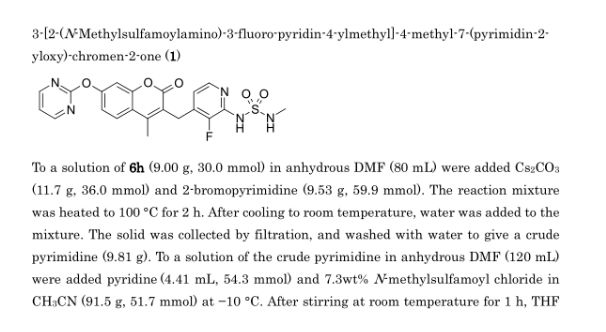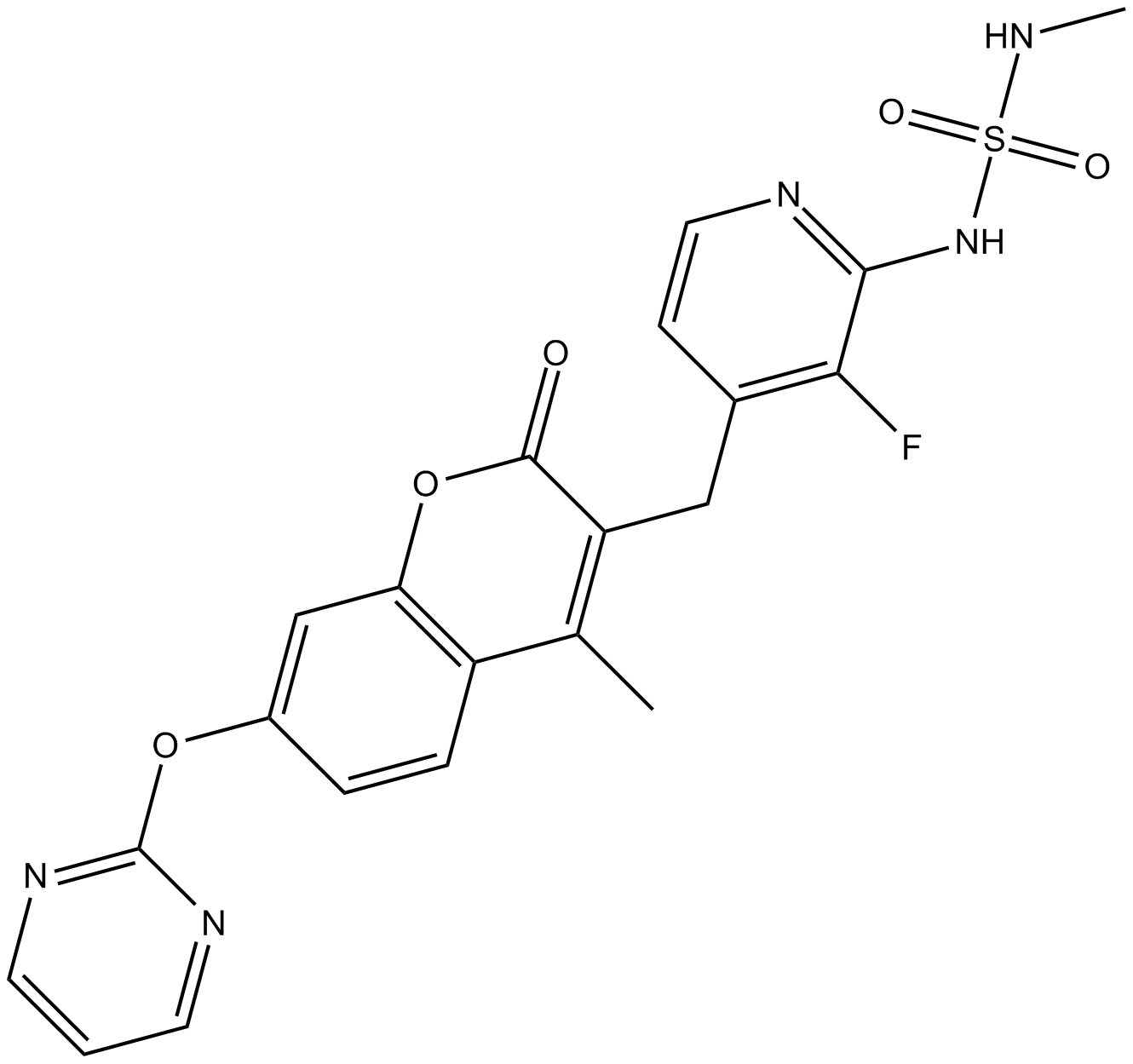
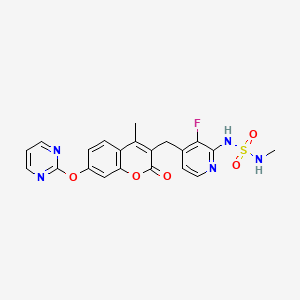
RO-5126766
| 946128-88-7 | |
| MW | 471.46 |
|---|---|
| MF | C21H18FN5O5S |
Phase I
3-[[2-[(Methylaminosulfonyl)amino]-3- fluoropyridin-4-yl]methyl]-4-methyl-7-[(pyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]- 2H-1-benzopyran-2-one
3-[[3-fluoro-2-(methylsulfamoylamino)pyridin-4-yl]methyl]-4-methyl-7-pyrimidin-2-yloxychromen-2-one

Hoffmann-La Roche

Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust
Collaborators:
Institute of Cancer Research, United Kingdom
Chugai Pharmaceutical
RO-5126766; RG-7304; CH-5126766; CKI-27; R-7304
CAS No. 946128-88-7

Although melanoma is the most aggressive skin cancer, recent advances in BRAF and/or MEK inhibitors against BRAF-mutated melanoma have improved survival rates. Despite these advances, a treatment strategy targeting NRAS-mutated melanoma has not yet been elucidated. We discovered CH5126766/RO5126766 as a potent and selective dual RAF/MEK inhibitor currently under early clinical trials. We examined the activity of CH5126766/RO5126766 in a panel of malignant tumor cell lines including melanoma with a BRAF or NRAS mutation. Eight cell lines including melanoma were assessed for their sensitivity to the BRAF, MEK, or RAF/MEK inhibitor using in vitro growth assays. CH5126766/RO5126766 induced G1 cell cycle arrest in two melanoma cell lines with the BRAF V600E or NRAS mutation. In these cells, the G1 cell cycle arrest was accompanied by up-regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and down-regulation of cyclinD1. CH5126766/RO5126766 was more effective at reducing colony formation than a MEK inhibitor in NRAS- or KRAS-mutated cells. In the RAS-mutated cells, CH5126766/RO5126766 suppressed the MEK reactivation caused by a MEK inhibitor. In addition, CH5126766/RO5126766 suppressed the tumor growth in SK-MEL-2 xenograft model
A method for producing a coumarin derivative of general formula (VII) is disclosed in Patent document 1 or 2. Patent document 1 or 2 discloses a method represented by the scheme below [In the scheme, DMF represents N,N-dimethylformamide, TBS represents a tert-butyldimethylsilyl group, dba represents dibenzylideneacetone, and BINAP represents 2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl. Also, the numerical values (%) and “quant.” given below some structural formulas indicate the yields of the respective compounds], for example (see the manufacturing example for “compound 1j-2-16-2K” in Patent document 1 or 2).
CITATION LIST Patent Literature
Patent document 1: WO 2007/091736
Patent document 2: WO 2009/014100
PATENT
- Compound 1j-2-16-2:
3-{2-(Methylaminosulfonyl)amino-3-fluoropyridin-4-ylmethyl}-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran

Methylamine (158 µL, 317 µmol) and DMAP (38.7 mg, 317 µmol) were added at -78 °C to a solution of sulfuryl chloride (28 µL, 340 µmol) in dichloromethane (2 mL), and the mixture was then stirred at room temperature for 2 hours to yield the corresponding sulfamoyl chloride. 3-(2-Amino-3-fluoropyridin-4-ylmethyl)-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran (compound 1h-2-16) (60 mg, 159 µmol), pyridine (65 µL, 795 µmol) and dichloromethane (2 mL) were added to the reaction solution, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. After addition of water, the organic layer was extracted with dichloromethane. After washing with sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated saline, the organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was distilled away under reduced pressure. The resultant residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to yield the title compound (32 mg, 43%).
1H NMR (CD3OD, 270 MHz) δ (ppm): 2.54 (3H, s), 2.62 (3H, s), 4.22 (2H, s), 6.84 (1H, dd, J = 5.4 Hz), 7.20-7.30 (3H, m), 7.80-7.95 (2H, m), 8.63 (2H, d, J = 4.9 Hz)
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 472 (M + H).
- Compound 1j-2-16-2Na:
3-(2-(N-Methylsulfamoyl)amino-3-fluoropyridin-4-ylmethyl)-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran sodium salt

The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-1Na, except that compound 1j-2-16-2 was used instead of compound 1j-1-5-1.
1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 270 MHz) δ (ppm): 2.30 (3H, s), 2.46 (3H, s), 3.89 (2H, s), 5.68 (1H, brs), 6.09-6.23 (1H, m), 7.20 (1H, dd, J = 2.4, 8.7 Hz), 7.34 (1H, t, J = 4.8 Hz), 7.38 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz), 7.55 (1H, d, J = 5.3 Hz), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 8.7 Hz), 8.69 (1H, d, J = 4.8 Hz).
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 472 (M + 2H - Na).
- Compound 1j-2-16-2K:
3-(2-(N-Methylsulfamoyl)amino-3-fluoropyridin-4-ylmethyl)-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran potassium salt

The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-1Na, except that compound 1j-2-16-2 was used instead of compound 1j-1-5-1, and that KOH was used instead of NaOH.
1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 270 MHz) δ (ppm): 2.36 (3H, s), 2.47 (3H, s), 3.93 (2H, s), 6.26-6.40 (1H, m), 7.27 (1H, dd, J = 2.3, 8.6 Hz), 7.34 (1H, t, J = 4.8 Hz), 7.39 (1H, d, J = 2.3 Hz), 7.64 (1H, d, J = 4.8 Hz), 7.91 (1H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 8.69 (1H, d, J = 4.8 Hz).
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 472 (M + 2H - K).
PAPER
ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters (2014), 5(4), 309-314.
Optimizing the Physicochemical Properties of Raf/MEK Inhibitors by Nitrogen Scanning
† Research Division, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., 200 Kajiwara, Kamakura, Kanagawa 247-8530, Japan
‡ Research Division, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., 1-135 Komakado, Gotemba, Shizuoka 412-8513, Japan
ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5 (4), pp 309–314
DOI: 10.1021/ml400379x
Publication Date (Web): January 22, 2014

Substituting a carbon atom with a nitrogen atom (nitrogen substitution) on an aromatic ring in our leads 11a and 13g by applying nitrogen scanning afforded a set of compounds that improved not only the solubility but also the metabolic stability. The impact after nitrogen substitution on interactions between a derivative and its on- and off-target proteins (Raf/MEK, CYPs, and hERG channel) was also detected, most of them contributing to weaker interactions. After identifying the positions that kept inhibitory activity on HCT116 cell growth and Raf/MEK, compound 1(CH5126766/RO5126766) was selected as a clinical compound. A phase I clinical trial is ongoing for solid cancers.
PATENT
Step 5 Synthesis of 4-methyl-3-(3-fluoro-2-aminopyridin-4-ylmethyl)-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran

Under a nitrogen atmosphere, potassium carbonate (2.3 g, 17 mmol) was added to a solution of the solid product of step 4 (3.0 g) and 2-bromopyrimidine (1.6 g, 9.8 mmol) in DMF (48 mL), and the mixture was stirred at 115° C. for 2.5 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to 28° C., water (48 mL) was added dropwise over a period of 5 minutes at that temperature, and after cooling to 0° C., the mixture was stirred for 2 hours. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration, washed with water (24 mL) and acetonitrile (24 mL) in that order, and dried under reduced pressure to obtain crude crystals (2.3 g). DMF (65 mL) was added to the crude crystals (2.3 g), and after heating to 60° C. and confirming the dissolution, the mixture was cooled to 25° C. Water (65 mL) was added at 25° C., and the mixture was further cooled to 0° C. and stirred for 4 hours. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration, washed with water (22 mL) and acetonitrile (22 mL) in that order, and dried under reduced pressure to obtain the title compound (2.1 g). The title compound is a compound disclosed in WO 2007/091736.
Yield (overall yield from the 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoropyridine used in step 2): 27%
Patent
Compound 1h-2-16:
The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1h-2-4 (synthesis scheme 2), except that compound 5d-0-16 was used instead of compound 4a-0-4.
1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 270 MHz) δ (ppm): 2.45-2.55 (3H, m), 3.94 (2H, s), 6.12 (2H, brs), 6.28 (1H, dd, J=4.7 Hz), 7.27 (1H, dd, J=8.6 Hz, J=2.1 Hz), 7.34 (1H, dd, J=4.9 Hz), 7.38 (1H, d, J=2.1 Hz), 7.58 (1H, d, J=4.7 Hz), 7.91 (1H, d, J=8.6 Hz), 8.68 (2H, d, J=4.7 Hz).
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 479 (M+H).
Compound 1j-2-4-2:
3-{2-Fluoro-3-(methylaminosulfonyl)aminobenzyl}-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran
The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-2, except that compound 1h-2-4 was used instead of compound 1h-1-5.
1H NMR (270 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 2.45 (3H, s), 3.99 (2H, s), 6.83-6.92 (1H, m), 6.97-7.06 (1H, m), 7.17 (1H, brs), 7.34-7.40 (4H, m), 7.91 (1H, d, J=8.4 Hz), 8.69 (2H, dd, J=4.8, 1.2 Hz), 9.38 (1H, br.s).
One of the CH3 peaks was overlapped with the DMSO peak.
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 471 (M+H).
Compound 1j-2-4-2Na:
3-{2-Fluoro-3-(methylaminosulfonyl)aminobenzyl}-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran sodium salt
The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-1Na, except that compound 1j-2-4-2 was used instead of compound 1j-1-5-1.
1H NMR (270 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 2.33 (3H, d, J=3.3 Hz), 2.43 (3H, s), 3.89 (2H, s), 6.10-6.19 (1H, m), 6.58-6.66 (1H, m), 7.17 (1H, ddd, J=8.3, 1.5 Hz, JHF=8.3 Hz), 7.25 (1H, dd, J=8.7, 2.3 Hz), 7.33 (1H, t, J=4.8 Hz), 7.37 (1H, d, J=2.3 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J=8.7 Hz), 8.69 (2H, d, J=4.8 Hz)
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 471 (M+2H—Na).
Compound 1j-2-4-2K:
3-{2-Fluoro-3-(methylaminosulfonyl)aminobenzyl}-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yl-oxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran potassium salt
The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-1Na, except that compound 1j-2-4-2 was used instead of compound 1j-1-5-1, and that KOH was used instead of NaOH.
1H NMR (270 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 8.69 (d, 2H, J=4.8 Hz), 7.88 (d, 1H, J=8.7 Hz), 7.36 (d, 1H, J=2.3 Hz), 7.33 (t, 1H, J=4.8 Hz), 7.25 (dd, 1H, J=8.7, 2.3 Hz), 7.16 (td, 1H, J=8.5, 1.4 Hz), 6.59 (t, 1H, J=7.8 Hz), 6.10 (t, 1H, J=6.3 Hz), 4.76 (q, 1H, J=5.8 Hz), 3.88 (s, 2H), 2.43 (s, 3H), 2.32 (d, 3H, J=5.6 Hz).
ESI (LC-MS positive mode) m/z: 471 (M+2H—K).
PATENT
WO 2013035754
3-{2-Fluoro-3-(methylaminosulfonyl)aminobenzyl}-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran

The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-2, except that compound 1h-2-4 was used instead of compound 1h-1-5.
1H NMR (270 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 2.45 (3H, s), 3.99 (2H, s), 6.83-6.92 (1H, m), 6.97-7.06 (1H, m), 7.17 (1H, brs), 7.34-7.40 (4H, m), 7.91 (1H, d, J=8.4 Hz), 8.69 (2H, dd, J=4.8, 1.2 Hz), 9.38 (1H, br.s).
One of the CH3 peaks was overlapped with the DMSO peak.
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 471 (M+H).
Compound 1j-2-4-2Na:
3-{2-Fluoro-3-(methylaminosulfonyl)aminobenzyl}-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran sodium salt

The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-1Na, except that compound 1j-2-4-2 was used instead of compound 1j-1-5-1.
1H NMR (270 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 2.33 (3H, d, J=3.3 Hz), 2.43 (3H, s), 3.89 (2H, s), 6.10-6.19 (1H, m), 6.58-6.66 (1H, m), 7.17 (1H, ddd, J=8.3, 1.5 Hz, JHF=8.3 Hz), 7.25 (1H, dd, J=8.7, 2.3 Hz), 7.33 (1H, t, J=4.8 Hz), 7.37 (1H, d, J=2.3 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J=8.7 Hz), 8.69 (2H, d, J=4.8 Hz)
ESI (LC/MS positive mode) m/z: 471 (M+2H—Na).
Compound 1j-2-4-2K:
3-{2-Fluoro-3-(methylaminosulfonyl)aminobenzyl}-4-methyl-7-(pyrimidin-2-yl-oxy)-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran potassium salt

The title compound was synthesized under the same conditions as in the manufacturing example for compound 1j-1-5-1Na, except that compound 1j-2-4-2 was used instead of compound 1j-1-5-1, and that KOH was used instead of NaOH.
1H NMR (270 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 8.69 (d, 2H, J=4.8 Hz), 7.88 (d, 1H, J=8.7 Hz), 7.36 (d, 1H, J=2.3 Hz), 7.33 (t, 1H, J=4.8 Hz), 7.25 (dd, 1H, J=8.7, 2.3 Hz), 7.16 (td, 1H, J=8.5, 1.4 Hz), 6.59 (t, 1H, J=7.8 Hz), 6.10 (t, 1H, J=6.3 Hz), 4.76 (q, 1H, J=5.8 Hz), 3.88 (s, 2H), 2.43 (s, 3H), 2.32 (d, 3H, J=5.6 Hz).
ESI (LC-MS positive mode) m/z: 471 (M+2H—K).
PATENT
WO 2013035754
Method for producing a coumarin derivative of formula (VII) are described in Patent Documents 1 and 2. Patent Documents 1 and 2, for example, in the following scheme [scheme, DMF is N, represents a N- dimethylformamide, TBS represents a tert- butyldimethylsilyl group, dba represents dibenzylideneacetone, BINAP is 2, I represents a 2'-bis (diphenylphosphino) -1,1'-binaphthyl. Further, numerical values given under the formula (%) or "quant." Indicates the yield of the compound. Methods have been described that are shown in (see Preparation of "Compound 1j-2-16-2K" in Patent Documents 1 and 2).
WO2007 / 091736 WO2009 / 014100
While coumarin derivatives of the general formula (VII) can be prepared by the methods described in Patent Documents 1 and 2, in the method described in Patent Documents 1 and 2, after the formylation reaction and a reduction reaction, and unintended Reaction To suppress, it is necessary to perform the introduction and removal steps of the protecting group for hydroxy group. Also, during the formylation reaction, from the viewpoint of cryogenic conditions of the reaction control (eg, -95 ℃ ~ -65 ℃) is required. Furthermore, the alkylation reaction (the seventh step in the above scheme), it is preferred that an excess amount of use of ethyl acetoacetate in terms of efficient synthesis, in which case, requires complicated operation of removing residual reagents become.
[Example 1]
Step 1:
Synthesis of 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoropyridine:
Step 1:
Synthesis of 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoropyridine:
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, acetamide (94.8g, 1.61mol) in DMF with (200mL) and THF (830mL) was added and heated to 50 ℃. The resulting solution was a THF solution of 40wt% sodium hexamethyldisilazide (629g, 1.37mol) was added dropwise and stirred at the same temperature for 2 hours. 5-chloro-2,3-difluoro pyridine (100.0g, 0.67mol) After adding, THF and (20mL), and the mixture was stirred at the same temperature for 3 hours. After cooling to 0 ℃, it is added to 2.8M HCl (500mL) to the reaction mixture, and the organic layer was separated and the temperature was raised to room temperature.The organic layer was washed with 20wt% sodium chloride solution (500mL), and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue in THF (500mL) was added, and the residue was dissolved by heating at 70 ℃. After confirming the solid precipitated by cooling to room temperature, n- heptane (1500mL) was added and further cooled to 0 ℃, followed by stirring at the same temperature for 3 hours. The The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration, to give after washing with a mixed solvent of THF (100mL) and n- heptane (500mL), and dried under reduced pressure to give the title compound (91.2g).
Yield: 72%
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 2.36 (3H, s), 7.49 (1H, dd, J = 2.0,9.5Hz), 7.78 (1H, br), 8.17 (1H, d, J = 2.0Hz).
MS (ESI +): 189 [M + 1] +
Yield: 72%
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 2.36 (3H, s), 7.49 (1H, dd, J = 2.0,9.5Hz), 7.78 (1H, br), 8.17 (1H, d, J = 2.0Hz).
MS (ESI +): 189 [M + 1] +
Step 2:
Synthesis of 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoro-4-formyl pyridine:
Synthesis of 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoro-4-formyl pyridine:
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, and dissolved at room temperature 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoropyridine (70.0g, 0.37mol) and 4-formyl-morpholine (128.2g, 1.11mol) to THF (840mL) It was. The solution was cooled to -20 ℃ and was added dropwise a THF solution of 24wt% of lithium hexamethyldisilazide (595g, 0.85mol), and stirred 5.5 hours at the same temperature. The reaction mixture, citric acid monohydrate (257g) and sodium chloride (70g) in an aqueous solution dissolved in water (420mL), and I was added at stirring at 0 ℃. The organic layer was separated and the resulting organic layer was successively washed with 50wt% phosphoric acid aqueous solution of potassium dihydrogen (350mL) and 20wt% sodium chloride solution (350mL) to (1458g). The portion of the organic layer was taken for analysis (292g), and evaporated remainder (1166g) at reduced pressure. The residue in THF (350mL) was added, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. Again, the residue in THF (350mL) was added to and evaporated under reduced pressure to give a solid (81.4g) containing the title compound. The product was used in the next step without further purification.
Some of the organic layer which had been collected (292g) to (29g), and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography: subjected to [eluent AcOEt / hexane (1 / 4-9 / 1)], I give the title compound (1.05g, 4.85mmol) as a white powdery solid.
Yield: 66%
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 2.40 (3H, s), 7,59 (1H, br), 8.34 (1H, br), 10.42 (1H, s).
MS (ESI +): 217 (M + 1)
Some of the organic layer which had been collected (292g) to (29g), and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography: subjected to [eluent AcOEt / hexane (1 / 4-9 / 1)], I give the title compound (1.05g, 4.85mmol) as a white powdery solid.
Yield: 66%
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 2.40 (3H, s), 7,59 (1H, br), 8.34 (1H, br), 10.42 (1H, s).
MS (ESI +): 217 (M + 1)
Step 3:
2 - [(4-2-acetylamino-3-fluoro-pyridin-yl) methyl] -3-oxobutanoic acid ethyl ester:
2 - [(4-2-acetylamino-3-fluoro-pyridin-yl) methyl] -3-oxobutanoic acid ethyl ester:
Under a nitrogen atmosphere to dissolve the solid product of Step 2 (81.4g) in 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (448mL), piperidine (4.4g, 51.7mmol), acetic acid (3.1g, 51 .7mmol) and 3-oxobutanoic acid ethyl (37.0g, 0.28mol) was added and stirred for 3 hours after raising the temperature to 50 ℃. After cooling the reaction mixture to room temperature, triethylamine (758mL, 5.5mol) and formic acid (172mL, 4.6mol) of 2-propanol (1248mL) solution and 20% Pd (OH) 2 carbon (21.2g, moisture content 46.2%) were added, followed by stirring for 4 hours the temperature was raised to 50 ℃. The reaction mixture was filtered through Celite, and the residue was washed with 2-propanol (679mL). Combined filtrate and washings (2795g), and evaporated under reduced pressure a part of the (399g) (remaining (2396g) I was saved). Ethyl acetate (24.2mL) was added to the residue obtained by evaporation of the solvent, and evaporated under reduced pressure. Again, the residue ethyl acetate (182mL) was added to the washed successively with an organic layer 20wt% brine (61mL), 10wt% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution (61mL) and 20wt% sodium chloride solution (61mL), under a reduced pressure The solvent was evaporated. Furthermore, in addition to the residue of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (24mL), and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain oil containing the title compound (15.0g). The product was used in the next step without further purification.
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 1.24 (3H, t, J = 7.0Hz), 2.27 (3H, s), 2.37 (3H, s), 3.16- 3.26 (2H, m), 3.86 (1H, t, J = 7.5Hz), 4.15-4.22 (2H, m), 6.98 (1H, t, J = 5.0Hz ), 7.68 (1H, br), 8.05 (1H, d, J = 5.0Hz).
MS (ESI +): 297 (M + 1)
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 1.24 (3H, t, J = 7.0Hz), 2.27 (3H, s), 2.37 (3H, s), 3.16- 3.26 (2H, m), 3.86 (1H, t, J = 7.5Hz), 4.15-4.22 (2H, m), 6.98 (1H, t, J = 5.0Hz ), 7.68 (1H, br), 8.05 (1H, d, J = 5.0Hz).
MS (ESI +): 297 (M + 1)
Step 4:
Synthesis of 3- (3-fluoro-2-amino-pyridin-4-ylmethyl) -7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran methanesulphonate:
Synthesis of 3- (3-fluoro-2-amino-pyridin-4-ylmethyl) -7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran methanesulphonate:
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, oily product of Step 3 (15.0g) and I were dissolved in 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (33mL). The solution of resorcinol (5.3g, 47.9mmol) and methane sulfonic acid (11.7mL, 181mmol) was added at 24 ℃, and stirred for 4 hours at 90 ℃. And allowed to stand for 13 hours and cooled to room temperature and ethanol (33mL) and water (11mL), and the mixture was stirred for 4.5 hours at 90 ℃. After adding 2-propanol (105mL) was cooled to 55 ℃, and allowed to stand for 14 hours then cooled to room temperature. The The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration to give 2-propanol was washed twice with (33mL), and dried under reduced pressure to give the title compound (8.2g).
(Total from 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoropyridine was used in step 2 Yield) Yield: 49%
MS (ESI +): 301 [M + 1-MsOH] +
(Total from 2-acetylamino-5-chloro-3-fluoropyridine was used in step 2 Yield) Yield: 49%
MS (ESI +): 301 [M + 1-MsOH] +
Step 5:
4-methyl-3- (3-fluoro-2-amino-pyridin-4-ylmethyl) -7- (pyrimidin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran Synthesis:
4-methyl-3- (3-fluoro-2-amino-pyridin-4-ylmethyl) -7- (pyrimidin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran Synthesis:
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 3- (3-fluoro-2-amino-pyridin-4-ylmethyl) -7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran methanesulphonate (7.6g, 19.2mmol) and 2-bromo-pyrimidine (4.0g, 24.9mmol) was dissolved in DMF (122mL), potassium carbonate (5.8g, 42.2mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred for 3.5 hours at 115 ℃. After cooling the reaction mixture to 28 ℃, water (122mL) was added dropwise over the same temperature for 0.5 hours, and stirred for 2 minutes. In addition, after cooling to 0 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour, and the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. The obtained crystals were washed successively with water (61mL) and acetonitrile (61mL), to give the title compound was dried under reduced pressure and crystals (6.5g).
The resultant was taken for analysis a portion of the crystals (0.1g), it was suspended remainder (6.4g) in DMF (70mL). The resulting suspension was stirred 60 ℃ and heated for 5 minutes and stirred for 80 minutes by the addition of acetonitrile (185mL) at the same temperature. Then, it was stirred for 0.5 hours and then cooled to 40 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours and further cooled to 25 ℃. After a further 1.5 hours with stirring and cooled to 0 ℃, the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. After washing the resulting crystals in acetonitrile (46mL), was obtained by drying under reduced pressure to the title compound (5.5g). Incidentally, the title compound is a compound described in WO2007 / 091736.
Yield: 76%
The resultant was taken for analysis a portion of the crystals (0.1g), it was suspended remainder (6.4g) in DMF (70mL). The resulting suspension was stirred 60 ℃ and heated for 5 minutes and stirred for 80 minutes by the addition of acetonitrile (185mL) at the same temperature. Then, it was stirred for 0.5 hours and then cooled to 40 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours and further cooled to 25 ℃. After a further 1.5 hours with stirring and cooled to 0 ℃, the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. After washing the resulting crystals in acetonitrile (46mL), was obtained by drying under reduced pressure to the title compound (5.5g). Incidentally, the title compound is a compound described in WO2007 / 091736.
Yield: 76%
Step 6:
3- {2- (methyl-aminosulfonyl) amino-3-fluoro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl} -4-methyl-7- (pyridin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran Synthesis:
3- {2- (methyl-aminosulfonyl) amino-3-fluoro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl} -4-methyl-7- (pyridin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran Synthesis:
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 4-methyl-3- (3-fluoro-2-amino-pyridin-4-ylmethyl) -7- (pyrimidin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran (1.7g, 4 the .5mmol) it was suspended in DMF (18mL). To this solution pyridine (0.8mL, 9.9mmol) was cooled to In 10 ℃ added, N- methyl-sulfamoyl chloride (1.05g, 8.1mmol) in acetonitrile (18mL) solution of the internal temperature of 15 ℃ it was dropped so as to maintain below. After stirring for 90 minutes at the same temperature, acetonitrile (3.4mL) was added and further water (50mL), was added dropwise the inner temperature so as to maintain the 20 ℃ below. It was cooled to an external temperature of 0 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for an internal temperature of 5 ℃ 2 hours after arrival. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration, washed with water (8.5mL), and dried to give the title compound (1.9g, 4.0mmol) was obtained.
Yield: 88%
MS (ESI +): 472 [M + 1] +
Yield: 88%
MS (ESI +): 472 [M + 1] +
Step 7:
Synthesis of 3- {2- (methyl-aminosulfonyl) amino-3-fluoro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl} -4-methyl-7- (pyridin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran potassium salt:
Synthesis of 3- {2- (methyl-aminosulfonyl) amino-3-fluoro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl} -4-methyl-7- (pyridin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran potassium salt:
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 3- {2- (methyl-aminosulfonyl) amino-3-fluoro-pyridin-4-ylmethyl} -4-methyl-7- (pyridin-2-yloxy) -2-oxo -2H-1- benzopyran ( 1.6g, was suspended 3.4mmol) in THF (10mL), water (3mL) was added. The suspension in 2.0M aqueous potassium hydroxide (1.8mL, 3.6mmol) was added dropwise over 10 min at 25 ℃, after raising the temperature to 60 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours at the same temperature. After cooling the reaction mixture to 20 ℃, it was added dropwise over a period of THF (8mL) 30 min. After completion of the dropwise addition, the mixture was cooled to an external temperature of -5 ℃, and the mixture was stirred for an internal temperature of 0 ℃ reached after 160 minutes. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration, then washed with a mixture of THF (14mL) and water (1.6mL) (pre-cooled to 5 ℃), further washed with THF (8mL), and dried to give the title compound (0 .72g, we got 1.4mmol).
Yield: 42%
MS (ESI +): 472 [M + 2H-K] +
Yield: 42%
MS (ESI +): 472 [M + 2H-K] +
CLIP
RO5126766 (CH5126766) is a first-in-class dual inhibitor of Raf/MEK [1].
The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway is an important signal transduction system and participates in cell differentiation, movement, division and death. Activated Ras activates RAF kinase, which then phosphorylates and activates MEK (MEK1 and MEK2) [1]. The mutations in BRAF, RAS, and NF1 are associated with many human tumors [2].
RO5126766 (CH5126766) is a first-in-class dual Raf/MEK inhibitor. In cell-free kinase assays, CH5126766 effectively inhibited the phosphorylation of MEK1 protein by RAF and the activation of ERK2 protein by MEK1 with IC50 values of 0.0082-0.056 and 0.16 μM, respectively. In NCI-H460 (KRAS Q61H) human lung large cell carcinoma cell line, RO5126766 induced cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 protein expression and caused G1 arrest. In HCT116 KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer cells, RO5126766 CH5126766 completely inhibited the phosphorylation of MEK and ERK [2].
In Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors, RO5126766 exhibited the maximum tolerable dose (MTD) of 2.25 mg/day once daily [1]. In a HCT116 (G13D KRAS) mouse xenograft model, RO5126766 (1.5 mg/kg) inhibited pERK and ERK signaling and exhibited ED50 value of 0.056 mg/kg [2].
The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway is an important signal transduction system and participates in cell differentiation, movement, division and death. Activated Ras activates RAF kinase, which then phosphorylates and activates MEK (MEK1 and MEK2) [1]. The mutations in BRAF, RAS, and NF1 are associated with many human tumors [2].
RO5126766 (CH5126766) is a first-in-class dual Raf/MEK inhibitor. In cell-free kinase assays, CH5126766 effectively inhibited the phosphorylation of MEK1 protein by RAF and the activation of ERK2 protein by MEK1 with IC50 values of 0.0082-0.056 and 0.16 μM, respectively. In NCI-H460 (KRAS Q61H) human lung large cell carcinoma cell line, RO5126766 induced cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 protein expression and caused G1 arrest. In HCT116 KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer cells, RO5126766 CH5126766 completely inhibited the phosphorylation of MEK and ERK [2].
In Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors, RO5126766 exhibited the maximum tolerable dose (MTD) of 2.25 mg/day once daily [1]. In a HCT116 (G13D KRAS) mouse xenograft model, RO5126766 (1.5 mg/kg) inhibited pERK and ERK signaling and exhibited ED50 value of 0.056 mg/kg [2].
References:
[1]. Honda K, Yamamoto N, Nokihara H, et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of RO5126766, a first-in-class dual Raf/MEK inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2013, 72(3): 577-584.
[2]. Ishii N, Harada N, Joseph EW, et al. Enhanced inhibition of ERK signaling by a novel allosteric MEK inhibitor, CH5126766, that suppresses feedback reactivation of RAF activity. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(13): 4050-4060.
[1]. Honda K, Yamamoto N, Nokihara H, et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic study of RO5126766, a first-in-class dual Raf/MEK inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2013, 72(3): 577-584.
[2]. Ishii N, Harada N, Joseph EW, et al. Enhanced inhibition of ERK signaling by a novel allosteric MEK inhibitor, CH5126766, that suppresses feedback reactivation of RAF activity. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(13): 4050-4060.
| WO2007091736A1 | 9 Feb 2007 | 16 Aug 2007 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | Novel coumarin derivative having antitumor activity |
| WO2009014100A1 | 18 Jul 2008 | 29 Jan 2009 | Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha | p27 PROTEIN INDUCER |
| JPH0236145A * | Title not available |
| Reference | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BIOORGANIC MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, vol. 13, 2005, pages 1393 - 1402 | |
| 2 | JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, vol. 47, 2004, pages 6447 - 6450 | |
| 3 | ORGANIC PREPARATIONS AND PROCEDURES INTERNATIONAL, vol. 36, 2004, pages 347 - 351 | |
| 4 | * | See also references of EP2754654A1 |
| 5 | * | STANCHO STANCHEV, ET AL.: "Synthesis and Inhibiting Activity of Some 4-Hydroxycoumarin Derivatives on HIV-1 Protease. Art 137637", ISRN PHARMACEUTICS, vol. 63, no. 10, 2011, pages 1 - 9, XP055145297 |
| 6 | * | STANCHO STANCHEV, ET AL.: "Synthesis, computational study and cytotoxic activity of new 4-hydroxycoumarin derivatives", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, vol. 43, no. 4, 2008, pages 694 - 706, XP022576473 |
| 7 | SYNTHETIC COMMUNICATIONS, vol. 34, 2004, pages 4301 - 4311 | |
| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7897792 | 2011-03-01 | Coumarin derivative having antitumor activity |
| US2011009398 | 2011-01-13 | p27 Protein Inducer |
| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2016024051 | 2016-01-28 | SALTS AND SOLID FORMS OF ISOQUINOLINONES AND COMPOSITION COMPRISING AND METHODS OF USING THE SAME |
| US2015290207 | 2015-10-15 | HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND USES THEREOF |
| US2015283142 | 2015-10-08 | TREATMENT OF CANCERS USING PI3 KINASE ISOFORM MODULATORS |
| US2015225410 | 2015-08-13 | HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND USES THEREOF |
| US2015111874 | 2015-04-23 | HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND USES THEREOF |
| US2014377258 | 2014-12-25 | Treatment Of Cancers Using PI3 Kinase Isoform Modulators |
| US2014213786 | 2014-07-31 | Method for Producing Coumarin Derivative |
| US2014038920 | 2014-02-06 | TFEB PHOSPHORYLATION INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF |
| US2011092700 | 2011-04-21 | Novel Coumarin Derivative Having Antitumor Activity |
| US7897792 | 2011-03-01 | Coumarin derivative having antitumor activity |
//////////////RO-512676, RG-7304, CH-5126766, CKI-27, R-730, 946128-88-7, PHASE 1, MEK1/Raf inhibitor, treatment of solid tumors and multiple myeloma, CANCER
CC(C1=C(O2)C=C(OC3=NC=CC=N3)C=C1)=C(C2=O)CC4=C(F)C(NS(NC)(=O)=O)=NC=C4