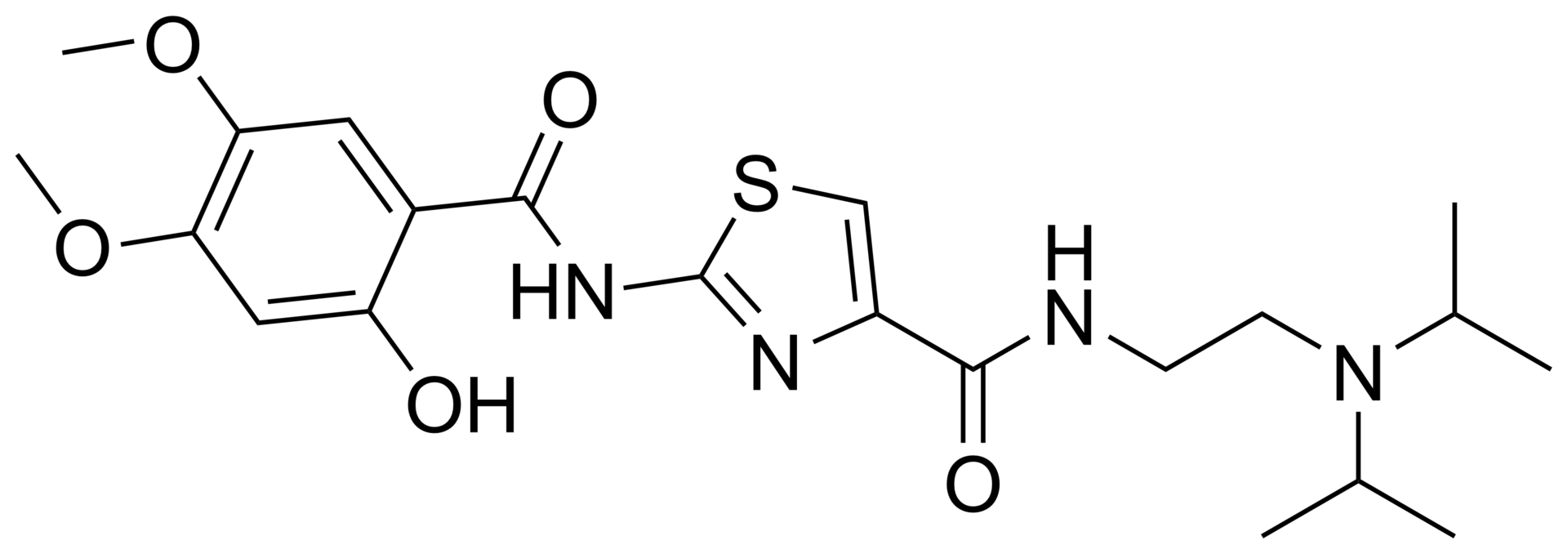
Acotiamide hydrochloride trihydrate
CAS#: 773092-05-0 (Acotiamide HCl hydrate, 1:1:3); 185104-11-4(Acotiamide HCl, 1:1); 185106-16-5 (Acotiamide free base)
Chemical Formula: C21H37ClN4O8S
Molecular Weight: 541.06
Elemental Analysis: C, 46.62; H, 6.89; Cl, 6.55; N, 10.36; O, 23.66; S, 5.93
Acotiamide, also known as YM-443 and Z-338, is a drug approved in Japan for the treatment of postprandial fullness, upper abdominal bloating, and early satiation due to functional dyspepsia. It acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Note: The Approved drug API is a cotiamide HCl trihydrate (1:1:3)
N-(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl)-2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzamido)thiazole-4-carboxamide hydrochloride trihydrate.
YM443; YM-443; YM 443; Z338; Z-338; Z 338; Acotiamide; Acotiamide hydrochloride trihydrate; Brand name: Acofide.
A peripheral acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor used to treat functional dyspepsia.
Acotiamide hydrochloride (acotiamide; N-[2-[bis(1-methylethyl) amino]ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] thiazole-4-carboxamide monohydrochloride trihydrate, Z-338) has been reported to improve meal-related symptoms of functional dyspepsia in clinical studies.
Acotiamide (Acofide(®)), an oral first-in-class prokinetic drug, is under global development by Zeria Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd and Astellas Pharma Inc. for the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia. The drug modulates upper gastrointestinal motility to alleviate abdominal symptoms resulting from hypomotility and delayed gastric emptying. It exerts its activity in the stomach via muscarinic receptor inhibition, resulting in enhanced acetylcholine release and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity. Unlike other prokinetic drugs that are utilized in the management of functional dyspepsia, acotiamide shows little/no affinity for serotonin or dopamine D2 receptors. Acotiamide is the world’s first approved treatment for functional dyspepsia diagnosed by Rome III criteria, with its first approval occurring in Japan. Phase III trials in this patient population are in preparation in Europe, with phase II trials completed in the USA and Europe.

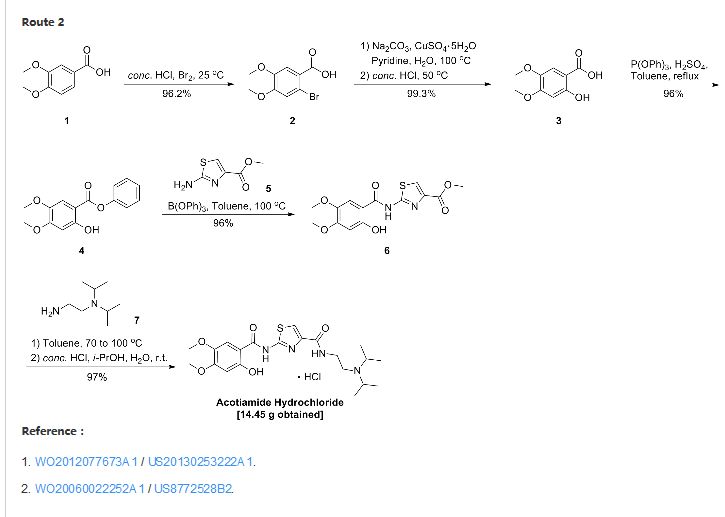
SYNTHESIS
| EP 0870765; US 5981557; WO 9636619 |
EP 0994108; WO 9858918
In a closely related procedure, acid chloride (II), prepared by treatment of 2,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid (VI) with SOCl2 in hot toluene, was condensed with aminothiazole (I), yielding amide (III). Displacement of the ethyl ester group of (III) by N,N-diisopropyl ethanediamine (V) furnished diamide (VII). Finally, upon formation of the hydrochloride salt of (VII) in isopropanol, the 2-methoxy group was simultaneously cleaved, directly leading to the title compound.
CN103709191A
Acotiamide hydrochloride, chemical name: N_ [2_ (diisopropylamino) ethyl] -2- [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino ] thiazole-4-carboxamide hydrochloride, the following structure:A test for the amine hydrochloride Japan Zeria Pharmaceutical Company and Astellas jointly developed acetylcholinesterase inhibitor class of prokinetic drugs, namely the treatment of functional dyspepsia drugs, is the world’s first approved specifically for the treatment of FD drugs, in June 2013 for the first time launched in Japan, under the trade name Acofide. Functional dyspepsia (Functional dyspepsia, FD) is a group of common symptoms include bloating, early satiety, burning sensation, belching, nausea, vomiting and abdominal discomfort and so difficult to describe, and no exact organic disease. Organic diseases because of lack of basic, functional dyspepsia harm to patients focus on the performance of gastrointestinal symptoms caused discomfort and possible impact on the quality of life in. Because some patients with functional dyspepsia symptoms caused by eating less, digestion and absorption efficiency is reduced, resulting in varying degrees of malnutrition (including nutrients are not full). With the people’s demands and improve the quality of life for functional dyspepsia know, the number of visits of the disease gradually increased, to become one of the most common disease of Gastroenterology partner waiting group. Such a high prevalence of functional dyspepsia treatment provides a huge market.
The present synthesis method has been reported in less divided into four methods are described below:
1, reference CN1084739C, synthetic route as shown below. Disadvantage of this patent is that: (I) using thionyl chloride and dichloroethane toxic, environmentally damaging substances; (2) demethylation low yield (64.6% to 86 reported in the literature %). Examples reported in this patent first and second step total yield was 84.6% and the total yield of the third-step reaction and recrystallization of 61%, the total yield of 51.6%.
The method, reported in the patent CN1063442C preparation A (page 25) reports (without reference to examples I and 6, referring to its general method). Patent CN102030654B (page 3) above: Step demethylation reaction generates a lot of by-products, it is difficult to take off only a selective protection of hydroxy groups, poor selectivity. Specific synthetic examples are shown below:
Preparation Method B 3 mentioned patent CN1063442C (prepared unprotected, p. 25), where the yield is very low two-step reaction. A test method for the preparation of amines referenced above example (Example 38) A test for specific preparation yield amine not mentioned in the text, but if you use the above method starting materials primary amino side reactions occur. Synthesis of solid concrete
Following is an example:
reported that patent CN101006040B in Method 4. The first step demethylation can also use titanium tetrachloride and aluminum chloride; the second reaction can also be used phenol / thionyl chloride. Synthetic route are higher yield and purity (total yield 73%).
The method of synthesis of the above methods 3 patent CN1063442C reported, though not suitable for the synthesis of amine A test, but may be modified on this basis.
the above patents, CN1084739 reagents using dichloroethane, toxic, environmentally destructive, and the total yield is low, is not conducive to industrial production; patent CN102030654B mentioned Step demethylation The reaction produces a lot of by-products, it is difficult to take off only selective hydroxy protecting group, the reaction selectivity, more side effects.
Example 4
[Amino-N- (2- tert-butoxycarbonyl group -4,5_ dimethoxybenzoyl)] _4_ Preparation of 2-methoxycarbonyl-1,3-thiazole: [0062] Step 1
2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxy-benzoic acid (100 g) was dissolved in dry toluene (400 ml) was added Boc20 (132 g) was stirred at rt for 3 hours at room temperature, was added a 10% aqueous citric acid (100 ml) and washed three times with purified water until neutral, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate was added (20 g) and dried 8 hours, filtered, and the filtrate was added thionyl chloride (64 g) and N, N-dimethyl- carboxamide (0.19 ml), followed by stirring 80 ° C for 4 hours, the compound was added 2-amino-4-methoxycarbonyl-1,3-thiazole (85 g), stirred for 5 hours at 100 ° C, the reaction was completed After cooling to room temperature, the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration, crystals were added to 1.6 liters of water, 400 g of ice was added with stirring, and added a mass ratio of 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution adjusted to pH 7.5, followed by stirring for 3 hours at room temperature, filtered The crystals were collected, washed with water, 60 ° C and dried to give the title compound (170 g).
Hl-NMR (DMSO, 400MHz) δ: 1.34 (s, 3H), 1.37 (s, 3H), 1.40 (s, 3H), 3.77 (s, 3H),
3.82 (s, 3H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 7.17 (s, 1H), 7.50 (s, 1H), 7.95 (s, 1H), 11.45 (bs, 1H).
Step 2: 2- [N- (2- hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] -4- [(2_ diisopropylamino ethyl) – aminocarbonyl] -1 , Preparation of 3-thiazole hydrochloride
The 2- [N- (2- tert-butoxycarbonyl group -4,5_ dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] _4_ methoxycarbonyl _1,3_ thiazole prepared (170 g) and N , N- diisopropyl-ethylenediamine (162 ml), N, N- dimethylacetamide (162 ml) was stirred at 135 ° C for 8 hours and cooled, 1-butanol (1.7 liters), with 0.5N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and washed with saturated brine, the mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, methanol (1.7 l), hydrogen chloride gas under cooling and stirred for 5 hours, the precipitate was collected by filtration, the crystals were washed with 2-propanol and water do recrystallized from a mixed solvent, to give the title compound. Melting point: 160 ° C.
[0067] Hl- bandit R (DMSO, 400ΜΗζ) δ: 1.33 (d, J = 6.4Hz, 6H); 1.36 (d, J = 6.4,6H), 3.17-3.20 (m, 2H); 3.57-3.69 ( m, 4H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.82 (s, 3H), 6.89 (s, 1H), 7.50 (s, 1H), 7.91 (s, 1H); 8
• 74 (t, 1H, J = 5.9Hz); 9.70 (s, 1H); 11.80 (s, 1H); 12.05-12.15 (bs, 1H).
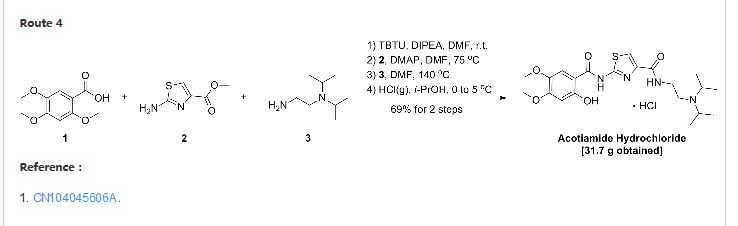
CN103387552A
A test for the amine hydrochloride (Z-338) is a new Ml Japan Zeria company’s original research, M2 receptor antagonist, for the treatment of functional dyspepsia clinic.Chinese patent application describes doxorubicin hydrochloride CN200580028537 test for amines (Z-338) preparation, reaction
Process is as follows.
A test for the amine hydrochloride (z-338) Compound Patent Application (CN96194002.6) choosing 2,4,5-trimethoxy benzoic acid as a starting material first with 2-aminothiazol-4-carboxylate reacts 2- [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] -1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylate, 2-methyl-benzene and then removed, the yield of this method lower demethylation selectivity bad. So choose the first 2-methyl-removal before subsequent reaction better.
The first patent application CN200580028537 2_ hydroxyl _4,5_ dimethoxy benzoic acid and triphenyl phosphite placed in toluene, was added a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst under reflux to give the intermediate 2-hydroxy – 4,5-dimethoxy-phenyl benzoate. After the above intermediate with 2-aminothiazol-4-carboxylate in place of toluene, was added triphenyl borate reacted, treated to give 2- [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxy- benzoyl) amino] -1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylate, and finally with N, N- diisopropylethylamine in toluene diamine salt in the system after the reaction.
2 – [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] thiazole Synthesis _1,3_ _4_ carboxylate
[0030] triphosgene dissolved in 90ml CH2Cl2 19.0g placed in a four-necked flask, under N2 stream, the 2_ hydroxyl _4,5_ dimethoxy benzoic acid (22.2g) was dissolved in 150ml CH2Cl2 and 45ml pyridine, at four-necked flask temperature dropped 0_5 ° C under ice-salt bath. Dropping finished within 45min, kept cold stirred lOmin. After warm to room temperature (20 ° C) was stirred for 50min, the reaction was stopped. Pressure filtration, and the filtrate by rotary evaporation at room temperature to a constant weight, adding 35g 2- aminothiazol-4-carboxylate and 240ml 1,2_ dichloroethane and heated to reflux, the reaction 6h. After stopping the cooling, suction filtration, washed with methanol and the resulting solid was refluxed in 40ml, hot filtration to give a white solid 32.18g, yield 85%. M + Na + 361; 2M + Na + 699. [0031] Example 2
2 – [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] thiazole Synthesis _1,3_ _4_ carboxylate
triphosgene dissolved in 15ml CH2Cl2 placed 3.0g four-necked flask, under N2 stream, the 2_ hydroxyl _4,5_ dimethoxy benzoic acid (3.0g) was dissolved in pyridine 30ml CH2Cl2 and 61,111, in four-necked flask temperature dropped 0_5 ° C under ice-salt bath. 20min Upon completion, kept cold stirring lh. After warm to room temperature (20 ° C) and stirred overnight, 24h after stopping the reaction. Rotary evaporation at room temperature to a constant weight is added 3.5g 2- aminothiazol-4-carboxylate and 30ml 1,2- dichloroethane burning, heated to reflux, the reaction 6h. The solvent was evaporated after stopping, add 30ml methanol reflux filtration to give a white solid 4.1g, 20ml methanol was added to the mother liquor evaporated leaching and washing a white solid 0.85g. After the merger was solid 4.95g, yield 97%.
Example 3
2 – [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] thiazole Synthesis _1,3_ _4_ carboxylate
The diphosgene 3.0g was dissolved into 15ml CH2Cl2 four-necked flask, under N2 stream, the 2_ hydroxyl _4,5_ dimethoxy benzoic acid (3.0g) was dissolved in 30ml CH2Cl2 and 61,111 pyridine, Under ice-salt bath temperature dropped a four-necked flask 0_5 ° C. 20min Upon completion, kept cold stirring lh. After warm to room temperature (20 ° C) and stirred overnight, 24h after stopping the reaction. Rotary evaporation at room temperature to a constant weight is added 3.5g 2- aminothiazol-4-carboxylate and 30ml 1,2- dichloroethane burning, heated to reflux, the reaction 6h. After the solvent was evaporated and stopped by adding 30ml of methanol was refluxed for leaching to give a white solid 4.57g, yield 89.6%.
Example 4
2 – [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] thiazole Synthesis _1,3_ _4_ carboxylate
triphosgene dissolved in 15ml CH2Cl2 placed 3.0g four-necked flask, under N2 stream, the 2_ hydroxyl _4,5_ dimethoxy benzoic acid (3.0g) `pyridine was dissolved in 30ml CH2Cl2 and 61 111, Under ice-salt bath temperature dropped a four-necked flask 0_5 ° C. 20min Upon completion, kept cold stirring lh. After warm to room temperature (20 ° C) and stirred overnight, 24h after stopping the reaction. Rotary evaporation at room temperature to a constant weight is added 3.7g 2- aminothiazol-4-carboxylic acid ethyl ester and 30ml 1,2- dichloroethane burning, heated to reflux, the reaction 6h. The solvent was evaporated after stopping, add 30ml methanol reflux filtration to give a white solid 3.8g, 20ml methanol was added to the mother liquor evaporated leaching and washing a white solid 0.54g. After the merger was solid 4.34g, yield 81.4%. M + Na + 375.
Example 5
N- [2_ (diisopropylamino) ethyl] -2 – [(hydroxy -4,5_ 2_ dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] -1,3-thiazol-4-carboxamide amide hydrochloride
2 – [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] thiazole _4_ _1,3_ carboxylate and 1.5g IOml 1,4- dioxane placed in a four-necked flask, N2 gas shielded at 75 ° C was added dropwise 1.5ml N, N- diisopropyl-ethylenediamine, rose after reflux, the reaction was stirred for 6 hours. The reaction was stopped, the solvent was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure, 30ml CH2Cl2 was added dissolved in 20ml10% NaCl solution was washed twice, and then the organic solvent was evaporated to dryness. IOml methanol was added, concentrated hydrochloric acid was added to adjust Xeon acidic. Evaporated methanol, washed with acetone to give the product 2.08g, yield 96.3%. M + H 451, MH 449.
Example 6
[0044] N- [2- (diisopropylamino) ethyl] -2 – [(hydroxy _4,5_ 2_ dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] -1,3-thiazol-4-carboxamide amide hydrochloride
2 – [(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl) amino] thiazole _4_ _1,3_ carboxylate and 1.5g IOml 1,4- dioxane placed in a four-necked flask, N2 gas shielded at 75 ° C was added dropwise 1.5ml N, N- diisopropyl-ethylenediamine, rose after reflux, the reaction was stirred for 6 hours. The reaction was stopped, the solvent was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure, 30ml CH2Cl2 was added dissolved in 20ml10% NaCl solution was washed twice, and then the organic solvent was evaporated to dryness. IOml methanol was added, concentrated hydrochloric acid was added to adjust Xeon acidic. Evaporated methanol, washed with acetone to give the product 1.76g, yield 84.7%.
PAPER
A Three-Step Synthesis of Acotiamide for the Treatment of Patients with Functional Dyspepsia
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, Shandong P.R. China
Org. Process Res. Dev., 2015, 19 (12), pp 2006–2011
DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.5b00256
Publication Date (Web): November 13, 2015
Copyright © 2015 American Chemical Society
*E-mail: chm_zhenggx@ujn.edu.cn. Tel.: +8653182765841.
Abstract
A three-step synthesis of acotiamide
is described. The agent is marketed in Japan for treatment of patients
with functional dyspepsia. We designed a one-pot method to prepare the
key intermediate 5a from 2 via an acyl chloride and amide and then reacted with 6 to obtain 1 under solvent-free condition. With the use of DCC, the unavoidable impurity 5b was also successfully converted into the desired 1. After isolation of 1,
we carried forward to the next step of HCl salt formation, which was
proved to be a very effective procedure for the removal of practically
all major impurities. The process is cost-effective, simple to operate,
and easy to scale-up.
References
Matsueda K, Hongo M, Tack J, Aoki H, Saito Y, Kato H (January 2010). “Clinical trial: dose-dependent therapeutic efficacy of acotiamide hydrochloride (Z-338) in patients with functional dyspepsia – 100 mg t.i.d. is an optimal dosage”. Neurogastroenterology and Motility : the Official Journal of the European Gastrointestinal Motility Society 22 (6): 618–e173. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01449.x. PMID 20059698.: Mayanagi S, Kishino M, Kitagawa Y, Sunamura M. Efficacy of acotiamide in combination with esomeprazole for functional dyspepsia refractory to proton-pump inhibitor monotherapy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2014;234(3):237-40. PubMed PMID: 25382232.
2: Zai H, Matsueda K, Kusano M, Urita Y, Saito Y, Kato H. Effect of acotiamide on gastric emptying in healthy adult humans. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014 Dec;44(12):1215-21. doi: 10.1111/eci.12367. PubMed PMID: 25370953.
3: Xiao G, Xie X, Fan J, Deng J, Tan S, Zhu Y, Guo Q, Wan C. Efficacy and safety of acotiamide for the treatment of functional dyspepsia: systematic review and meta-analysis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:541950. doi: 10.1155/2014/541950. Epub 2014 Aug 12. PubMed PMID: 25197703; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4146483.
4: Sun Y, Song G, McCallum RW. Evaluation of acotiamide for the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2014 Aug;10(8):1161-8. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2014.920320. Epub 2014 May 31. PubMed PMID: 24881488.
5: Matsunaga Y, Tanaka T, Saito Y, Kato H, Takei M. [Pharmacological and clinical profile of acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate (Acofide(®) Tablets 100 mg), a novel therapeutic agent for functional dyspepsia (FD)]. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2014 Feb;143(2):84-94. Review. Japanese. PubMed PMID: 24531902.
6: Nowlan ML, Scott LJ. Acotiamide: first global approval. Drugs. 2013 Aug;73(12):1377-83. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0100-9. Erratum in: Drugs. 2014 Jun;74(9):1059. Nolan, Mary L [corrected to Nowlan, Mary L]. PubMed PMID: 23881665.
7: Altan E, Masaoka T, Farré R, Tack J. Acotiamide, a novel gastroprokinetic for the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia: postprandial distress syndrome. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Sep;6(5):533-44. doi: 10.1586/egh.12.34. Review. PubMed PMID: 23061703.
8: Nagahama K, Matsunaga Y, Kawachi M, Ito K, Tanaka T, Hori Y, Oka H, Takei M. Acotiamide, a new orally active acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, stimulates gastrointestinal motor activity in conscious dogs. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012 Jun;24(6):566-74, e256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01912.x. Epub 2012 Mar 19. PubMed PMID: 22429221.
9: Kusunoki H, Haruma K, Manabe N, Imamura H, Kamada T, Shiotani A, Hata J, Sugioka H, Saito Y, Kato H, Tack J. Therapeutic efficacy of acotiamide in patients with functional dyspepsia based on enhanced postprandial gastric accommodation and emptying: randomized controlled study evaluation by real-time ultrasonography. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012 Jun;24(6):540-5, e250-1. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01897.x. Epub 2012 Mar 4. PubMed PMID: 22385472.
10: McLarnon A. Dyspepsia: Acotiamide can relieve symptoms of functional dyspepsia. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Jan 17;9(2):62. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.262. PubMed PMID: 22249733.
| CN103665023A * | Dec 23, 2013 | Mar 26, 2014 | 华润赛科药业有限责任公司 | Synthetic method of acotiamide hydrochloride |
| CN103980226A * | May 10, 2014 | Aug 13, 2014 | 杭州新博思生物医药有限公司 | Acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate crystal form and preparation method thereof |
| CN104031001A * | Jun 30, 2014 | Sep 10, 2014 | 山东诚创医药技术开发有限公司 | Method for preparing 2-(N-(2,4,5-trimothoxyaniline) amino]-4-carbethoxy-1,3-thiazole by using one-pot process |
| CN104031001B * | Jun 30, 2014 | Sep 30, 2015 | 山东诚创医药技术开发有限公司 | 一锅烩制备2-[n-(2,4,5-三甲氧基苯甲胺基)氨基]-4-乙氧羰基-1,3-噻唑的方法 |
| CN104045606A * | Jul 11, 2014 | Sep 17, 2014 | 杭州新博思生物医药有限公司 | One-pot method for preparing acotiamide hydrochloride |
| CN104045606B * | Jul 11, 2014 | Sep 30, 2015 | 杭州新博思生物医药有限公司 | 一锅法制备阿考替胺盐酸盐的方法 |
| CN103665023A * | Dec 23, 2013 | Mar 26, 2014 | 华润赛科药业有限责任公司 | Synthetic method of acotiamide hydrochloride |
| CN104045606A * | Jul 11, 2014 | Sep 17, 2014 | 杭州新博思生物医药有限公司 | One-pot method for preparing acotiamide hydrochloride |
| CN104045606B * | Jul 11, 2014 | Sep 30, 2015 | 杭州新博思生物医药有限公司 | 一锅法制备阿考替胺盐酸盐的方法 |
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
N-{2-[Bis(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl}-2-{[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)carbonyl]amino}-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Legal status |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 185106-16-5 |
| ATC code | None |
| PubChem | CID: 5282338 |
| ChemSpider | 4445505 |
| UNII | D42OWK5383 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2107723 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C21H30N4O5S |
| Molecular mass | 450.55 g/mol |
Approval in Japan for Treating Functional Dyspepsia with Acofide®
Press Release
Tokyo, March 25, 2013 – Zeria Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Tokyo: 4559; “Zeria”) and Astellas Pharma Inc. (Tokyo: 4503; “Astellas”) announced today that as of March 25, Zeria has obtained the marketing approval of Acofide® Tablets 100mg (nonproprietary name: acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate; “Acofide”; Zeria’sdevelopment code: “Z-338”; Astellas’s development code: “YM443”) for the treatment of functional dyspepsia(FD) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan. Acofide has been co-developed by both companies.
Acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate is a new chemical entity originated by Zeria, and inhibits peripheralacetylcholinesterase activities. Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter to regulate gastrointestinalmotility, and through the inhibition of degradation of acetylcholine, Acofide improves the impaired gastricmotility and delayed gastric emptying, and consequently the subjective symptoms of FD such as postprandialfullness, upper abdominal bloating, and early satiation.
Acofide, the world first FD treatment which demonstrated efficacy in the patients with FD diagnosed by the Rome III, will be launched in Japan ahead of the rest of the world.Also, since Acofide will be the first treatment with FD indication, Zeria and Astellas will co-promote Acofide for the sake of the increase of disease awareness of FD, the prompt market penetration, and the maximization of product potential.
In March 2008, Zeria and Astellas concluded the agreement for the co-development and co-marketing of Acofide and, subsequently conducted the co-development. In September 2010, Zeria submitted the application for marketing approval to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan.
We believe that Acofide will contribute to alleviate the subjective symptoms and improve QOL of patients with FD.
Summary of Approval
Product name: Acofide® Tablets 100mg
Nonproprietary name: Acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate
Formulation: Tablet
Indication: Postprandial fullness, upper abdominal bloating, and early satiation due to functional dyspepsia
Dosage regimen: Normally in adults, 100mg of acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate is taken orally three times per day before a meal.
About Functional Dyspepsia (FD)
According to the Rome III, FD is a gastrointestinal disease comprised of subjective symptoms including postprandial fullness, early satiation and epigastric pain without any organic abnormality on gastrointestinal tract. The etiology of FD is still unclear, but it has been shown that delayed gastric emptying is closely associated with FD.
For inquiries or additional information
Zeria Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Public Relations
TEL:+81-3-3661-1039, FAX:+81-3-3663-4203
http://www.zeria.co.jp/english
Astellas Pharma Inc.
Corporate Communications
TEL: +81-3-3244-3201, FAX:+81-3-5201-7473
http://www.astellas.com/en
Tokyo, March 25, 2013 – Zeria Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Tokyo: 4559; “Zeria”) and Astellas Pharma Inc. (Tokyo: 4503; “Astellas”) announced today that as of March 25, Zeria has obtained the marketing approval of Acofide® Tablets 100mg (nonproprietary name: acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate; “Acofide”; Zeria’sdevelopment code: “Z-338”; Astellas’s development code: “YM443”) for the treatment of functional dyspepsia(FD) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan. Acofide has been co-developed by both companies.
Acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate is a new chemical entity originated by Zeria, and inhibits peripheralacetylcholinesterase activities. Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter to regulate gastrointestinalmotility, and through the inhibition of degradation of acetylcholine, Acofide improves the impaired gastricmotility and delayed gastric emptying, and consequently the subjective symptoms of FD such as postprandialfullness, upper abdominal bloating, and early satiation.
Acofide, the world first FD treatment which demonstrated efficacy in the patients with FD diagnosed by the Rome III, will be launched in Japan ahead of the rest of the world.Also, since Acofide will be the first treatment with FD indication, Zeria and Astellas will co-promote Acofide for the sake of the increase of disease awareness of FD, the prompt market penetration, and the maximization of product potential.
In March 2008, Zeria and Astellas concluded the agreement for the co-development and co-marketing of Acofide and, subsequently conducted the co-development. In September 2010, Zeria submitted the application for marketing approval to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan.
We believe that Acofide will contribute to alleviate the subjective symptoms and improve QOL of patients with FD.
Summary of Approval
Product name: Acofide® Tablets 100mg
Nonproprietary name: Acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate
Formulation: Tablet
Indication: Postprandial fullness, upper abdominal bloating, and early satiation due to functional dyspepsia
Dosage regimen: Normally in adults, 100mg of acotiamide hydrochloride hydrate is taken orally three times per day before a meal.
About Functional Dyspepsia (FD)
According to the Rome III, FD is a gastrointestinal disease comprised of subjective symptoms including postprandial fullness, early satiation and epigastric pain without any organic abnormality on gastrointestinal tract. The etiology of FD is still unclear, but it has been shown that delayed gastric emptying is closely associated with FD.
For inquiries or additional information
Zeria Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Public Relations
TEL:+81-3-3661-1039, FAX:+81-3-3663-4203
http://www.zeria.co.jp/english
Astellas Pharma Inc.
Corporate Communications
TEL: +81-3-3244-3201, FAX:+81-3-5201-7473
http://www.astellas.com/en
COC1=CC(O)=C(C=C1OC)C(=O)NC1=NC(=CS1)C(=O)NCCN(C(C)C)C(C)C