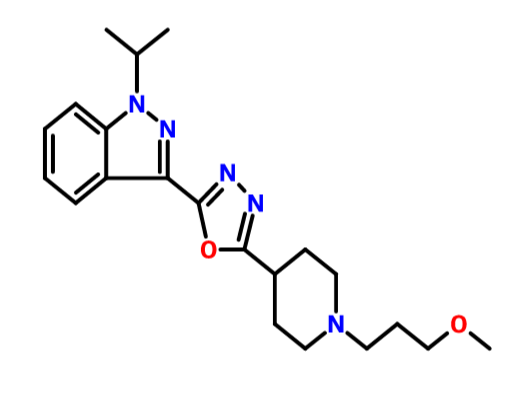
1H-Indazole, 3-[5-[1-(3-methoxypropyl)-4-piperidinyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl]-1-(1-methylethyl)-
CAS BASE 1428862-32-1, C21 H29 N5 O2, 383.49
SUVN-D4010

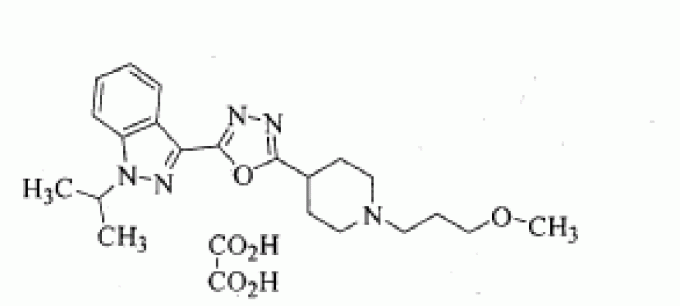
C21 H29 N5 O2 . C2 H2 O4
1H-Indazole, 3-[5-[1-(3-methoxypropyl)-4-piperidinyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl]-1-(1-methylethyl)-, ethanedioate (1:1)
1-isopropyl-3-{5-[1-(3-methoxypropyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-[1,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-1H-indazole oxalate
l-isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxy propyl) piperidin-4-yl]- [l,3>4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate salt
SUVN-1004028; SUVN-D-1208045; SUVN-D1003019; SUVN-D1104010; SUVN-D1108121;
l-ISOPROPYL-3-{5-[l-(3-METHOXYPROPYL) PIPERIDIN-4-YL]-[l,3,4]OXADIAZOL-2-YL}-1H-INDAZOLE OXALATE
OXALATE CAS 1428862-33-2
IN 2011CH03203, WO2013042135, WO 2015092804,
In phase I, for treating cognitive dysfunction associated with Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia and neurological diseases.
Suven Life Sciences Limited, Phase I Alzheimer's disease; Schizophrenia
- Class Antidementias
- Mechanism of Action Serotonin 4 receptor agonists
Used as 5-HT4 receptor agonist for treating Alzheimer's disease, cognitive disorders, Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, Parkinson's and schizophrenia
- 05 Jan 2016Suven Life Sciences has patent protection for chemical entities targeting serotonin receptors for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders in Canada, Africa and South Korea
- 11 Dec 2015Suven Life Sciences receives patent allowance for chemical entities targeting serotonin receptors in Eurasia, Europe, Israel and Macau
- 02 Nov 2015SUVN D4010 is available for licensing as of 02 Nov 2015. www.suven.com
SUVN-D4010 for Cognition in Alzheimer’s disease commenced Phase 1 Clinical Trial in USA under US-IND 126099
HYDERABAD, INDIA (Sept 02, 2015) – Suven Life Sciences today informed that their NCE SUVN-D4010 has commenced Phase 1 clinical trial in USA. SUVN-D4010 is a potent, selective, brain penetrant and orally active 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction associated with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Suven submitted Investigational New Drug Application (IND) to US FDA to conduct Phase-1 clinical trial for Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease, under 505(1) of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act (FDCA) which was assigned an IND number 126099.
Based on the IND# 126099, "A Single Center, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Randomized, Phase 1 Study to Evaluate the safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of SUVN-D4010 after Single Ascending Doses and Multiple Ascending Doses in Healthy Male Subjects” for Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease is underway in USA
"We are very pleased that the third compound from our pipeline of molecules in CNS has moved into clinical trial that is being developed for cognitive disorders in Alzheimer’s and Schizophrenia, a high unmet medical need which has huge market potential globally” says Venkat Jasti, CEO of Suven.
Suven Life Science is a biopharmaceutical company focused on discovering, developing and commercializing novel pharmaceutical products, which are first in class or best in class CNS therapies through the use of GPCR targets.Suven has 3 clinical stage compounds, a Phase 2 initiated candidate SUVN-502, Phase 1 completed candidate SUVN-G3031 and Phase 1 initiated candidate SUVN-D4010 for Alzheimer’s disease and Schizophrenia. In addition to that the Company has ten (10) internally-discovered therapeutic drug candidates currently in pre-clinical stage of development targeting conditions such as ADHD, dementia, depression, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and pain
 SUVEN Life Sciences Ltd
SUVEN Life Sciences Ltd
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder of advanced age characterized by loss of memory, accumulation of amyloid beta protein (Αβ) deposits and decreased levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Approximately forty percent of AD patients suffer from significant depression. 5-HT4 receptor partial agonists may be of benefit for both the symptomatic and disease-modifying treatment for AD and may offer improved clinical efficacy and/or tolerability relative to acetylcholine esterase inhibitors. 5-HT4 receptor agonists also have antidepressant like properties (Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 2007, 7, 1357-1374; Experimental Neurology, 2007, 203(1), 274- 278; Neuroscience & Medicine, 201 1 , 2, 87 - 92; Schizophrenia Bulletin, 2007, 33 (5), 1 100 - 1 1 19).
1 -Isopropyl-3 - { 5 - [ 1 -(3 -methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl] - [ 1 ,3 ,4]oxadiazol-2-y 1 } -1 H-indazole oxalate of formula (I) is a promising pharmaceutical agent, which is a potent, selective and orally bioavailable 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist intended for both disease modifying and symptomatic treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other disorders of memory and cognition like Attention deficient hyperactivity,
Parkinson's and Schizophrenia. . In addition to the pro-cognitive effects, the compound also demonstrated dose dependent antidepressant like effects in the mouse forced swim test. l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate and its synthesis is disclosed by Ramakrishna et al. in WO2013042135.
At present, l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l,3,4] oxadiazol-2-yl}-l H-indazole oxalate of formula (I) has completed preclinical studies and is ready to enter human clinical trials. The demand for l-Isopropyl-3-{ 5- [ 1 -(3 -methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]- [ 1 ,3 ,4]oxadiazol-2-yl } - 1 H-indazole oxalate of formula (I) as a drug substance would be increased substantially with the advent of its human clinical trials. The future need for much larger amounts is projected due to the intended commercialization of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l ,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate of formula (I).
For the person skilled in art, it is a well known fact that various parameters will change during the manufacturing of a compound on a large scale when compared to the synthetic procedures followed in laboratory. Therefore, there is a need to establish and optimize large scale manufacturing process. The process for the preparation of l -Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l ,3,4] oxadiazol-2-yl}-l H-indazole oxalate of formula (I) which was disclosed in WO2013042135 had been proved to be unsatisfactory for the large scale synthesis. Eventually, it is highly desirable to establish optimized manufacturing process for l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l ,3,4] oxadiazol-2-yl}-l H-indazole oxalate of formula (I) which is amenable to the large scale preparation.
PATENT
WO2013042135
Example 3: Preparation of l-isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxy propyl) piperidin-4-yl]- [l,3>4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate salt
Step (i): Preparation of l-isopropyI-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxy propyl) piperidin-4-yI]- [l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazo!e
To the mixture of l-isopropyl-lH-indazole-3-carboxylic acid hydrazide (15.0 grams, 68.8 mmol) and l-(3-Methoxy propyl)-piperidine-4-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (20.9 grams, 88.2 mmol, obtained in preparation 7) cooled at 0 °C was added phosphoryl chloride (130 mL). The reaction temperature was gradually raised to 100 °C and stirred was 2 hours. Upon completion of the reaction, it was cooled to 0 °C and triturated with hexanes (3 x 250 mL). The crude product was basified with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and extracted with 5% methanol in dichloromethane. The combined organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulphate and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain l-isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxy propyl) piperidin-4-yl]- [l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole (15.78 grams)
Yield: 59 %.
Ή - NMR (CDCb): δ 8.35 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (t, J *= 7.0 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 5.05-4.90 (m, 1H), 3.44 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 3.35 (s, 3H), 3.15-2.97 (m, 3H), 2.48 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 2.26-2.02 (m, 6H), 1.88-1.75 (m, 2H), 1.67 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 384.5 (M+H)+.
Step (ii): Preparation of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxy-propyl)-piperidin-4-yl]- [l,3,4]oxadiazoI-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate salt
To a stirred solution of l-isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxy propyl) piperidin-4-yl]- [l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole (12.55 grams, 32.7 mmol, obtained in the above step) in 2-propanol (200 mL), oxalic acid (4.12 grams, 32.7 mmol) was added. After stirring at room temperature for 1 hour the reaction was further diluted with 2-propanol and refluxed for 2 hours. The crystalline product which was precipitated after cooling the reaction mixture to room temperature was filtered, dried under vacuum to obtain 1- isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxy propyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH- indazole oxalate salt (16.4 grams)
Yield: 88 %
Ή - NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 8.18 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.38 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 5.23 - 5.10 (m, 1H), 3.50 - 3.40 (m, 3H), 3.37 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 3.23 (s, 3H), 3.10 -2.96 (m, 4H), 2.35 - 2.25 (m, 2H), 2.18-2.02 (m, 2H), 1.94 - 1.85 (m, 2H), 1.53 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 384.3 (M+H)+.
Patent
The large scale manufacturing process for preparation of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l ,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate of

Scheme-1
Preparation 1: Preparation of l-Isopropyl-lH-indazoIe-3-carboxylic acid

To a stirred solution of dimethylformamide (DMF) (50 L) at 25 °C to 30 °C under nitrogen atmosphere, sodium tert-butoxide (6.0 Kg, 62.43 mols) was added over a period of 15 minutes. The reaction mixture was stirred for 10 minutes after which it was cooled to 0 °C to 5 °C. A solution of indazole-3-carboxylic acid (4.0 Kg, 24.67 mols) in DMF (50 L) was added slowly into the reactor over a period of 45 minutes, maintaining the reaction mass temperature at 0 °C to 5 °C. The cooling was removed and the reaction temperature was gradually raised to 25 °C to 30 °C over a period of 30 minutes. After stirring at this temperature for 1 hour the reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and isopropyl iodide (6.32 Kg, 37.18 mo!s) was added over a period of 30 minutes. The cooling was removed and the reaction temperature was allowed to rise to 25 °C to 30 °C. After 17 hours of stirring, the HPLC analysis of the reaction mixture revealed <10 % of indazole-7-carboxylic acid remaining. The reaction mass was diluted cautiously with water (200 L) and washed with ethylacetate (2 x 100 L). The resultant aqueous layer was acidified to 4.0 - 4.5 pH with aqueous hydrochloride solution (6.0 N, 21.5 L) and extracted with ethylacetate (2 x 144 L). The combined organic layer was washed with water (2 x 100 L), brine solution (200 L) and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (4.0 Kg). The filtered organic layer was subjected to solvent removal under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 50 °C to 60 °C to obtain a crude mass. The obtained crude mass was diluted with dichloromethane (DCM) (28.0 L) and was stirred for 15 minutes. The solids precipitated (un-reacted indazole-7-carboxylic acid) were filtered through nutsche filter and the filter bed was washed once with DCM (8.0 L). The combined filtrate was distilled under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 45 °C to 55 °C to obtain a crude mass which was stirred with ether (7.0 L) for 30 minutes and filtered through nutsche filter to obtain the wet solid which was dried further in vacuum oven under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 45 °C to 55 °C to obtain above titled compound (3.0 Kg) as an off-white crystalline powder.
Yield: 59.5 %;
Purity: 99.86 %;
IR (cm-'): 2980, 1729, 1682, 1487, 1287, 1203, 1 170, 1 127, 1085, 754;
Ή-NMR (δ ppm, CDC13): 8.27 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (d, J= 8.4 Hz, 1H), .7.46 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 5.01 - 4.95 (m, 1H), 1 .68 (d, J = 6.65 Hz, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 205.1 (M+H)+.
Preparation 2: Preparation of l-(3-Methoxypropyl) piperidine-4-carboxyIic acid hydrazide

Step (i): Preparation of Ethyl 1 -(3-methoxj propyl) piperidine-4-carboxylate

To a stirred solution of acetonitrile (97.5 L) under nitrogen atmosphere at 25 °C to 30 °C, ethyl isonipecotate (6.5 Kg, 41.35 mols) was added. The contents were stirred for 10 minutes after which potassium carbonate powder (7.35 Kg, 53.2 mols) and l-Bromo-3-methoxy propane (6.89 Kg, 45.0 mols) were sequentially added. The reaction mixture was gradually heated to reflux (82 °C - 85 °C) over a period of 30 minutes and was maintained at this temperature for 7 hours. At this time, the TLC revealed complete consumption of ethylisonipecotate. The volatiles were distilled off under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 50 °C to 60 °C. The crude mass was cooled to 25 °C to 30 °C and was diluted with water (71.5 L) and DCM (136.5 L). After stirring the contents the two layers were separated. The organic layer was washed with water (71.5 L), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (6.5 Kg) and the volatiles were removed under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 50 °C to 55 °C to obtain the desired product (9.3 Kg) as pale yellow colored liquid.
Yield: 98 %;
Purity: 98.8 %;
IR (cm"'): 2949, 1732, 1449, 1376, 1 179, 11 19, 1048;
Ή-NMR (6 ppm, CDC13): 4.06 (q, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 3.37 - 3.34 (t, J - 6.4 Hz, 2H), 3.27 (s, 3H), 2.83 - 2.80 (m, 2H), 2.34 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 2.22 - 2.18 (m, 1H), 1.96 - 1.94 (m, 2H), 1.85 - 1.82 (m, 2H), 1.74 -1.68 (m, 4H), 1.19 (t, J= 7.04 Hz, 3H);
Mass (m/z): 230.4 (M+H)+.
Step (ii): Preparation of l-(3-Methoxypropyl) piperidine-4-carboxylic acid hydrazide

To a stirred solution of methanol (38 L) under nitrogen atmosphere at 25 °C to 30 °C, ethyl l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidine-4-carboxylate (5.0 Kg, 21.8 mols, obtained in above step) was added. After stirring the reaction mixture for 15 minutes, hydrazine hydrate (80 % w/v, 4.1 Kg, 65.4 mols) was added over a period of 15 minutes. The reaction mixture was gradually heated to reflux (70 °C) over 30 minutes and continued stirring for 4 hours. Additional amount of hydrazine hydrate (80 % w/v, 4.1 Kg, 65.4 mols) was added and the stirring continued for another 4 hours. Another installment of hydrazine hydrate (80 % w/v, 4.1 Kg, 65.4 mols) was added and the stirring was continued for 16 hours at 70 °C, upon which the Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) reveals < 5 % of ester. The volatiles were distilled off under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 60 °C until syrupy mass appeared. After cooling syrypy mass to room temperature (25 °C - 30 °C), it was diluted with DCM (38.0 L) and was stirred for 15 minutes. The observed two layers were then separated. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (5.0 Kg) and the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 55 °C until dryness. The solid product which was separated was cooled to 25 °C to 30 °C, diluted with hexanes (15.0 L) and the resultant slurry was filtered at nutsche filter. The filter bed was washed once with hexanes (15.0 L) and ethylacetate (2 x 10.0 L). The product cake was vacuum dried and the solid material thus separated was further dried in vacuum oven under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) at 50 °C for 6 hours to obtain the above titled compound (4.1 Kg) as an off-white crystalline powder.
Yield: 87 %;
Purity: 99.79 %;
IR (cm-'): 3290, 3212, 2948, 2930, 1637, 1530, 1378, 1 124, 1 1 13, 986, 948, 789, 693;
Ή-NMR (δ ppm, CDC13): 6.83 (s, 1H), 3.86 (bs, 2H), 3.41 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 3.32 (s, 3H), 2.99 - 2.96 (m, 2H), 2.42 (t, J= 7.44 Hz, 2H), 2.1 1 - 1.96 (m, 3H), 1.82 - 1.73 (m, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 216.3 (M+H)+.
Example 1: Preparation of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yI]-[l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate
Step (i): Preparation of N-[l-(3-Methoxypropyl) piperidine-4-carbonyI] '-(l-isopropyI-lH-indazole-3-carbonyl) hydrazine

To a stirred solution of 1 ,2-dichloroethane (19.8 L) under nitrogen atmosphere at 25 °C to 30 °C, l -isopropyl-lH-indazole-3-carboxylic acid (3.0 Kg, 14.69 moles, obtained in preparation 1 ) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 15 minutes for complete dissolution. Thionyl chloride (3.6 Kg, 30.25 mols) was then added to the reaction mixture by maintaining its temperature below 30 °C over a period of 15 minutes. The reaction temperature was then gradually raised to 75 °C over a period of 30 minutes and was stirred for 2 hours at that temperature. The TLC revealed complete conversion of acid to acid chloride. The solvent 1,2-dichloroethane and excess thionyl chloride was removed under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) below 60 °C temperature. The obtained residual mass was cooled to 25 °C to 30 °C, and diluted with DCM (15.6 L). The contents were further cooled to 0 °C to 5 °C. A solution of l-(3-Methoxypropyl) piperidine-4-carboxylic acid hydrazide (3.0 Kg, 1 3.94 mols, obtained in the preparation 2) in DCM (18.0 L) was added to the reaction mass over a period of 30 minutes. The reaction temperature was then gradually raised to 25 °C to 30 °C and the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 hours. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC which showed absence of hydrazide (< 1.0 %). The reaction mixture was then diluted with water (30.0 L), stirred for 15 minutes and the two layers were separated. The aqueous layer was washed with DCM (1 x 30.0 L), cooled to 0 °C to 5 °C and cautiously basified to pH 7.6 with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution (10 % w/v, 46.5 L). The basified aqueous layer was then extracted with DCM (2 x 30.0 L). The combined organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (6.0 Kg) and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) below 55 °C. The residue was then cooled to 25 °C - 30 °C and diluted with solvent hexane (9.0 L). The slurry, thus obtained, was centrifuged at room temperature under nitrogen atmosphere and the wet product cake was washed with hexanes (6.0 L). The wet product was then dried in oven at 55 °C -60 °C until loss on drying was < 1.0 % to obtain the above titled compound (4.4 Kg) as an off white crystalline powder.
Yield: 74.5 %;
Purity: 98.75 %;
IR (cm-1): 3506, 3233, 2943, 1703, 1637, 1523, 1487, 1 195, 1 1 16, 750;
Ή-NMR (δ ppm, CDC13): 9.35 (bs, 1H), 8.70 (bs, 1H), 8.30 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 4.90 -4.85 (m, 1H), 3.40 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 3.33 (s, 3H), 2.94 - 2.85 (m, 2H), 2.39 -2.31 (m, 3H), 1.92 - 1.88 (m, 4H), 1.76 - 1.65 (m, 4H), 1.59 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 6H); Mass (m/z): 402.2 (M+H)+.
Step (ii): Preparation of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l,3»4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole

To a stirred solution of 1 ,2-dichloroethane (60 L) under nitrogen atmosphere at 25 °C to 30 °C, N-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidine-4-carbonyl] N'-(l -isopropyl-1 H-indazole-3-carbonyl) hydrazine (3.0 Kg, 7.47 mols, obtainted in above step) was added and the contents were stirred for 15 minutes afterwhich, thionyl chloride (1.77 Kg, 15.0 mols) was added over 15 minutes time. The reaction mixture temperature was then gradually raised to 79 °C - 83 °C over a period of 30 minutes at which the reaction mixture starts refluxing. Upon completion of 9 hours, the reaction mass showed complete consumption of starting material when checked by TLC. The excess thionyl chloride and solvent 1,2-dichloroethane were distilled off under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) below 60 °C. The reaction mass was cooled to 25 °C - 30 °C, diluted with water (39.0 L) and solvent ether (19.5 L). The resulting mass was stirred for 15 minutes and the two layers were separated. The pH of the aqueous layer was adjusted to 9 - 10 by adding an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (2.5N, 3.0 L). The basified aqueous layer was then extracted with DCM (2 x 54.0 L). The combined organic layer was washed with cold (5 °C - 10 °C) aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (0.6 N, 54.0 L), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (6.0 Kg) and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) below 55 °C, which yielded above titled compound (2.6 Kg) as brown colored syrupy mass.
Yield: 90.5 %;
Purity: 99.3 %;
IR (cm"1): 3054, 2946, 2808, 1599, 1563, 1462, 1389, 121 1, 1 120, 1069, 999, 749; Ή-NMR (6 ppm, CDC13): 8.34 (d, J = 8.12 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (d, J - 8.44 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 7.58 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (t, J = 7.44 Hz, 1H), 4.98 - 4.93 (m, 1H), 3.44 (t, J = 6.44 Hz, 2H), 3.03 - 3.00 (m, 3H), 3.34 (s, 3H), 2.46 (t, J = 7.54 Hz, 2H), 2.20 -2.02 (m, 6H), 1.80 (t, J= 7.27 Hz, 2H), 1.66 (d, J= 6.72 Hz, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 384.3 (M+H)+.
Step (iii): Purification of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyI) piperidin-4-yl]-[l,3.4]oxadiazoI-2-yl}-lH-indazole
The above obtained crude step (ii) product was dissolved in a stirring aqueous acetic acid solution (10 % w/v, 26.0 L) and washed with ethylacetate (2 x 26.0 L). The resultant aqueous layer pH was adjusted to 9.0 - 10.0 by adding an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (0.5N, 52.0 L). The basified aqueous layer was extracted with solvent ether (2 x 26.0 L) and the combined organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate (3.0 Kg). The volatiles were removed under reduced pressure (> 500 mm of Mercury) below 55 °C to obtain a brown colored syrupy mass (2.19 Kg).
Yield: 84 %;
Purity: 99.72 %;
IR (cm"1): 3054, 2978, 2946, 2808, 2772, 1599, 1563, 1462, 1389, 1 194, 1 177, 1 120, 1069, 999, 749;
Ή-NMR (δ ppm, CDC13): 8.34 (d, J = 8.12 Hz, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 8.44 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 7.58 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (t, J = 7.44 Hz, l H), 4.98 - 4.93 (m, 1H), 3.44 (t, J = 6.44 Hz, 2H), 3.03 - 3.00 (m, 3H), 3.34 (s, 3H), 2.46 (t, J = 7.54 Hz, 2H), 2.20 -2.02 (m, 6H), 1.80 (t, J= 7.27 Hz, 2H), 1.66 (d, J = 6.72 Hz, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 384.4 (M+H)+.
Step (iv): Preparation of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yI]-[l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yi}-lH-indazole oxalate
To a stirred solution of isopropanol (60.8 L) under nitrogen atmosphere at 25 °C -30 °C, l-isopropyl-3-{5-[l -(3-methoxypropyl) piperidin-4-yl]-[l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole (6.08 Kg, 15.86 mols, obtained in step (iii) was added, followed by oxalic acid (1.46 Kg, 16.2 mols) addition. The reaction mixture was stirred for 2 hours and solid product that is precipitated was filtered through nutsche filter under nitrogen atmosphere. The wet product bed was washed with isopropanol (10.0 L) and solvent ether (60.8 L) to obtain a technical grade product.
IR (cm"1): 3437, 2975, 2932, 2890, 1703, 1604, 1564, 1458, 1391, 1281, 1217, 1 192, 1 1 14, 992, 750;
Ή-NMR (δ ppm, DMSO-d6): 10.72, (bs, 2H), 8.16 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.51 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1 H), 7.35 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 5.20 - 5.07 (m, 1H), 3.55 - 3.43 (m, 3H), 3.36 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 3.21 (s, 3H), 3.1 8 - 2.98 (m, 4H), 2.40 - 2.30 (m, 2H), 2.26-2.12 (m, 2H), 1.96 - 1.85 (m, 2H), 1.53 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 384.4 (M+H)+.
Step (v): Recrystallization of l-Isopropyl-3-{5-[l-(3-methoxypropyI) piperidin-4-yl]-[l,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl}-lH-indazole oxalate
The above obtained product was suspended in a mixture of isopropanol (35.26 L) and water (7.3 L) and refluxed (76 °C) for 4 hours until complete dissolution. The homogenous solution thus obtained was gradually cooled to 25 °C - 30 °C and maintained at this temperature under slow stirring for 16 hours. The precipitated oxalate salt was centrifuged under nitrogen atmosphere. The product cake was washed with isopropanol (15.0 L) and ether (60.8 L). The suction dried product was then dried in vacuum oven at 25 °C - 30 °C for 2 hours and at 65 °C for 1 hour to obtain above titled compound (4.24 Kg) as light cream colored crystalline material.
Yield: 60 %;
Purity: 99.92 %;
Salt content (oxalate salt): 20.37 %;
Heavy metals: < 20 ppm;
IR (cm-1): 3437, 2975, 2932, 2890, 1703, 1604, 1564, 1458, 1391, 1281, 1217, 1 192, 1 1 14, 992, 750;
1H-NMR (δ ppm, DMSO-d6): 10.72, (bs, 2H), 8.16 (d, J- 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.85 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.51 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 5.20 - 5.07 (m, 1H), 3.55 - 3.43 (m, 3H), 3.36 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 3.21 (s, 3H), 3.18 - 2.98 (m, 4H), 2.40 - 2.30 (m, 2H), 2.26-2.12 (m, 2H), 1.96 - 1.85 (m, 2H), 1.53 (d, J= 6.6 Hz, 6H);
Mass (m/z): 384.4 (M+H)+.
REFERENCES
SUVN-D4010: Novel 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease
45th Annu Meet Soc Neurosci (October 17-21, Chicago) 2015, Abst 54.08
45th Annu Meet Soc Neurosci (October 17-21, Chicago) 2015, Abst 54.08
SEE BELOW
Characterization of SUVN-D1104010: A potent, selective and orallyactive 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist
Alzheimer's Assoc Int Conf (AAIC) (July 14-19, Vancouver) 2012, Abst P2-392
Alzheimer's Assoc Int Conf (AAIC) (July 14-19, Vancouver) 2012, Abst P2-392
SUVN-D1104010 displayed IC50 values > 45 and > 10 mcM for cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2D6, respectively. In dog, rat and human liver microsome preparations, it showed respective stabilities of 64, 26 and 26%. It displayed rat brain, rat plasma and human plasma protein binding values of 94, 89 and 93%, respectively. For parmacokinetic studies, the agent was administered to male Wistar rats (1 mg/kg i.v.; 3 mg/kg p.o.) and male Beagle dogs (1 mg/kg i.v. and p.o.). Following intravenous administration, the rats showed AUC(0-24 h), t1/2, MRT Last, Cl and Vdss values of 245 ng·h/mL, 1.1 hours, 1.1 hours, 67 mL/min/kg and 5.3 L/kg, respectively. Following intravenous administration to dogs, these respective values were 951 ng·h/mL, 6 hours, 3.9 hours, 18 mL/min/kg and 5.1 L/kg. Following oral administration to rats, the respective values were 136 ng·h/mL, 0.42 hours, 222 hours, 1.4 mL/min/kg and 1.4 L/kg. For dogs, these respective values were 179 ng·h/mL, 0.58 hours, 711 hours, 4.6 mL/min/kg and 4.0 L/kg. Oral bioavailabilty values in rats and dogs were 30 and 72%, respectively. The brain penetration profile was studied 1 hour after the administration of 1, 3 and 10 mg/kg p.o. in rats. Plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), whole brain samples were collected and drug concentrations were analyzed by liquid chromatography - mass spectrometry. Dosing at 1, 3 and 10 mg/kg p.o. was associated with respective plasma concentrations of 42, 136 and 537 nM; respective brain concentrations of 120, 352 and 1674 nM; respective CSF concentrations of 7, 18 and 90 nM; ratios of CSF concentrations over Ki values of 0.3, 0.8 and 3.8; ratios of brain concentrations over Ki values of 5, 5 and 70; and ratios of brain over plasma concentrations of 2.8, 2.5 and 3. Further studies included in vivo receptor occupancy (brain 5-HT4 receptor) analysis. The drug showed dose-dependent occupancy in the rat striatum and gained ready access to the brain. An ED50 of 2.75 mg/kg p.o. was noted. Brain cortical soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha (sAPPalpha) levels were assessed in male C57BL6 mice injected with 1-10 mg/kg s.c. and sacrificed 30/60 minutes later. Results were compared to vehicle-treated mice. At 3 and 10 mg/kg doses, significant increases in sAPPalpha levels were noted (P values < 0.05 and < 0.01, respectively) using ELISA. To study changes in CSF beta-amyloid levels, Wistar rats were administered the drug orally at 0.03-3 mg/kg and 2 hours later, CSF was collected and analyzed for beta-amyloid protein 42 (Abeta42) and 40 (Abeta40) by ELISA. The drug induced a decrease of 19-35% in Abeta42 levels and a decrease of 20-38% in Abeta40 levels in rat CSF at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg (P < 0.01). Toxicity studies are currently under way.
March 16, 2015
Drug firm Suven Life Sciences has been granted a patent each by the US and New Zealand for a drug used in the treatment of neuro-degenerative diseases.
The patents are valid until 2030 and 2031, respectively, Suven Life Sciences said in a filing to the BSE.
Commenting on the development, Suven Life CEO Venkat Jasti said: “We are very pleased by the grant of these patents to Suven for our pipeline of molecules in CNS arena that are being developed for cognitive disorders with high unmet medical need with huge market potential globally.”
SUVEN, Chief executive and chairman Venkat Jasti

The company has “secured patents in USA and New Zealand to one of their new chemical entity (NCE) for CNS therapy through new mechanism of action – H3 Inverse agonist…,” Suven Life Sciences said.
With these new patents, Suven has a total of 20 granted patents from US and 23 granted patents from New Zealand.
“These granted patents are exclusive intellectual property of Suven and are achieved through the internal discovery research efforts.
“Products out of these inventions may be out-licensed at various phases of clinical development like at Phase-I or Phase-II,” Suven said.

Suven Life Sciences secures 2 (two) Product Patents for their NCE’s through New mechanism of action – H3 Inverse Agonist in USA & New Zealand HYDERABAD, INDIA (March 16, 2015) – Suven Life Sciences Ltd (Suven) announced today that they secured patents in USA (us 8912179) and New Zealand (614567) to one of their New Chemical Entity (NCE) for CNS therapy through new mechanism of action – H3 Inverse agonist and these patents are valid until 2030 and 2031 respectively. The granted claims of the patent include the class of selective H3 ligands discovered by Suven and are being developed as therapeutic agents and are useful in the treatment of cognitive impairment associated with neurodegenerative disorders



Suven Life Sciences Ltd.
6th Floor, SDE Serene Chambers,
Avenue – 7, Road No. 5, Banjara Hills,
Hyderabad-500 034, Telangana, INDIA
6th Floor, SDE Serene Chambers,
Avenue – 7, Road No. 5, Banjara Hills,
Hyderabad-500 034, Telangana, INDIA
INDIAN PATENT
- Nirogi, Ramakrishna; Shinde, Anil Karbhari; Kambhampati, Ramasastri; Namala, Rambabu; Dwarampudi, Adi Reddy; Kota, Laxman; Gampa, Murlimohan; Kodru, Padmavathi; Tiriveedhi, Taraka Naga Vinaykumar; Kandikere, Vishwottam Nagaraj; et al
- From Indian Pat. Appl. (2012), IN 2010CH02551
PATENT
The present invention relates to heterocyclyl compounds of formula (I) and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, its process of preparation and compositions containing them, for the treatment of various disorders that are related to Histamine H3 receptors.
ONE EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE 1
Example 1
Preparation of 1-[2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-6,7-dihydro-4H-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-5-yl]-propan-1-one tartrate
Step (i): Preparation of 2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-6,7-dihydro-4H-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-ol (1.6 grams, 10 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) was treated with cooled and stirred suspension of sodium hydride (0.9 grams, 18 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (20 mL) slowly over a period of 30 minutes; the reaction mixture was stirred for 1 hour. A solution of 2-Bromo-6,7-dihydro-4H-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (3 grams, 9 mmol, obtained in preparation 1) in tetrahydrofuran (30 mL) was added drop wise over a period of 15 minutes and refluxed the reaction for 6 hours. Reaction mass was quenched with ice cold water and the product was extracted with ethyl acetate (3×50 mL). Combined organics were washed with water followed by brine and dried over anhydrous sodium sulphate. Organic volatiles were evaporated under vacuum. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (ethylacetate/n-hexane, 1/1) to obtain the title compound (2.0 grams).
1H-NMR (δ ppm): 1.48 (9H, s), 1.65-1.72 (2H, m), 1.85-1.92 (4H, m), 2.01-2.07 (4H, m), 2.18-2.19 (2H, m), 2.57 (2H, m), 2.62-2.66 (2H, m), 2.71-2.75 (1H, m), 3.70 (2H, m), 4.43 (2H, m), 4.93 (1H, m);
Mass (m/z): 394.2 (M+H)+.
Step (ii): Preparation of 2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridineA solution of 2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-6,7-dihydro-4H-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridine-5-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester (2.0 grams, 5 mmol, obtained in above step) in dichloromethane (30 mL) was treated with trifluroacetic acid (5.0 mL, 50 mmol) at 0° C. Reaction mass was stirred for 4 hours. After completion of reaction, the reaction mass was quenched into ice cold water and adjust pH to 10, by using 40% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. The product was extracted with dichloromethane (3×50 mL), combined organics were washed with water followed by brine and dried over anhydrous sodium sulphate. Organic volatiles were evaporated under vacuum to obtain the title compound (1.3 grams).
1H-NMR (δ ppm): 1.68-1.74 (2H, m), 1.85-1.93 (4H, m), 2.06 (4H, m), 2.19 (2H, m), 2.60-2.61 (4H, m), 2.73-2.80 (1H, m), 2.90-3.10 (1H, m), 3.13-3.16 (2H, m), 3.85 (2H, s), 4.90-4.93 (1H, m);
Mass (m/z): 294.2 (M+H)+.
Step (iii): Preparation of 1-[2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-6,7-dihydro-4H-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-5-yl]-propan-1-oneA solution of 2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridine (1.3 grams, 4 mmol, obtained in above step) and triethylamine (1.9 mL, 13 mmol) in dichloromethane (30 mL) was cooled to 0° C. Propionylchloride (0.4 mL, 5 mmol) in dichloromethane (5 mL) was added drop wise over a period of 15 minutes and stirred the reaction for 30 minutes. Reaction mass was poured onto ice cold water and the product was extracted with ethyl acetate (3×50 mL). Combined organics were washed with water followed by brine and dried over anhydrous sodium sulphate. Organic volatiles were evaporated under vacuum. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (methanol/chloroform, 2/98) to obtain the title compound (1.0 gram).
1H-NMR (δ ppm): 1.17-1.21 (3H, m), 1.65-1.72 (5H, m), 1.87-1.91 (4H, m), 2.01-2.07 (4H, m), 2.22 (1H, m), 2.38-2.45 (2H, m), 2.45 (1H, m), 2.68-2.76 (3H, m), 3.72-3.74 (1H, m), 4.47-4.62 (2H, m), 4.92-4.94 (1H, m).
Mass (m/z): 350.4 (M+H)+.
Step (iv): Preparation of 1-[2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-6,7-dihydro-4H-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-5-yl]-propan-1-one tartrateA solution of 1-[2-(1-Cyclobutyl-piperidin-4-yloxy)-6,7-dihydro-4H-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-5-yl]-propan-1-one (0.8 grams, 2.3 mmol, obtained in above step) in methanol (10 mL) was treated with L(+)-Tartaric acid (0.34 grams, 2.3 mmol) at 0° C. Stirred the reaction mass for about 1 hour and the solvent was evaporated under vacuum to dryness. The solids were washed with diethyl ether and dried under vacuum to obtain the title compound (1.1 grams).
1H-NMR (δ ppm): 1.12-1.20 (3H, m), 1.82-1.87 (2H, m), 2.16-2.32 (7H, m), 2.45-2.55 (2H, m), 2.63-2.66 (3H, m), 2.72 (1H, m), 3.20 (2H, m), 3.47-3.50 (1H, m), 3.66-3.70 (1H, m), 3.81-3.88 (2H, m), 4.45 (2H, s), 4.60 (2H, s), 5.18 (5H, m);
Mass (m/z): 350.4 (M+H)+.| Publication number | US8912179 B2 |
| Publication type | Grant |
| Application number | US 13/818,152 |
| PCT number | PCT/IN2010/000740 |
| Publication date | Dec 16, 2014 |
| Filing date | Nov 15, 2010 |
| Priority date | Sep 2, 2010 |
| Also published as | CA2812970A1, 4 More » |
| Inventors | Ramakrishna Nirogi, Anil Karbhari Shinde,Ramasastri Kambhampati, Rambabu Namala,Adi Reddy Dwarampudi, Laxman Kota,Murlimohan Gampa, Padmavathi Kodru,Taraka Naga Vinaykumar Tiriveedhi,Vishwottam Nagaraj Kandikere, Nageshwara Rao Muddana, Ramanatha Shrikantha Saralaya, Pradeep Jayarajan, Dhanalakshmi Shanmuganathan, Ishtiyaque Ahmad,Venkateswarlu Jasti, Less « |
| Original Assignee | Suven Life Sciences Limited |
| Export Citation | BiBTeX, EndNote, RefMan |
| Patent Citations (12), Non-Patent Citations (10), Classifications (16),Legal Events (1) | |
| External Links: USPTO, USPTO Assignment, Espacenet | |
……………….
Banjara Hills,Hyderabad
Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana
 TAJ KRISHNA
TAJ KRISHNA
SUBWAY RESTAURANT

//////
CC(C)n4nc(c1nnc(o1)C2CCN(CCCOC)CC2)c3ccccc34

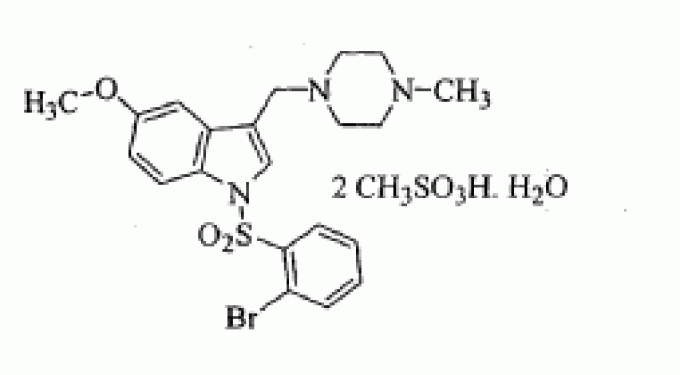
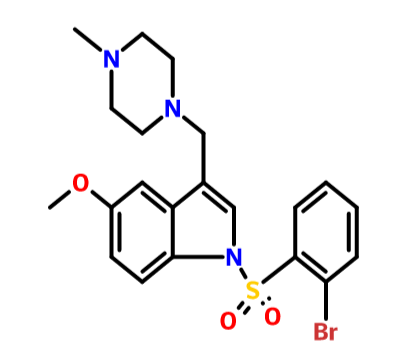



 l -[(2-Bromophenyl)sulfonyl]-5-methoxy-3-[( l -piperazinyl)methyl]-lH-indole.
l -[(2-Bromophenyl)sulfonyl]-5-methoxy-3-[( l -piperazinyl)methyl]-lH-indole.









