasive diagnosis, diagnostic imaging procedures are an important tool. In the last few years has mainly PET technology (P ositronen- E mission-Tomographie) proved to be particularly useful. The sensitivity and specificity of PET technology depends significantly on the used signal-emitting substance (tracer) and their distribution in the body from. In the search for suitable tracers one tries to take advantage of certain properties of tumors differ, the tumor tissue from healthy, surrounding tissue. The preferred commercially used isotope which finds application for PET, 18 F 18 F represents by its short half-life of less than 2 hours special requirements for the preparation of suitable tracer.Complex, long synthetic routes and purifications are with this isotope is not possible, because otherwise a significant portion of the radioactivity of the isotope has already decayed before the tracer can be used for diagnosis. It is therefore often not possible to established synthetic routes for non-radioactive fluorination to be applied to the synthesis of18 F-tracer. Furthermore, the high specific activity of 18 F (80 GBq / nmol) at very low substance amounts of [18 F] fluoride for the tracer synthesis, which in turn an extreme excess of precursor-related and the success of a non-radioactive fluorination based Radio synthetic strategy designed unpredictable
FDG ([18 F] F 2 luoro d esoxy lukose g) -PET is a widely accepted and popular tool in the diagnosis and other clinical tracking of tumor diseases. Malignant tumors compete with the host organism to glucose supply to the nutrient supply (Warburg O. About the metabolism of carcinoma cell Biochem;.. Kellof G. Progress and Promise of FDG PET Imaging for Cancer Patient Management and Oncologic Drug Development Clin Cancer Res 2005;.. 11 (8): 2785-2807) where tumor cells compared to surrounding cells of normal tissue usually an increased glucose metabolism. This is used when using fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), a glucose derivative, which is amplified transported into the cells, but there included metabolically after phosphorylation as FDG-6-phosphate (“Warburg effect”). 18 F-labeled FDG is Therefore, an effective tracer for the detection of tumors in patients using PET technology. Imaging were looking for new PET tracers in recent years increasingly amino acids for 18 F PET used (eg (review): Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002 May; 29 (5):.. 681-90). In this case, some of the 18F-labeled amino acids for the measurement of the speed rate of protein synthesis, the most useful derivatives but for the direct measurement of the cellular uptake in the tumor. Known 18 F-labeled amino acids are, for example, from tyrosine, phenylalanine, proline, aspartic and unnatural amino acids derived (eg J. Nucl Med 1991; 32:.. 1338-1346, J Nucl Med 1996; 37: 320-325, J Nucl Med 2001; 42: 752-754 J Nucl Med and 1999, 40: 331-338).. Glutamic acid and glutamine than 18 F-labeled derivatives not known, whereas non-radioactive fluorinated glutamine and glutamic acid derivatives are well known; Thus, for Example those which at γ-position (for Ex (review):Amino Acids (2003) April; 24 (3):… 245-61).. or at β-position (e.g. ExTetrahedron. Lett. .; 30; 14; 1989, 1799-1802, J. Org Chem .; 54; 2; 1989, 498-500,Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 12, 9; 2001; 1303-1312) havefluorine..
Of glutamic acid having the chemical functionalities protecting groups in β and γ position or a leaving group, has already been reported in the past. So was informed of glutamate as mesylate or bromide in γ-position whose acid and amine functions were provided with ester or Z-protecting groups (J. Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1;.. 1986, 1323-1328) or, for example, of γ-chloro-glutamic acid without protecting groups(Synthesis, (1973); 44-46). About similar derivatives, but where the leaving group is positioned in β-position has also been reported on several occasions. Z Ex. Chem. Pharm. Bull .; 17; 5; (1969); 879-885,J.Gen.Chem.USSR (Engl.Transl.); 38; (1968); 1645-1648, Tetrahedron Lett .; 27; 19; (1986); 2143-2144, Chem. Pharm. Bull .; EN; 17; 5; 1969;873-878, patent FR 1461184 , Patent JP 13142 .)
The current PET tracers, which are used for tumor diagnosis have some undisputed disadvantages: in FDG accumulates preferably in those cells with increased glucose metabolism on, but there are also other pathological and physiological conditions of increased glucose metabolism in the cells involved and tissues, eg, Ex. of infection or wound healing (summarized in J. Nucl. Med. Technol. (2005), 33, 145-155). It is still often difficult to decide whether a detected by FDG-PET lesion actually neoplastic origin or due to other physiological or pathological state of the tissue. Overall, the diagnostic activity by FDG-PET in oncology has a sensitivity of 84% and a specificity of 88% to(Gambhir et al., ” A tabulated summary of the FDG PET literature “J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 1- 93S). Tumors in the brain can be represented very difficult in healthy brain tissue, for example, by the high accumulation of FDG.
The previously known 18 F-labeled amino acid derivatives are in some cases well suited to detect tumors in the brain ((review): Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002 May; 29 (5):. 681-90), but they can in other tumors do not compete with the imaging properties of the “gold standard”[18 F] 2-FDG. The metabolic accumulation and retention of previously F-18 labeled amino acids in tumorous tissue is usually lower than for FDG. Moreover, the accessibility of isomerically pure F-18-labeled non-aromatic amino acids is chemically very demanding.
Similar to glucose increased metabolism in proliferating tumor cells has been described (Medina, J Nutr 1131: 2539S-2542S, 2001; Souba, Ann Surg 218:. 715-728, 1993) for glutamic acid and glutamine. The increased rate of protein and nucleic acid synthesis and energy production per se be accepted as reasons for increased Glutaminkonsum of tumor cells. The synthesis of the corresponding C-11 and C-14 labeled with the natural substrate thus identical compounds, has already been described in the literature (eg. Ex.Antoni, enzymes Catalyzed Synthesis of L- [4-C-11] Aspartate and L – [5-C-11] Glutamate J. Labelled Compd Radiopharm 44; (4) 2001: 287-294) and Buchanan, The biosynthesis of showdomycin: studies with stable isotopes and the determination of principal precursor J….. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun .;EN; 22; 1984, 1515-1517). First indications with the C-11 labeled compound indicate no significant tumor accumulation.
Although the growth and proliferation of most tumors is fueled by glucose, some tumors are more likely to metabolize glutamine. In particular, tumor cells with the upregulated c-Myc gene are generally reprogrammed to utilize glutamine. We have developed new 3-fluoropropyl analogs of glutamine, namely [(18)F](2S,4R)- and [(18)F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 3 and 4, to be used as probes for studying glutamine metabolism in these tumor cells. Optically pure isomers labeled with (18)F and (19)F (2S,4S) and (2S,4R)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine were synthesized via different routes and isolated in high radiochemical purity (≥95%). Cell uptake studies of both isomers showed that they were taken up efficiently by 9L tumor cells with a steady increase over a time frame of 120 min. At 120 min, their uptake was approximately two times higher than that of l-[(3)H]glutamine ([(3)H]Gln). These in vitro cell uptake studies suggested that the new probes are potential tumor imaging agents. Yet, the lower chemical yield of the precursor for 3, as well as the low radiochemical yield for 3, limits the availability of [(18)F](2S,4R)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 3. We, therefore, focused on [(18)F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4. The in vitro cell uptake studies suggested that the new probe, [(18)F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4, is most sensitive to the LAT transport system, followed by System N and ASC transporters. A dual-isotope experiment using l-[(3)H]glutamine and the new probe showed that the uptake of [(3)H]Gln into 9L cells was highly associated with macromolecules (>90%), whereas the [(18)F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4, was not (<10%). This suggests a different mechanism of retention. In vivo PET imaging studies demonstrated tumor-specific uptake in rats bearing 9L xenographs with an excellent tumor to muscle ratio (maximum of ∼8 at 40 min). [(18)F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4, may be useful for testing tumors that may metabolize glutamine related amino acids.
[18F](2S,4S)-4-(3-Fluoropropyl)glutamine as a Tumor Imaging Agent
†Departments of Radiology and ‡Pharmacology, University of Pennsylvania, 3700 Market Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, United States
Mol. Pharmaceutics, 2014, 11 (11), pp 3852–3866
DOI: 10.1021/mp500236y
Publication Date (Web): August 05, 2014
Copyright © 2014 American Chemical Society
This article is part of the Positron Emission Tomography: State of the Art special issue.
Abstract
Although the growth and proliferation of most tumors is fueled by glucose, some tumors are more likely to metabolize glutamine. In particular, tumor cells with the upregulated c-Myc gene are generally reprogrammed to utilize glutamine. We have developed new 3-fluoropropyl analogs of glutamine, namely [18F](2S,4R)- and [18F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 3 and 4, to be used as probes for studying glutamine metabolism in these tumor cells. Optically pure isomers labeled with 18F and 19F (2S,4S) and (2S,4R)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine were synthesized via different routes and isolated in high radiochemical purity (≥95%). Cell uptake studies of both isomers showed that they were taken up efficiently by 9L tumor cells with a steady increase over a time frame of 120 min. At 120 min, their uptake was approximately two times higher than that of l-[3H]glutamine ([3H]Gln). These in vitro cell uptake studies suggested that the new probes are potential tumor imaging agents. Yet, the lower chemical yield of the precursor for 3, as well as the low radiochemical yield for 3, limits the availability of [18F](2S,4R)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 3. We, therefore, focused on [18F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4. The in vitro cell uptake studies suggested that the new probe, [18F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4, is most sensitive to the LAT transport system, followed by System N and ASC transporters. A dual-isotope experiment using l-[3H]glutamine and the new probe showed that the uptake of [3H]Gln into 9L cells was highly associated with macromolecules (>90%), whereas the [18F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4, was not (<10%). This suggests a different mechanism of retention. In vivo PET imaging studies demonstrated tumor-specific uptake in rats bearing 9L xenographs with an excellent tumor to muscle ratio (maximum of ∼8 at 40 min). [18F](2S,4S)-4-(3-fluoropropyl)glutamine, 4, may be useful for testing tumors that may metabolize glutamine related amino acids.
PATENT
US 20100290991
PATENT
WO 2009141091
PATENT
REFERENCES
Molecular Pharmaceutics (2014), 11(11), 3852-3866
| EP1923382A1 * | 18 Nov 2006 | 21 May 2008 | Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft | [18F] labelled L-glutamic acid, [18F] labelled glutamine, their derivatives, their use and processes for their preparation |
| FR1461184A | Title not available | |||
| JPS58113142A | Title not available | |||
| WO2008052788A1* | 30 Oct 2007 | 8 May 2008 | Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft | [f-18]-labeled l-glutamic acid, [f-18]-labeled l-glutamine, derivatives thereof and use thereof and processes for their preparation |
////////










![[1860-5397-11-134-i8]](http://www.beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-11-134-i8.png?max-width=550&background=EEEEEE)