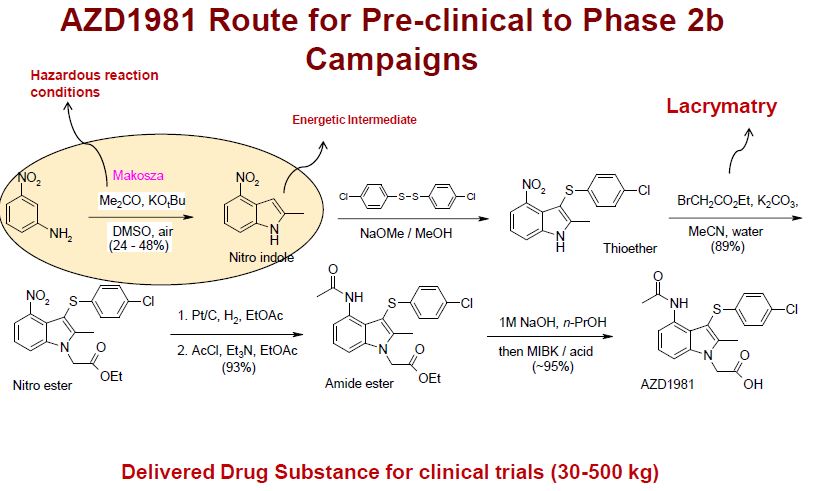
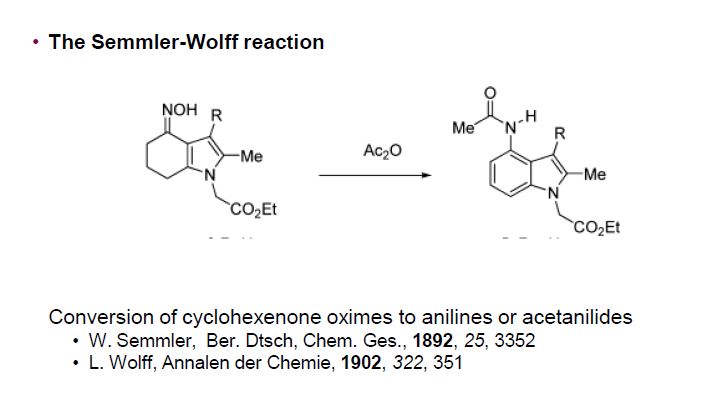
| AZD1981; AZD-1981; 802904-66-1; UNII-2AD53WQ2CX; ; AZD 1981; |
| Molecular Formula: | C19H17ClN2O3S |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 388.86788 g/mol |
|---|
1H-Indole-1-acetic acid, 4-(acetylamino)-3-[(4-chlorophenyl)thio]-2-methyl-
- 2-[4-acetamido-3-(4-chlorophenyl)sulfanyl-2-methylindol-1-yl]acetic acid
- Originator AstraZeneca
- Developer AstraZeneca; Johns Hopkins University
- Class Antiasthmatics
- Mechanism of Action Prostaglandin D2 receptor antagonists
- Phase II Urticaria
- Discontinued Asthma; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Most Recent Events
- 09 Mar 2016 AZD 1981 is still in phase II trials for Urticaria in USA (PO)
- 07 Mar 2016 Johns Hopkins University in collaboration with AstraZeneca completes a phase II trial in Urticaria in USA (PO) (NCT02031679)
- 04 Mar 2016 Efficacy and safety data from a phase II trial in Urticaria presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI-2016)
SEE
AZD1981 is a potent, selective CRTh2 (DP2) receptor antagonist with IC50 of 4 nM, showing >1000-fold selectivity over more than 340 other enzymes and receptors, including DP1. Phase 2.
118 patients were randomised to treatment (AZD1981 n = 61; placebo n = 57); 83% of patients were male and the mean age was 63 years (range 43-83). There were no significant differences in the mean difference in change from baseline to end of treatment between AZD1981 and placebo for the co-primary endpoints of pre-bronchodilator FEV1 (AZD1981-placebo: -0.015, 95% CI: -0.10 to 0.070; p = 0.72) and CCQ total score (difference: 0.042, 95% CI: -0.21 to 0.30; p = 0.75). Similarly, no differences were observed between treatments for the other outcomes of lung function, COPD symptom score, 6-MWT, BODE index, and use of reliever medication. AZD1981 was well tolerated.
CONCLUSION:
There was no beneficial clinical effect of AZD1981, at a dose of 1000 mg twice daily for 4 weeks, in patients with moderate to severe COPD. AZD1981 was well tolerated and no safety concerns were identified.
Biological Activity
| Description | AZD1981 is a potent, selective CRTh2 (DP2) receptor antagonist with IC50 of 4 nM, showing >1000-fold selectivity over more than 340 other enzymes and receptors, including DP1. Phase 2. |
|---|
| Targets | CRTh2 (DP2) receptor [1] |
|---|
| IC50 | 4 nM |
|---|
| In vitro | AZD1981, as a potent antagonist in a disease relevant cell system, inhibits DK-PGD2-induced CD11b expression in human eosinophils with IC50 of 10 nM. [1] AZD1981 blocks DP2-mediated shape change in human eosinophils and basophils in blood, as well as DP2-mediated chemotaxis of human Th2 cells and eosinophils. Moreover, AZD1981 also blocks the binding of [3H]PGD2 to mouse, rat, guinea pig, rabbit and dog recombinant DP2. [2] |
|---|
| In vivo | AZD1981 has high oral bioavailability in male sprague dawley rats. [1] In guinea pig hind limb model, AZD1981 (100 nM) completely inhibits DK-PGD2-induced eosinophil mobilization. [2] |
|---|
| Features | An orally available selective DP2(CRTh2) receptor antagonist in clinical development for asthma. |
|---|
Protocol(Only for Reference)
Kinase Assay: [2]
| DP2 binding studies | A scintillation proximity assay (SPA) following [3H]PGD2 binding to membranes of HEK cells expressing recombinant DP2 is used. The potency of AZD1981 as an antagonist is determined by quantifying its ability to displace specific radio-ligand binding. Briefly, membranes from HEK293 expressing recombinant human DP2 are pre-bound to Wheat Germ Agglutinin-coated PVT-SPA beads for 18 h at 4°C. Assays were started by the addition of 25 μL of membrane-coated beads (10 mg/mL of beads) to an assay buffer (50 mm HEPES pH 7.4 containing 5 mm MgCl2) containing 2.5 nM [3H]PGD2 in the absence or the presence of increasing concentrations of the tested compounds (50 μL final volume). Non-specific binding is determined in the same conditions but in the presence of 10 μM DK-PGD2. Plates are incubated for 2 h at room temperature, and bead-associated radioactivity is measured using a Wallac Microbeta counter. The concentration of the compounds causing 50% inhibition of binding of [3H]PGD2 to the receptor is calculated (IC50). Ki values have not been derived from IC50, as there is no evidence of a simple competitive interaction with PGD2. The same methodology is used for recombinant human, murine, rat, guinea pig, dog and rabbit DP2. Reversibility of binding to the human receptor was assessed by recovery of [3H]PGD2 binding after removal of AZD1981 by washing of the membrane-coated SPA beads. HEK-membrane-coated beads are incubated in the presence of AZD1981 for 2 h at room temperature to bind the compound to DP2. To remove the bound AZD1981, beads are centrifuged (1 min at 1300× g), and the pellet resuspended in 1 mL of assay buffer. This is repeated four times. Aliquots (30 μL) are transferred to 96-well plates, and [3H]PGD2 binding is evaluated as above. Parallel samples containing (i) 10 μM DK-PGD2 during the 2 h incubation and in the wash buffer; (ii) AZD1981 at 2 μM in the wash buffer; and (iii) vehicle are processed alongside to determine non-specific binding and the ‘no wash’ condition whilst controlling for loss of beads during the washing process. The time from first wash to end of first reading is approximately 13 min. |
|---|
Animal Study: [1]
| Animal Models | Male sprague dawley rats. |
|---|
| Formulation | |
|---|
| Dosages | 1 mg/kg(i.v.), 4 mg/kg(oral) |
|---|
| Administration | i.v. or oral administration |
|---|
Conversion of different model animals based on BSA (Value based on data from FDA Draft Guidelines)
| Species | Mouse | Rat | Rabbit | Guinea pig | Hamster | Dog |
| Weight (kg) | 0.02 | 0.15 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 10 |
| Body Surface Area (m2) | 0.007 | 0.025 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.5 |
| Km factor | 3 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 20 |
| Animal A (mg/kg) = Animal B (mg/kg) multiplied by | Animal B Km |
| Animal A Km |
For example, to modify the dose of resveratrol used for a mouse (22.4 mg/kg) to a dose based on the BSA for a rat, multiply 22.4 mg/kg by the K
m factor for a mouse and then divide by the K
m factor for a rat. This calculation results in a rat equivalent dose for resveratrol of 11.2 mg/kg.
| Rat dose (mg/kg) = mouse dose (22.4 mg/kg) × | mouse Km(3) | = 11.2 mg/kg |
| rat Km(6) |
References
Clinical Trial Information( data from http://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2016-07-09)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor
/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|
| NCT02031679 | Recruiting | Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria | Johns Hopkins University|AstraZeneca | January 2014 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01311635 | Completed | Healthy | AstraZeneca | April 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01254461 | Completed | Drug Interaction | AstraZeneca | February 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01265641 | Completed | Asthma | AstraZeneca | January 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01199341 | Completed | Pharmakokinetic | AstraZeneca | October 2010 | Phase 1 |
| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|
| US2015210655 | 2015-07-30 | CERTAIN (2S)-N-[(1S)-1-CYANO-2-PHENYLETHYL]-1,4-OXAZEPANE-2-CARBOXAMIDES AS DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE 1 INHIBITORS |
| US2015072963 | 2015-03-12 | COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR REGULATING HAIR GROWTH |
| US2014328861 | 2014-11-06 | Combination of CRTH2 Antagonist and a Proton Pump Inhibitor for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis |
| US8772305 | 2014-07-08 | Substituted pyridinyl-pyrimidines and their use as medicaments |
| US8227622 | 2012-07-24 | Pharmaceutical Process and Intermediates 714 |
| US2012178764 | 2012-07-12 | Novel Compounds |
| US2011263614 | 2011-10-27 | Novel compounds |
| US7781598 | 2010-08-24 | Process for the preparation of substituted indoles |
| US7687535 | 2010-03-30 | Substituted 3-sulfur indoles |
| US2009163518 | 2009-06-25 | Novel Compounds |
///////////
CC1=C(C2=C(N1CC(=O)O)C=CC=C2NC(=O)C)SC3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl