
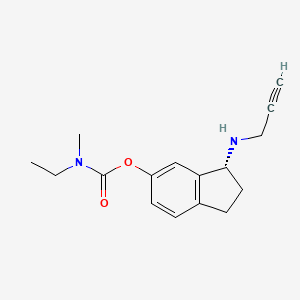
Ladostigil, TV-3,326
(N-propargyl-(3R) aminoindan-5yl)-ethyl methyl carbamate
(3R)-3-(Prop-2-ynylamino)indan-5-yl ethyl(methyl)carbamate; R-CPAI
Carbamic acid, ethylmethyl-, (3R)-2,3-dihydro-3-(2-propynylamino)-1H-inden-5-yl ester
Condition(s): Mild Cognitive Impairment
U.S. FDA Status: Mild Cognitive Impairment (Phase 2)
Company: Avraham Pharmaceuticals Ltd
U.S. FDA Status: Mild Cognitive Impairment (Phase 2)
Company: Avraham Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Target Type: Cholinergic System
| CAS No: | 209349-27-4 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms: | Ladostigil, TV-3326, UNII-SW3H1USR4Q |
| Molecular Weight: | 272.346 g/mol |
| Chemical Formula: | C16-H20-N2-O2 |
| IUPAC Name: | (3R)-3-(Prop-2-ynylamino)indan-5-yl ethyl(methyl)carbamate N-Propargyl-(3R)-aminoindan-5-yl) ethyl methyl carbamate |

CAS 209394-46-7, Ladostigil tartrate
N-Ethyl-N-methylcarbamic acid 3(R)-(2-propynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl ester L-tartrate
In 2010, ladostigil tartrate was licensed by Technion Research & Development Foundation and Yissum to Avraham for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other neurogenerative diseases.
Ladostigil (TV-3,326) is a novel neuroprotective agent being investigated for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders likeAlzheimer's disease, Lewy body disease, and Parkinson's disease.[1] It acts as a reversible acetylcholinesterase andbutyrylcholinesterase inhibitor, and an irreversible monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, and combines the mechanisms of action of older drugs like rivastigmine and rasagiline into a single molecule.[2][3] In addition to its neuroprotective properties, ladostigil enhances the expression of neurotrophic factors like GDNF and BDNF, and may be capable of reversing some of the damage seen in neurodegenerative diseases via the induction of neurogenesis.[4] Ladostigil also has antidepressant effects, and may be useful for treating comorbid depression and anxiety often seen in such diseases as well.[5][6]
Ladostigil [(N-propargyl-(3R) aminoindan-5yl)-ethyl methyl carbamate] is a dual acetylcholine-butyrylcholineesterase and brain selective monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A and -B inhibitor in vivo (with little or no MAO inhibitory effect in the liver and small intestine), intended for the treatment of dementia co-morbid with extrapyramidal disorders and depression (presently in a Phase IIb clinical study). This suggests that the drug should not cause a significant potentiation of the cardiovascular response to tyramine, thereby making it a potentially safer antidepressant than other irreversible MAO-A inhibitors. Ladostigil was shown to antagonize scopolamine-induced impairment in spatial memory, indicating that it can cause significant increases in rat brain cholinergic activity. Furthermore, ladostigil prevented gliosis and oxidative-nitrative stress and reduced the deficits in episodic and spatial memory induced by intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Ladostigil was demonstrated to possess potent anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective activities in vitro and in various neurodegenerative rat models, (e.g. hippocampal damage induced by global ischemia in gerbils and cerebral oedema induced in mice by closed head injury). These neuroprotective activities involve regulation of amyloid precursor protein processing; activation of protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways; inhibition of neuronal death markers; prevention of the fall in mitochondrial membrane potential and upregulation of neurotrophic factors and antioxidative activity. Recent findings demonstrated that the major metabolite of ladostigil, hydroxy-1-(R)-aminoindan has also a neuroprotective activity and thus, may contribute to the overt activity of its parent compound. This review will discuss the scientific evidence for the therapeutic potential use of ladostigil in Alzheimer's and Lewy Body diseases and the molecular signaling pathways that are considered to be involved in the biological activities of the drug
LADOSTIGIL
Recently, Yissum Research Development Company associated with the Hebrew University of Jerusalem announced that the University will use a portion of a $9 million dollar grant awarded to Avraham Pharmaceuticals, Pontifax, Clal Biotechnology Industries and Professor Marta Weinstock-Rosin to complete the Phase II efficacy trial in patients afflicted with Alzheimer’s disease.
The trial will be conducted over the course of 52 weeks and will involve the novel drug, Ladostigil. Ladostigil is a new comprehensive drug used to combat symptoms of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, depression, and anxiety. The drug is deemed multi-functional because it addresses a host of neurodegenerative problems. Ladostigil is a brain-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that protects the neurons.
The trial will be conducted over the course of 52 weeks and will involve the novel drug, Ladostigil. Ladostigil is a new comprehensive drug used to combat symptoms of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, depression, and anxiety. The drug is deemed multi-functional because it addresses a host of neurodegenerative problems. Ladostigil is a brain-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that protects the neurons.
PATENT
US 20140243544 http://www.google.co.in/patents/US20140243544PATENT
WO 2008074816PATENT
- Example 3Ethylmethyl-carbamic acid 3-oxo-indan-5-yl ester
- Ethylmethyl carbamyl chloride (15.5 g, 127.57 mmol) was added to a stirred suspension of 6-hydroxy-1-indanone (17.2 g, 116.1 mmol) and potassium carbonate (31.8 g, 188 mmol) in acetonitrile (800 mL) at room temperature over a period of 15 minutes. The reaction mixture was heated to reflux and refluxed for 18 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to ambient temperature, the solvent evaporated and the residue was diluted with water (250 mL) and extracted three times with toluene (250 mL). The combined organic phase was dried on MgSO4 and toluene was evaporated in a rotary evaporator. The crude crystalline product was purified by crystallization from 2-propanol (200 mL), collected by filtration, and dried under vacuum at 50° C. to afford the title compound (22 g, 81.5%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 7.47-7.44 (2H, m, Ar), 7.36 (1H, dd, J 8.4 and 2.1, Ar), 3.52-3.37 (2H, m, NCH2CH3), 3.14-3.108 [2H, m, OCCH2CH2 and incl. NCH3 (two rotamers), at 3.08 and 2.99 (3H, s, Me)], 2.74-2.71 (2H, m, OCCH2CH2) and 1.25 and 1.19 (two rotamers) (3H,two triplets, J 6.9). Mass Spectrum (FAB+) [MH+=234
- Example 6(S)-Dimethyl-carbamic acid 3-prop-2-ynylamino-indan-5-yl ester
- Methanesulfonyl anhydride (296 mg, 1.7 mmol) as a solution in dichloromethane (1.5 mL+0.5 mL) was added to a stirred solution of (R)-dimethyl-methyl-carbamic acid 3-hydroxy-indan-5-yl ester (188 mg, 0.8 mmol, product of example 1a) and triethylamine (0.47 mL, 3.4 mmol) in dichloromethane (2 mL) at −78° C. (external) over 10 minutes. The reaction was maintained at this temperature for 1 hour before propargylamine (1.20 mL, 17.0 mmol) was added. The reaction was allowed to warm slowly to room temperature overnight before being partitioned between ethyl acetate (20 mL) and ice-water (20 mL). The organic material was concentrated under reduced pressure to afford a brown oil which was partitioned between methyl tert-butyl ether (10 mL) and aqueous hydrochloric acid (1M, 10 mL). The aqueous layer was basified by addition of aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (2M, 16 mL) before being extracted with ethyl acetate (10 mL). This final organic extract was dried (MgSO4), filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to afford the title compound (175 mg, 80%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 7.19 (1H, d, J 8, Ar), 7.09 (1H, d, J 2, Ar), 6.94 (1H, dd, J 8 and 2, Ar), 4.39 (1H, dd, J 6 and 6, CHNH), 3.54 (1H, Dd, J 17 and 3, NCHH), 3.49 (1H, Dd, J 16 and 3, HNCHH), 3.09 (3H, s, Me), 3.03-2.96 [4H, m, NCHCHH and Me incl. at 3.00 (3H, s, Me)], 2.83-2.75 (1H, m, NCHCHH), 2.48-2.39 (1H, m, NCHCH2CHH), 2.25 (1H, t, J 2, ≡CH) and 1.92-1.83 (1H, m, NCHCH2CHH). Analysis of this material by chiral LC indicated it to be 70% e.e.
- Example 7b(R)-Ethyl-methyl-carbamic acid 3-prop-2-ynylamino-indan-5-yl ester (ladostigil)
- The procedure of example 7a is repeated with (S)-ethyl-methyl-carbamic acid 3-hydroxy-indan-5-yl ester instead of (R)-ethyl-methyl-carbamic acid 3-hydroxy-indan-5-yl ester. The R-enantiomer is produced.
PAPER
Tetrahedron: Asymmetry (2012), 23(5), 333-338

 (R)-3-(Prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl ethyl(methyl)carbamate (R)-3-(Prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl ethyl(methyl)carbamateC16H20N2O2 |
ee: 89%
Source of chirality: the precursor
Absolute configuration: (R)
|
 (R)-3-(Prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl ethyl(methyl)carbamate hemi((2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxysuccinate) (R)-3-(Prop-2-ynylamino)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl ethyl(methyl)carbamate hemi((2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxysuccinate)C36H46N4O10 |
ee: 99%
Source of chirality: the precursor
Absolute configuration: (R,R,R)
|
Avraham Pharmaceuticals Announces Commencement of a Phase 2 Study of Ladostigil for the Treatment of MCI
Posted on May 17, 2012
Yaacov Michlin appointed Chairman of the Board and Dr. Yona Geffen appointed Chief Executive Officer
Yavne, Israel, May 17, 2012 — Avraham Pharmaceuticals Ltd. announced today the commencement of a Phase 2 clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ladostigil in patients diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). This 36-month, multi-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial will include at least 200 patients in 16 centers in Europe and Israel.In parallel, Avraham Pharmaceuticals has also completed the enrollment of 200 patients in a Phase 2 trial of ladostigil, a novel molecule for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. The Phase 2 study is a double-blind, closed-label, placebo-controlled trial taking place at 20 sites in five countries across Europe. In January 2012, the Company performed an interim analysis of this Phase 2 trial, which indicated that the drug is safe and well tolerated, as well as shows a positive trend toward efficacy. Final results of the 26-week trial are expected in the fourth quarter of 2012.
The Company also announced today that it has appointed Yaacov Michlin, CEO of Yissum Research Development Company of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem Ltd., the technology transfer arm of the University, as Chairman of the Board and Yona Geffen, Ph.D., as Chief Executive Officer.
“We strongly believe in ladostigil and are confident that Yona’s background and extensive experience in developing therapies for neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases renders her the perfect choice to lead Avraham,” said Yaacov Michlin, Chairman of Avraham Pharmaceuticals and Chief Executive Officer of Yissum. “In further researches performed by Prof. Weinstock-Rosin, ladostigil has showed promise also for the treatment of MCI in addition to Alzheimer’s disease. We are pleased that another Phase 2 clinical trial in patients with MCI has begun in parallel, and look forward to the final results of the Phase 2 study for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease expected at the end of this year.”
“I am delighted to lead Avraham in these exciting times for the company, as we advance ladostigil in 2 Phase 2 clinical trials simultaneously. We believe that this unique drug candidate has the potential to transform the treatment of various neurodegenerative diseases,” said Dr. Yona Geffen, Avraham Pharmaceuticals Chief Executive Officer.
Dr. Yona Geffen joined Avraham Pharmaceuticals in January 2011 as Senior Vice President of Clinical Affairs and Chief Operating Officer. Dr. Geffen has more than 12 years of experience in the field of drug development in biopharmaceutical companies. Prior to Avraham, she was Executive Drug Development Director at BiolineRx (NASDAQ: BLRX). Before that, Dr. Geffen was a project manager at Proneuron Biotechnologies. Dr. Geffen received her Ph.D. from Ben Gurion University in Beer Sheva, Israel. She also holds an M.Sc. in business management.
Yaacov Michlin has been CEO of Yissum since 2009. Prior to Yissum, Mr. Michlin spent over a decade in leading and assisting pharmaceutical, hi-tech and biomedical companies in various technology commercialization deals, licensing agreements, capital raising activities, partnerships, mergers and acquisitions. Michlin holds a Bachelor of Law and Economics cum laude, and a Master of Law all from Bar-Ilan University, Ramat Gan, Israel. In addition, he has an MBA cum laude from the Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel.
About Ladostigil
Ladostigil is a novel cholinesterase and brain-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor, and neuroprotective agent for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment and other neurodegenerative diseases. The drug, which was exclusively licensed to Avraham Pharmaceuticals by Yissum Research Development Company Ltd., and by the Technion Research and Development Foundation Ltd. (TRDF), has proven to be safe and well tolerated in Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials. Like other cholinesterase inhibitors currently on the market, ladostigil targets symptomatic relief in Alzheimer’s disease patients. But unlike these drugs, ladostigil, which also causes brain selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase (MAO) provides the potential to improve the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia such as depression and anxiety. Moreover, ladostigil has the potential to slow progression of clinical symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease for sustained periods of time and to modify the pathology associated with the disease. In addition, the neuroprotective activity of ladostigil provides a drug candidate that may have the potential to slow progression to Alzheimer’s disease in patients diagnosed with MCI. This potential has been amply demonstrated in animal models, especially in studies of ageing rats.
Ladostigil was designed by Professor Marta Weinstock-Rosin of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, inventor of Exelon® and Professor Moussa B.H. Youdim of the Technion Israel Institute of Technology, inventor of Azilect®. The drug substance was first synthesized by Professor Michael Chorev of the Hebrew University, who is now based at Harvard University. All three distinguished scientists act as scientific advisors to Avraham Pharmaceuticals.
About Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia worldwide, affecting about one in 20 people 65 years of age or older, accounting for 60-80% of dementia cases. In 2010, 5.4 million people were affected by Alzheimer’s disease in the U.S., where it is the 6th leading cause of death. In Europe, more than 6 million are living with the disease. Approximately half of Alzheimer’s patients also suffer from depression, and up to 40% also exhibit Parkinson-like symptoms.
About Mild Cognitive Impairment
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a syndrome defined as an intermediate stage between the expected cognitive decline of normal aging and the more pronounced decline of dementia. It involves problems with memory, language, thinking and judgment that are greater than typical age-related changes. Although MCI can present with a variety of symptoms, when memory loss is the predominant symptom it is termed “amnestic MCI” and is frequently seen as a prodromal stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Prevalence in population-based epidemiological studies ranges from 3% to 19% in adults older than 65 years. There is no proven treatment or therapy for MCI.
About Avraham Pharmaceutical
Founded in 2010, Avraham Pharmaceuticals has raised more than $12 million to advance the development of its unique, multi-functional drug substance, ladostigil, currently undergoing two Phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. The Company has been capitalized by Clal Biotechnology Industries Ltd., the Pontifax Fund and Yissum Research Development Company Ltd., the technology transfer arm of the Hebrew University.
References
- Weinstock M, Bejar C, Wang RH, et al. (2000). "TV3326, a novel neuroprotective drug with cholinesterase and monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease". Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementum (60): 157–69.PMID 11205137.
- Weinreb O, Mandel S, Bar-Am O, et al. (January 2009). "Multifunctional neuroprotective derivatives of rasagiline as anti-Alzheimer's disease drugs". Neurotherapeutics : the Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics 6 (1): 163–74.doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2008.10.030. PMID 19110207.
- Weinstock M, Luques L, Bejar C, Shoham S (2006). "Ladostigil, a novel multifunctional drug for the treatment of dementia co-morbid with depression". Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementum (70): 443–6. PMID 17017566.
- Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Youdim MB (December 2007). "Induction of neurotrophic factors GDNF and BDNF associated with the mechanism of neurorescue action of rasagiline and ladostigil: new insights and implications for therapy". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1122: 155–68.doi:10.1196/annals.1403.011. PMID 18077571.
- Weinstock M, Poltyrev T, Bejar C, Youdim MB (March 2002). "Effect of TV3326, a novel monoamine-oxidase cholinesterase inhibitor, in rat models of anxiety and depression".Psychopharmacology 160 (3): 318–24. doi:10.1007/s00213-001-0978-x. PMID 11889501.
- Weinstock M, Gorodetsky E, Poltyrev T, Gross A, Sagi Y, Youdim M (June 2003). "A novel cholinesterase and brain-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor for the treatment of dementia comorbid with depression and Parkinson's disease". Progress in Neuro-psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 27 (4): 555–61. doi:10.1016/S0278-5846(03)00053-8.PMID 12787840.
Contact Us
Yona Geffen CEO
Avraham Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
42 Hayarkon st.
Northern Industrial Zone
Yavneh, 81227
Israel
Avraham Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
42 Hayarkon st.
Northern Industrial Zone
Yavneh, 81227
Israel
| WO1998027055A1 * | 18 Dec 1997 | 25 Jun 1998 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Aminoindan derivatives |
| WO2005051371A1 | 28 Sep 2004 | 9 Jun 2005 | Technion Research & Development Foundation Ltd. | Compositions and methods for treatment of cardiovascular disorders and diseases |
| WO2006130726A2 | 31 May 2006 | 7 Dec 2006 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Use of ladostigil for the treatment of multiple sclerosis |
| WO2007087029A2 * | 11 Dec 2006 | 2 Aug 2007 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem | Use of low-dose ladostigil for neuroprotection |
| WO2009022345A1 | 14 Aug 2008 | 19 Feb 2009 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem | Phenyl carbamates for the treatment of multiple sclerosis |
| WO2009022346A2 | 14 Aug 2008 | 19 Feb 2009 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem | Phenyl carbamates for treating gastrointestinal inflammation |
| WO2012059920A1 | 2 Nov 2011 | 10 May 2012 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem Ltd. | Ladostigil dosage regime |
| US6251938 | 18 Jun 1999 | 26 Jun 2001 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd., | Phenylethylamine derivatives |
| US6303650 | 18 Jun 1999 | 16 Oct 2001 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem | Aminoindan derivatives |
| US6538025 | 31 Aug 2001 | 25 Mar 2003 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Aminoindan derivatives |
| US7335685 | 22 Feb 2006 | 26 Feb 2008 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Crystals of ladostigil tartrate, methods of production and pharmaceutical compositions thereof |
| US7375249 | 21 Feb 2006 | 20 May 2008 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | Process for the synthesis of enantiomeric indanylamine derivatives |
| US7476757 | 15 Apr 2008 | 13 Jan 2009 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | Process for the synthesis of enantiomeric indanylamine derivatives |
| US7491847 | 15 Nov 2006 | 17 Feb 2009 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Methods for isolating propargylated aminoindans |
| US20050222123 | 27 Jan 2005 | 6 Oct 2005 | North Shore-Long Island Jewish Research Institute | Cholinesterase inhibitors for treating inflammation |
| US20060189685 | 24 Feb 2006 | 24 Aug 2006 | Daniella Licht | Formulations of ladostigil tartrate |
| US20060189819 | 22 Feb 2006 | 24 Aug 2006 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Crystals of ladostigil tartrate, methods of production and pharmaceutical compositions thereof |
| US20060199974 | 21 Feb 2006 | 7 Sep 2006 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | Process for the synthesis of enantiomeric indanylamine derivatives |
| US20070088082 | 28 Sep 2006 | 19 Apr 2007 | Judith Aronhime | Polymorphic forms of ladostigil tartrate |
| US20070093549 | 28 Sep 2006 | 26 Apr 2007 | Judith Aronhime | Methods for preparation of ladostigil tartrate crystalline form A1 |
| US20070112217 | 15 Nov 2006 | 17 May 2007 | Anton Frenkel | Methods for isolating propargylated aminoindans |
| US20070135518 | 8 Dec 2006 | 14 Jun 2007 | Marta Weinstock-Rosin | Use of low-dose ladostigil for neuroprotection |
| US20070203232 | 23 Feb 2007 | 30 Aug 2007 | Victor Piryatinsky | Propargylated aminoindans, processes for preparation, and uses thereof |
| US20070232691 | 28 Mar 2007 | 4 Oct 2007 | Tamar Goren | Use of ladostigil for the treatment of schizophrenia |
| US20070293583 | 11 Dec 2006 | 20 Dec 2007 | Marta Weinstock-Rosin | Use of low-dose ladostigil for neuroprotection |
| US5532415 * | Mar 28, 1995 | Jul 2, 1996 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. | R-enantiomer of N-propargyl-1-aminoindan, salts, compositions and uses thereof |
| US5703059 * | Jan 19, 1994 | Dec 30, 1997 | British Biotech Pharmaceuticals Ltd. | Disaccharide ligands for selectins |
| US5936000 * | Jan 16, 1996 | Aug 10, 1999 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Company | 2-aminoindans as selective dopamine D3 ligands |
| US6271261 * | Jun 24, 1997 | Aug 7, 2001 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | IL-8 receptor antagonists |
| US6271263 * | Mar 2, 1999 | Aug 7, 2001 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Compositions containing and methods of using 1-aminoindan and derivatives thereof and process for preparing optically active 1-aminoindan derivatives |
| US6303650 * | Jun 18, 1999 | Oct 16, 2001 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem | Aminoindan derivatives |
| US6462222 * | Aug 31, 2001 | Oct 8, 2002 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem | Aminoindan derivatives |
| US6538025 * | Aug 31, 2001 | Mar 25, 2003 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Aminoindan derivatives |
| US6737547 * | Sep 15, 1999 | May 18, 2004 | Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. | Compositions containing and methods of using N-acyl-1H-aminoindenes |
| US20040010038 * | Feb 27, 2003 | Jan 15, 2004 | Eran Blaugrund | Propargylamino indan derivatives and propargylamino tetralin derivatives as brain-selective MAO inhibitors |
| Citing Patent | Filing date | Publication date | Applicant | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7649115 | Jun 1, 2006 | Jan 19, 2010 | Jenrin Discovery, Inc. | MAO-B inhibitors useful for treating obesity |
| US8541475 | Dec 31, 2009 | Sep 24, 2013 | Jenrin Discovery, Inc. | MAO-B inhibitors useful for treating obesity |
| US8569545 | Jun 2, 2009 | Oct 29, 2013 | Generics (Uk) Limited | Process for the preparation of enantiomerically pure amines |
| US8809589 | Jul 18, 2013 | Aug 19, 2014 | Generics [Uk] Limited | Process for the preparation of enantiomerically pure amines |
| US20070088004 * | Jun 1, 2006 | Apr 19, 2007 | Mcelroy John F | MAO-B inhibitors useful for treating obesity |
| US20100168068 * | Dec 31, 2009 | Jul 1, 2010 | Jenrin Discovery | Mao-b inhibitors useful for treating obesity |
| US20110184071 * | Jun 2, 2009 | Jul 28, 2011 | Vinayak Gore | process for the preparation of amines |
| US20110218360 * | Sep 8, 2011 | Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. | Preparation of rasagiline and salts thereof | |
| CN103443111A * | Apr 2, 2012 | Dec 11, 2013 | 高砂香料工业株式会社 | Novel ruthenium complex and process for producing optically active alcohol compound using same as catalyst |
| CN103443111B * | Apr 2, 2012 | Mar 2, 2016 | 高砂香料工业株式会社 | 钌配合物以及以该配合物作为催化剂的光学活性醇化合物的制备方法 |
| WO2013118126A1 | Feb 11, 2013 | Aug 15, 2013 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem Ltd. | Ladostigil therapy for immunomodulation |
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| [(3R)-3-(prop-2-ynylamino)indan-5-yl]-N-propylcarbamate | |
| Clinical data | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 209349-27-4 |
| ATC code | none |
| PubChem | CID 208907 |
| ChemSpider | 181005 |
| UNII | SW3H1USR4Q |
| Synonyms | [N-propargyl-(3R)-aminoindan-5yl]-N-propylcarbamate |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C16H20N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 272.34 g/mol |
///////////Ladostigil, TV-3,326
c1c(cc2c(c1)CC[C@H]2NCC#C)OC(=O)N(CC)C



