Temanogrel
APD 791
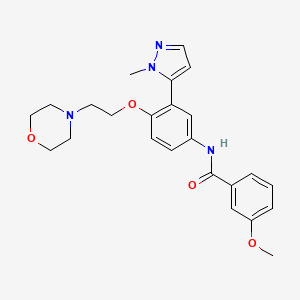
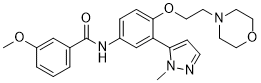
3-methoxy-N-[3-(2-methylpyrazol-3-yl)-4-(2-morpholinoethoxy)phenyl]benzamide
Benzamide,3-methoxy-N-[3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-4-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]-
UNII:F42Z27575A
| TEMANOGREL; APD791; CHEMBL1084617; UNII-F42Z27575A; 887936-68-7; 3-Methoxy-N-[3-(2-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-benzamide; | |
| Molecular Formula: | C24H28N4O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 436.50352 g/mol |
- Originator Arena Pharmaceuticals
- Developer Arena Pharmaceuticals; Ildong Pharmaceutical
- Class Antithrombotics; Small molecules
- Mechanism of Action Serotonin 2A receptor inverse agonists
Phase I Arterial thrombosis 

Most Recent Events
- 30 Mar 2016 Arena Pharmaceuticals has patents pending for Temanogrel in 12 regions, including Brazil (Arena Pharmaceuticals 10-K; march 2016)
- 30 Mar 2016 Arena Pharmaceuticals has patent protection for Temanogrel in 87 regions, including USA, Japan, China, Germany, France, Italy, the United Kingdom, Spain, Canada, Russia, India, Australia and South Korea
- 01 Mar 2015 Ildong Pharmaceutical initiates enrolment in a phase I trial for Arterial thrombosis in South Korea (NCT02419820)
A 5-HT2A inverse agonist potentially for the reduction of the risk of arterial thrombosis.


APD-791
CAS No. 887936-68-7
Temanogrel hydrochloride
- Molecular FormulaC24H29ClN4O4
- Average mass472.965
957466-27-2 CAS
Benzamide, 3-methox
Temanogrel hydrochl
UNII:5QEY8NZP3T
Temanogrel, also known as APD791, is a highly selective 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor inverse agonist under development for the treatment of arterial thrombosis. APD791 displayed high-affinity binding to membranes (K(i) = 4.9 nM) and functional inverse agonism of inositol phosphate accumulation (IC(50) = 5.2 nM) in human embryonic kidney cells stably expressing the human 5-HT(2A) receptor. APD791 was greater than 2000-fold selective for the 5-HT(2A) receptor versus 5-HT(2C) and 5-HT(2B) receptors. APD791 inhibited 5-HT-mediated amplification of ADP-stimulated human and dog platelet aggregation (IC(50) = 8.7 and 23.1 nM, respectively)
Arterial thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot or thrombus inside an artery or arteriole that restricts or blocks the flow of blood and, depending upon location, can result in acute coronary syndrome or stroke. The formation of a thrombus is usually initiated by blood vessel injury, which triggers platelet aggregation and adhesion of platelets to the vessel wall. Treatments aimed at inhibiting platelet aggregation have demonstrated clear clinical benefits in the setting of acute coronary syndrome and stroke. Current antiplatelet therapies include aspirin, which irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase (COXa
) and results in reduced thromboxane production, clopidogrel and prasugrel, which inhibit platelet adenosine diphosphate (ADP) P2Y12 receptors, and platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor antagonists. Another class of antiplatelet drugs, protease-activated thrombin receptor (PAR-1) antagonists, are also being evaluated in the clinic for the treatment of acute coronary syndrome. The most advanced candidate in this class, N-[(1R,3aR,4aR,6R,8aR,9S,9aS)-9-{2-[5-(3-fluorophenyl)pyridin-2-yl]vinyl}-1-methyl-3-oxoperhydro-naphtho[2,3-c]furan-6-yl]-carbamic acid ethyl ester (SCH-530348), is currently in phase 3 trials for the prevention of arterial thrombosis.
Abbreviations: COX, cyclooxygenase; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; SAR, structure−activity relationship; hERG, human ether-a-go-go-related gene; CNS, central nervous system; 5-HT, serotonin; AUC, area under the plasma concentration time curve, iv, intravenous; IP, inositol phosphate.
The 5-HT2A receptor is one of 15 different serotonin receptor subtypes.
In the cardiovascular system, modulation of 5-HT2A receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells and platelets is thought to play an important role in the regulation of cardiovascular function. Platelets are activated by a variety of agonists such as ADP, thrombin, thromboxane, serotonin, epinephrine, and collagen. Upon platelet activation at the site of blood vessel injury, a number of factors including serotonin (5-HT) are released. Although by itself serotonin is a weak activator of platelet aggregation, in vitro it can amplify aggregation induced by other agonists as mentioned above. Therefore, serotonin released from activated platelets may induce further platelet aggregation and enhance thrombosis.
The 5-HT2A receptor antagonist ketanserin was shown in clinical studies to reduce early restenosis(7) and decrease myocardial ischemia during coronary balloon angioplasty.(8)However, in another study, ketanserin did not significantly improve clinical outcomes, and the rate of adverse events was higher than that observed in the control group.(9) Some of the adverse events reported in the latter study could be specific to ketanserin and resulted from its lack of 5-HT2A receptor selectivity. Other 5-HT2A antagonists with improved selectivity profiles have shown promise in clinical studies. For example, sarpogrelate was shown to inhibit restenosis following coronary stenting.

Figure 1. Serotonin and known 5-HT2A receptor antagonists.
Because the 5-HT2A receptor is expressed both in peripheral tissues and in the central nervous system (CNS), compounds with limited CNS partitioning would be preferred to maximize cardiovascular and blood platelet pharmacological activity while minimizing CNS effects. In addition, because 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonists are thought to reduce thrombus formation via inhibition of serotonin-mediated amplification of platelet aggregation without inhibiting agonist driven aggregation per se, it is possible that this class of inhibitors will have an improved bleeding risk side effect profile compared to what has been observed with other classes of antithrombotic drugs.
SYNTHESIS
PAPER
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2010), 53(11), 4412-4421.
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jm100044a

Serotonin, which is stored in platelets and is released during thrombosis, activates platelets via the 5-HT2A receptor. 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonists thus represent a potential new class of antithrombotic agents. Our medicinal program began with known compounds that displayed binding affinity for the recombinant 5-HT2A receptor, but which had poor activity when tested in human plasma platelet inhibition assays. We herein describe a series of phenyl pyrazole inverse agonists optimized for selectivity, aqueous solubility, antiplatelet activity, low hERG activity, and good pharmacokinetic properties, resulting in the discovery of 10k (APD791). 10k inhibited serotonin-amplified human platelet aggregation with an IC50 = 8.7 nM and had negligible binding affinity for the closely related 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors. 10k was orally bioavailable in rats, dogs, and monkeys and had an acceptable safety profile. As a result, 10k was selected further evaluation and advanced into clinical development as a potential treatment for arterial
Discovery and Structure−Activity Relationship of 3-Methoxy-N-(3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-4-(2-morpholinoethoxy)phenyl)benzamide (APD791): A Highly Selective 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A Receptor Inverse Agonist for the Treatment of Arterial Thrombosis
Arena Pharmaceuticals, 6166 Nancy Ridge Drive, San Diego, California 92121
J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53 (11), pp 4412–4421
DOI: 10.1021/jm100044a
Publication Date (Web): May 10, 2010
Copyright © 2010 American Chemical Society
*To whom correspondence should be addressed. Phone: +1 858-453-7200. Fax: +1 858-453-7210. E-mail:yxiong@arenapharm.com.
3-Methoxy-N-[3-(2-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-benzamide (10k)
10k was prepared in a manner similar to that described for 10c, using 9d (120 mg, 0.40 mmol) and 3-methoxybenzoyl chloride (81 mg, 0.48 mmol) to give the TFA salt of 10k as a white solid (88 mg, 51%); mp (HCl salt, recrystallized from iPrOH) 214−216 °C. 1H NMR (acetone-d6, 400 MHz) δ: 2.99−3.21 (m, 2H), 3.22−3.45 (m, 2H), 3.66 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.79−3.89 (m, 4H), 4.58 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 6.29 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (dd, J = 2.5, 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.52 (t, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.80−7.83 (m, 1H), 7.91−7.96 (m, 1H), 9.54 (s, 1H). LCMSm/z = 437.5 [M + H]+.
Additional Information
Oral administration of APD791 to dogs resulted in acute (1-h) and subchronic (10-day) inhibition of 5-HT-mediated amplification of collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation in whole blood. Two active metabolites, APD791-M1 and APD791-M2, were generated upon incubation of APD791 with human liver microsomes and were also indentified in dogs after oral administration of APD791. The affinity and selectivity profiles of both metabolites were similar to APD791. These results demonstrate that APD791 is an orally available, high-affinity 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist with potent activity on platelets and vascular smooth muscle.(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19628629). PATENT WO 2006055734 https://google.com/patents/WO2006055734A2?cl=en Example 1.88: Preparation of 3-methoxy-N-[3-(2-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-(2-morpholin~ 4-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-benzamide (Compound 733).A mixture of 3-(2-methyl-2H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)-phenylamine (120 mg, 0.40 mmole), 3-methoxy-benzoyl chloride (81 mg, 0.48 mmole), and triethylamine (0.1 mL, 0.79 mmole) in 5 mL THF was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes. The mixture was purified by HPLC to give the title compound as a white solid (TFA salt, 88 mg, 51 %). 1H NMR ( Acetone-^, 400 MHz) 2.99-3.21 (m, 2H), 3.22-3.45 (m, 2H), 3.66 (t, J= 4.80 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.79-3.89 (m, 4H), 4.58 (t, J= 4.80 Hz, 2H), 6.29 (d, J= 2.02 Hz IH), 7.13 (dd, J= 8.34, 2.53 Hz, IH), 7.22 (d, J= 8.84 Hz, IH), 7.42 (t, J= 7.83 Hz, IH), 7.47 (d, J= 1.77 Hz, IH), 7.52 (t, J= 1.77 Hz, IH), 7.56 (d, J= 7.07 Hz, IH), 7.80-7.83 (m, IH), 7.91-7.96 (m, IH), 9.54 (s, NH). Exact mass calculated for C24H28N4O4 436.2, found 437.5 (MH+).
References
1: Xiong Y, Teegarden BR, Choi JS, Strah-Pleynet S, Decaire M, Jayakumar H, Dosa PI, Casper MD, Pham L, Feichtinger K, Ullman B, Adams J, Yuskin D, Frazer J, Morgan M, Sadeque A, Chen W, Webb RR, Connolly DT, Semple G, Al-Shamma H. Discovery and structure-activity relationship of 3-methoxy-N-(3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-4-(2-morpholinoethoxy)phenyl)benzamide (APD791): a highly selective 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor inverse agonist for the treatment of arterial thrombosis. J Med Chem. 2010 Jun 10;53(11):4412-21. doi: 10.1021/jm100044a. PubMed PMID: 20455563. 2: Przyklenk K, Frelinger AL 3rd, Linden MD, Whittaker P, Li Y, Barnard MR, Adams J, Morgan M, Al-Shamma H, Michelson AD. Targeted inhibition of the serotonin 5HT2A receptor improves coronary patency in an in vivo model of recurrent thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2010 Feb;8(2):331-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03693.x. Epub 2009 Nov 17. PubMed PMID: 19922435; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2916638. 3: Adams JW, Ramirez J, Shi Y, Thomsen W, Frazer J, Morgan M, Edwards JE, Chen W, Teegarden BR, Xiong Y, Al-Shamma H, Behan DP, Connolly DT. APD791, 3-methoxy-n-(3-(1-methyl-1h-pyrazol-5-yl)-4-(2-morpholinoethoxy)phenyl)benzamide, a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor antagonist: pharmacological profile, pharmacokinetics, platelet activity and vascular biology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Oct;331(1):96-103. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.153189. Epub 2009 Jul 23. PubMed PMID: 19628629.| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2015361031 | 2015-12-17 | STAT3 INHIBITOR |
| US8785441 | 2014-07-22 | 3-phenyl-pyrazole derivatives as modulators of the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor useful for the treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US2013296321 | 2013-11-07 | CRYSTALLINE FORMS AND PROCESSES FOR THE PREPARATION OF PHENYL-PYRAZOLES USEFUL AS MODULATORS OF THE 5-HT2A SEROTONIN RECEPTOR |
| US2012252813 | 2012-10-04 | CRYSTALLINE FORMS OF CERTAIN 3-PHENYL-PYRAZOLE DERIVATIVES AS MODULATORS OF THE 5-HT2A SEROTONIN RECEPTOR USEFUL FOR THE TREATMENT OF DISORDERS RELATED THERETO |
| US8148417 | 2012-04-03 | PRIMARY AMINES AND DERIVATIVES THEREOF AS MODULATORS OF THE 5-HT2A SEROTONIN RECEPTOR USEFUL FOR THE TREATMENT OF DISORDERS RELATED THERETO |
| US8148418 | 2012-04-03 | ETHERS, SECONDARY AMINES AND DERIVATIVES THEREOF AS MODULATORS OF THE 5-HT2A SEROTONIN RECEPTOR USEFUL FOR THE TREATMENT OF DISORDERS RELATED THERETO |
| US2011105456 | 2011-05-05 | 3-PHENYL-PYRAZOLE DERIVATIVES AS MODULATORS OF THE 5-HT2A SEROTONIN RECEPTOR USEFUL FOR THE TREATMENT OF DISORDERS RELATED THERETO |
| US7884101 | 2011-02-08 | 3-Phenyl-pyrazole derivatives as modulators of the 5-HT2a serotonin receptor useful for the treatment of disorders related thereto |
| US2010234380 | 2010-09-16 | CRYSTALLINE FORMS AND PROCESSES FOR THE PREPARATION OF PHENYL-PYRAZOLES USEFUL AS MODULATORS OF THE 5-HT2A SEROTONIN RECEPTOR |
| US2007244086 | 2007-10-18 | 3-Phenyl-Pyrazole Derivatives as Modulators of the 5-Ht2A Serotonin Receptor Useful for the Treatment of Disorders Related Thereto |
///////////APD-791 , 887936-68-7, Temanogrel , PHASE 1, ARENA,
CN1C(=CC=N1)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)NC(=O)C3=CC(=CC=C3)OC)OCCN4CCOCC4
C(=O)
