Talazoparib, BMN-673, MDV-3800
(2S,3S)-methyl-7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate
(8S,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3(7H)-one
(8S,9R)-5-Fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-2,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3-one
CAS 1207456-01-6
Chemical Formula: C19H14F2N6O
Exact Mass: 380.11972
BMN673, BMN673, BMN-673, LT673, LT 673, LT-673, Talazoparib
BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc
phase 3
Poly ADP ribose polymerase 2 inhibitor; Poly ADP ribose polymerase 1 inhibitor
cancer
(85,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3(7H)-one toluenesulfonate salt

CAS 1373431-65-2(Talazoparib Tosylate)

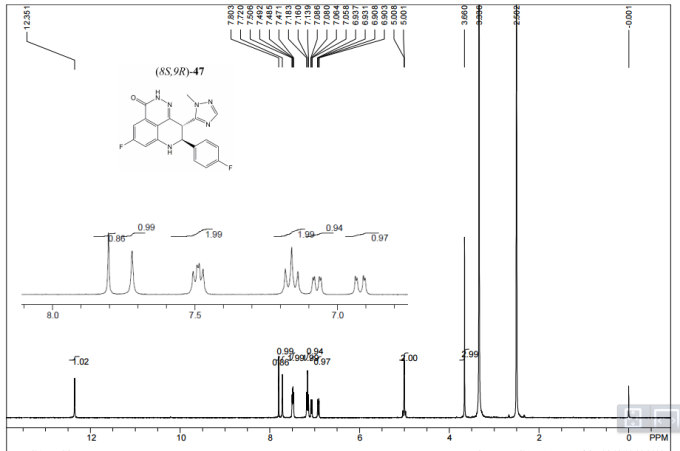
1H NMR DMSOD6
13C NMR DMSOD6

HMBC NMR

HSQC NMR

Talazoparib (BMN-673)
Talazoparib (BMN-673) is an investigational drug that acts as a PARP inhibitor. It is in clinical trials for various cancers.
Medivation, under license from BioMarin Pharmaceuticals, following its acquisition of LEAD Therapeutics, is developing a PARP-1/2 inhibitor, talazoparib, for treating cancer, particularly BRCA-mutated breast cancer. In February 2016, talazoparib was reported to be in phase 3 clinical development
Talazoparib, also known as BMN-673, is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the nuclear enzyme poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) with potential antineoplastic activity (PARP1 IC50 = 0.57 nmol/L). BMN-673 selectively binds to PARP and prevents PARP-mediated DNA repair of single strand DNA breaks via the base-excision repair pathway. This enhances the accumulation of DNA strand breaks, promotes genomic instability and eventually leads to apoptosis. PARP catalyzes post-translational ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins that signal and recruit other proteins to repair damaged DNA and is activated by single-strand DNA breaks. BMN-673 has been proven to be highly active in mouse models of human cancer and also appears to be more selectively cytotoxic with a longer half-life and better bioavailability as compared to other compounds in development. Check for active clinical trials or closed clinical trials using this agent.
Talazoparib is C19H14F2N6O.
Talazoparib tosylate is C26H22F2N6O4S.[1]

Approvals and indications
None yet.Mechanism of action
Main article: PARP inhibitor
Clinical trials
After trials for advanced hematological malignancies and for advanced or recurrent solid tumors.[2] it is now in phase 3 for metastatic germline BRCA mutated breast cancer.[3] Trial estimated to complete in June 2016.[4]As of January 2016 it in 14 active clinical trials.[5]
WO2010017055, WO2015069851, WO 2012054698, WO 2011130661, WO 2013028495, US 2014323725, WO 2011097602
PAPER
Discovery and Characterization of (8S,9R)-5-Fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-2,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3-one (BMN 673, Talazoparib), a Novel, Highly Potent, and Orally Efficacious Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1/2 Inhibitor, as an Anticancer Agent
BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., 105 Digital Drive, Novato, California 94949, United States
J. Med. Chem., 2016, 59 (1), pp 335–357
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01498
Publication Date (Web): December 10, 2015
Copyright © 2015 American Chemical Society
*Phone: 1-415-506-3319. E-mail: bwang@bmrn.com.
Abstract

We discovered and developed a novel series of tetrahydropyridophthlazinones as poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) 1 and 2 inhibitors. Lead optimization led to the identification of (8S,9R)-47 (talazoparib; BMN 673; (8S,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-2,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3-one). The novel stereospecific dual chiral-center-embedded structure of this compound has enabled extensive and unique binding interactions with PARP1/2 proteins. (8S,9R)-47 demonstrates excellent potency, inhibiting PARP1 and PARP2 enzyme activity with Ki = 1.2 and 0.87 nM, respectively. It inhibits PARP-mediated PARylation in a whole-cell assay with an EC50 of 2.51 nM and prevents proliferation of cancer cells carrying mutant BRCA1/2, with EC50 = 0.3 nM (MX-1) and 5 nM (Capan-1), respectively. (8S,9R)-47 is orally available, displaying favorable pharmacokinetic (PK) properties and remarkable antitumor efficacy in the BRCA1 mutant MX-1 breast cancer xenograft model following oral administration as a single-agent or in combination with chemotherapy agents such as temozolomide and cisplatin. (8S,9R)-47 has completed phase 1 clinical trial and is currently being studied in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials for the treatment of locally advanced and/or metastatic breast cancer with germline BRCA1/2 deleterious mutations.
Preparation of (8S,9R)-5-Fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-2,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3-one Tosylate Salt ((8S,9R)-47 Tosylate Salt)
A suspension of (8S,9R)-47 (BMN 673) (400 mg, 1.05 mmol) in a mixture of acetone (27 mL) and THF (13 mL) was heated to reflux until the suspension became clear. TsOH (220 mg, 1.16 mmol) was then added to the solution. White solids started to precipitate out from the solution shortly after the addition of TsOH. After stirring at 25 °C for 30 min, the mixture was filtered to collect the white crystal solids, which were washed with a mixture of acetone (10 mL) and 1,4-dioxane (4 mL) and then dried under vacuum at 45 °C for 3 days. This afforded the product as a white crystalline solid (540 mg, yield 93%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm) 2.29 (s, 3H), 3.67 (s, 3H), 4.97–5.06 (m, 2H), 6.91–6.94 (dd, J1 = 2.0 Hz, J2 = 10.8 Hz, 1H), 7.06–7.19 (m, 5H), 7.19–7.51 (m, 4H), 7.74 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 10.32 (brs, 1H), 12.36 (s, 1H). LC-MS (ESI)m/z: 381 (M + H)+. Anal. Calcd for C19H14F2N6O·toluene sulfonic acid: C, 56.52; H, 4.01; N, 15.21. Found: C, 56.49; H, 3.94; N, 15.39.
(8S,9R)-5-Fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-2,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3-one (8S,9R)-47 or BMN 673 and (8R,9S)-5-Fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-2,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3-one (8R,9S)-47
Compound 47 was dissolved in DMF, and chiral resolution was performed using supercritical-fluid chromatography (SFC) with a CHIRALPAK IA chiral column and methanol (20% with 0.1% DEA) and CO2 (80%) as the eluents. Yield 90%. For (8S,9R)-47 (BMN 673): retention time 8.8 min and ee 99.3%. For (8R,9S)-47: retention time 10.2 min and ee 99.2%.
Alternatively, compound (8S,9R)-47 could also be made using (2S,3R)-60a as a starting material and employing the same procedure described for the conversion of 60a to 47.
The optical rotation for both (8S,9R)-47 and (8R,9S)-47 was measured using a RUDOLPH (AUTOPOL V) automatic polarimeter at a concentration of 6.67 mg/mL in MeOH/MeCN/DMF = 0.5:0.5:1 at 20 °C. The specific rotation for (8S,9R)-47 was +92.2°, whereas it was −93.4° for (8R,9S)-47.
PATENT
WO-2016019125WO2016019125
The compound (85,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3(7H)-one toluenesulfonate salt (Compound (A))

Compound (A)
is an inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP). Methods of making it are described in WO2010017055, WO2011097602, and WO2012054698. However, the disclosed synthetic routes require chiral chromatography of one of the synthetic intermediates in the route to make Compound (A), methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l -methyl- lH-1, 2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo- 1 ,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (Intermediate (A)),

Intermediate (A)
to yield the chirally pure (2S,35)-methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH- 1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (Compound (1))

Compound (1).
Using conventional chiral chromatography is often solvent and time intensive.
Use of more efficient chromatography methods, such as simulated moving bed (SMB) chromatography still requires the use of expensive chiral chromatography resins, and is not practical on a large scale to purify pharmaceutical compounds. Also, maintaining
Compound (1) in solution for an extended time period during chromatography can lead to epimerization at the 9-position and cleavage of the methyl ester group in Compound (1). Replacing the chromatography step with crystallization step(s) to purify Compound (1) is desirable and overcomes these issues. Therefore, it is desirable to find an alternative to the use of chiral chromatography separations to obtain enantiomeric Compound (1).
Scheme 1 below describes use of Ac49 as a coformer acid for the preparation of Compound (la) and for the chiral resolution of Compound (1).
Scheme 1

Compound (1 )
Example 2 - Preparation of Compound (1) Using Scheme 1
Step la
Intermediate (A) (5 g, 12.5 mmol) was dissolved in 9: 1 v/v MIBK/ethanol (70 mL, 14 vol.) at 50 °C with stirring and dissolution was observed in less than about 5 minutes. [(lS)-en<io]-(+)-3-bromo-10-camphor sulfonic acid monohydrate (4.1 g, 12.5 mmol) was added and dissolution was observed in about 10-20 minutes. Seeding was then performed with Compound (la) (95% e.e., 5 mg, 0.1% w.) and the system was allowed to equilibrate for about 1 hour at 50 °C, was cooled to about 20 °C at 0.15 °C/min, and then equilibrated at 20 °C for 2 hours. The solid phase was isolated by filtration, washed with ethanol, and dried at about 50 °C and 3 mbar for about 2 to 3 hours to yield Compound (la) as a 0.6 molar equiv. EtOH solvate and 0.6 molar equiv. hydrate (93.4% e.e.).
Step lb
Compound (la) was then suspended in MIBK/ethanol 95/5% by volume (38 mL, 10 vol.) at 50 °C with stirring. After about 2 hours at 50 °C, the suspension was cooled to about 5 °C for 10 to 15 hours. The solid phase was recovered by filtration and dried at about 50 °C and 3 mbar for about 3 hours. Compound (la) (97.4% e.e.) was recovered. Step 2
000138] Compound (1) was released by suspending Compound (la) (3.9 g, 5.5 mmoi), without performing the optional reslurrying in Step 1, in 20 mL of water at room temperature and treating with 5M sodium hydroxide in water (1.3 mL, 1.2 mol). The mixture was kept at room temperature for about 15 hours and the solid was isolated by filtration and dried at 50 °C and 3 mbar for about 3 hours. Compound (1) was recovered (94.4% e.e.).
Example 3 - Large Scale Preparation of Compound (1) Using Scheme 1
The procedure of Example 1 was followed using 3.3 kg of Intermediate (A) and the respective solvent ratios to provide 95.7% e.e. in Step la; 99.2% e.e. in Step lb; and 99.2% e.e. in Step 2.
Example 4 - Alternative Preparation of Compound (1) Using Scheme 1
Step la
Intermediate (A) (751 mg, 1.86 mmol)) was dissolved in 9: 1 v/v
MIBK/ethanol (7.5 mL, 10 vol.) at 50 °C with stirring. [(15)-eni o]-(+)-3-bromo-10-camphor sulfonic acid monohydrate (620 mg, 1.88 mmol, 1 equiv.) was added. Formation of a precipitate was observed at about 1 hour at 50 °C. The system was then cooled to about 5 °C at 0.1 °C/min, and then equilibrated at 5 °C for about 60 hours. The solid phase was isolated by filtration and dried at about 50 °C and 3 mbar for about 2 hours to yield
Compound (la)(92% e.e.). See Figures 1-4 for XRPD (Figure 1), chiral HPLC (Figure 2), Ή NMR (Figure 3), and TGA/DSC analyses (Figure 4). The XRPD pattern from the material in Example 3 is similar to that in Example 1 with some slight shifts in the positions of specific diffraction peaks (highlighted by black arrows in Figure l). The 'H NIVIR was consistent with a mono-salt of Compound (la) containing 0.5 molar equivalent of EtOH and 0.6% by weight residual MIBK. The TGA analysis showed a stepwise mass loss of 3.5% between 25 and 90 °C (potentially representing loss of the 0.5 molar equivalent of EtOH) and a gradual mass loss of 1.2% between 90 and 160 °C (potentially representing the loss of adsorbed water). The DSC analysis had a broad endotherm between 25 and 90 °C
representing desolvation and an endotherm at 135 °C representing melt/degradation.
Step lb
Compound (la) (100.3 mg, 0.141 mmol) was re-suspended in 95:5 v/v MIBK EtOH (1 mL, 10 vol.) at 50 °C and stirred for 1 hour before cooling to 5 °C at
0.1 °C/min. The solid (99.4% e.e.) was recovered by filtration after 1 night at 5 °C. Shifts in the XRPD diffraction peaks were no longer detected (Figure 5; compare Figure 1). Figure 6 shows the chiral HPLC for Compound (la).
Step 2
Compound (la) (100.2 mg, 0.141 mmol) from Step la was suspended in water (2 mL, 20 vol.) at 50 °C and 5 M NaOH in water (34 μL·, 1.2 molar equiv) was added. The resulting suspension was kept at 50 °C for one night, cooled to room temperature
(uncontrolled cooling) and filtered to yield Compound (1) (92% e.e.). The chiral purity was not impacted by this step and no [(15)-enJo]-(+)-3-bromo-10-camphor sulfonic acid was detected by NMR. Figure 7 compares the XRPD of Compound (1) in Step 2 with
Intermediate (A), the starting material of Step 1. Figure 8 shows the NMR of Compound (1) in Step 2 with Intermediate (A), the starting material of Step 1.
Example 5 - Alternative Preparation of Compound (1) Using Scheme 1 Step la
000144] Intermediate (A) (1 equiv.) was added with stirring to a solution of MIBK (12-13 vol), ethanol (1-1.5 vol), and water (0.05-0.10 vol) and the reaction was heated within 15 minutes to an internal temperature of about 48 °C to about 52 °C . [(lS)-endo]-(+)-3-bromo- 10-camphor sulfonic acid (1 equiv) was added and the reaction was stirred for about 5-10 mins at an internal temperature of about 48 °C to about 52 °C until dissolution occurred. Seed crystals of Compound (la) were added and the reaction was allowed to proceed for 1 hour at an internal temperature of about 48 °C to about 52 °C. The reaction was cooled at a rate of 0.15 °C /min to about 19-21 °C. The suspension was stirred for 2 hours at an internal temperature of about 19 °C to 21 °C and then was collected by filtration and washed twice with ethanol. The product was characterized by 1H NMR and 13C NMR (Figures 13a and 13b), IR Spectrum (Figure 14), DSC (Figure 15), and chiral HPLC (Figure 16).
Step 2a
To Compound (la) (1 equiv.) was added acetone (1.1 vol), IPA (0.55 vol), and methanol (0.55 vol) and the reaction was heated to an internal temperature of about 38 °C to 42 °C. Aqueous ammonia (25%) (1.3 equiv) was added and the reaction was stirred for about 10 minutes. The pH of the reaction was confirmed and the next step performed if > 7. Water was added (0.55 vol), the reaction was cooled to an internal temperature of about 35 °C, seed crystals of Compound (1) were added, and the reaction was stirred for about 10 mins. Water was added (3.3 vol) dropwise within about 30 minutes, the suspension was cooled within 30 minutes to an internal temperature of about 0 °C to 5 °C, and the reaction was stirred for 15 minutes. The solid was collected by filtration and washed three times with water.
Step 2b
To the product of Step 2a) was added acetone (4 vol), ΓΡΑ (1 vol), and methanol (1 vol) and the reaction was heated to an internal temperature of about 38 °C to 42 °C resulting in a clear solution. Water (2 vol) and seed crystals of Compound (1) were added and the system was stirred for about 15 minutes at an internal temperature of about 35 °C. Water (342 mL) was added dropwise in about 30 minutes. The suspension was then cooled in 30 min to an internal temperature of about 0 °C to 5 °C and was stirred for an additional 15 minutes. The solid was collected by filtration, washed twice with water, and chiral purity was determined. If > 99% e.e., then the solid was dried at an internal temperature of about 60 °C under reduced pressure to yield Compound (1). The product was characterized by Ή NMR (Figure 19), 13C NMR (Figure 20), IR (Figure 21), DSC (Figure 22), chiral HPLC (Figure 23).
Scheme 2 below describes use of Acl 10 as a coformer acid for the preparation of Compound (lb) and the chiral resolution of Compound (1).

Intermediate (A)
Compound (1 b)

Compound (1 )
Example 6 - Preparation of Compound (1) Using Scheme 2
Step la
Intermediate (A) (102 mg, 0.256 mmol) was dissolved in MIBK (1 mL, 10 vol.) at 65 °C with stirring. (lS)-phenylethanesulfonic acid, prepared using procedures known to one of skill in the art, in MIBK (3.8 M, 80 μί, 1 molar equiv.) was added and a suspension was observed after 30 minutes at 65 °C. The system was kept at 65 °C for another 30 minutes before cooling to 5 °C at 0.1 C/min. After one night at 5 °C, the solid was filtered, dried at 50 °C, 3 mbar pressure for about 2 hours to yield Compound (lb). See Figures 9-12 for XRPD (Figure 9), chiral HPLC (Figure 10), Ή NMR (Figure 11), and TGA/DSC analyses (Figures 12a and 12b). The XRPD diffraction pattern of the solid obtained in Example 5 differed from the XRPD pattern obtained with the solid from in the salt screen of Example 1 and was consistent with the production of different solids in Examples 1 and 5. The Ή NMR was consistent with the mono-salt with a 0.3% by weight residue of dioxane. In Figure 12a, the thermal behavior was consistent with a non-solvated form exhibiting a melt/degradation at 201 °C. Figure 12b compares the melt pattern of Compound (lb) in Example 5 with Compound (lb) in Example 1.
Steps lb and 2 can be carried out using procedures similar to those used in Examples 2-5.
Example 7 - Polymorphism of Compound (la)
Compound (1) (92% e.e., 10 mg, mmol) was placed in 1.5 mL vials and the solvents (1 mL or less) of Table 3 were added at 50 °C until dissolution was achieved. [(1S)-eni o]-(+)-3-bromo-10-camphorsulfonic acid was added as a solid at 50 °C. The samples were kept at 50 °C for about 1 hour prior to being cooled to room temperature overnight
(uncontrolled cooling rate). Clear solutions were successively cooled to 4 °C, -20 °C and evaporated at room temperature. Any gum obtained after evaporation was re-suspended in diethyl ether. The solid phases generated were characterized by XRPD and if relevant, by Ή NMR and TGA/DSC.
Table 3. Compound (la) Polymorphism Conditions
C.S. means clear solution and Susp. means suspension. "A" means the XRPD diffraction pattern was new but similar to that for Ac49 in
Example 1. "B" means the XRPD diffraction pattern was the same as that for Ac49 in Example 1. "M.E." means molar equiv.

Page 38 of 64
NAI- 1500460480V I
Each of the seven solvents in which solvates were observed (heterosolvates not included) were mixed with MIBK (90% vol). Solutions of Intermediate (A) were prepared in the solvent mixtures (10 vol) at 50 C and [(15)-en<io]-(+)-3-bromo-10-camphor sulfonic acid (1 molar equivalent) was added. The resulting clear solutions were cooled to 5 °C at 0.2 C/min. Surprisingly, no crystallization was reported in any sample. Seeding was performed with a few crystals of each solvate at about 25 °C. The solid phases were analyzed by XRPD and the liquid phases were analyzed by chiral HPLC. See Table 4 for a summary of the results (where "Dias 2" is the (2R, 3R) diastereomer of Compound (la)) .
Table 4. Compound (la) Solvate Analysis

As seen in Table 4 above, the ethanol/MIBK system yielded 93% pure Compound (la) which demonstrates that Compound (la) does crystallize in a very pure form as an ethanolate solvate.
Other objects, features and advantages of the compounds, methods and compositions described herein will become apparent from the following description. It should be understood, however, that the description and the specific examples, while indicating specific embodiments, are given by way of illustration only, since various changes and modifications within the spirit and scope of the present description will become apparent from this detailed description.
All publications including patents, patent applications and published patent applications cited herein are hereby incorporated by reference for all purposes.
PATENT
US 2011196153
http://www.google.co.ve/patents/US20110237581

Patent
US 2011237581PATENT

PATENT
http://www.google.com/patents/WO2015069851A1?cl=en
SYNTHETIC EXAMPLES
Example 1
\ ,

(1 a) (2) (3) (la) (5)
To a flask was added N-methyl-l,2,4-triazole (la)(249.3 g, 3.0 mol, 1 equiv.),
2-methyl-THF (1020 mL, about 1 :4 m/v), and DMF (2)(230.2 g, 3.15 mol, 1.05 equiv.), in any order. The solution was cooled to an internal temperature of about -5 to 0 °C. To the flask was added LiHMDS (3) as a 20% solution in 2-methyl-THF (3012 g, 3.6 mol, 1.2 equiv.) dropwise within about 60 minutes. During the addition of the LiHMDS (3), the desired Compound (la) was precipitated as the 2-methyl-THF solvate, and the flask was cooled to about -30 °C. The reaction was stirred for about 30 minutes at an internal temperature of about -5 to 0 °C.
The precipitated crystals were removed from the reaction mixture by filtration and washed with 2-methyl-THF. The product, Compound (la) as the 2-methyl-THF solvate, was dried under vacuum at an internal temperature of about 60 °C (about 72.5% as measured by NMR) to yield Compound (la).
Example 2

As shown in Example 2, the Compounds of Formula I are useful in the synthesis of more complex compounds. See General Scheme 1 for a description of how the first step can be accomplished. Compounds of Formula I can be reacted with compound (6) to yield Compounds of Formula II. In Example 2, Compound (la) can be reacted with
Compound (6) to yield Compound (7). The remaining steps are accomplished using procedures known to one of ordinary skill in the art, for example, as disclosed in
WO2010017055 and WO2011097602 to yield Compound (12).
PATENT
US 2014323725/http://www.google.com/patents/WO2011097602A15-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9- dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-Je]phthalazin-3(7H)-one, as shown in formula (1), and its enantiomer compounds, as shown in formulas (la) and (lb):
Example 1
(Z)-6-Fluoro-3-(( 1 -methyl- IH- 1 ,2,4-triazol-5 -yl)methylene)-4-nitroisobenzofuran- 1 (3H)-one (3)
[0053] To a 80 L jacketed glass reactor equipped with a chiller, mechanical stirrer, thermocouple, and nitrogen inlet/outlet, at 15 - 25 °C, anhydrous 2-methyl-tetrahydrofuran (22.7 kg), 6-fluoro-4- nitroisobenzofuran-l(3H)-one (2) (2.4 kg, 12.2 mol, 1.00 eq.), and 2-methyl-2H-l,2,4-triazole-3- carbaldehyde (49.6 - 52.6 % concentration in dichloromethane by GC, 3.59 - 3.38 kg, 16.0 mol, 1.31 eq.) were charged consecutively. Triethylamine (1.50 kg, 14.8 mol, 1.21 eq.) was then charged into the above reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was stirred for another 10 minutes. Acetic anhydride (9.09 - 9.10 kg, 89.0 - 89.1 mol, 7.30 eq.) was charged into the above reaction mixture at room temperature for 20 - 30 minutes. The reaction mixture was heated from ambient to reflux temperatures (85 - 95 °C) for 80 - 90 minutes, and the mixture was refluxed for another 70 - 90 minutes. The reaction mixture was monitored by HPLC, indicating compound (2) was reduced to < 5 %. The resulting slurry was cooled down to 5 - 15 °C for 150 - 250 minutes. The slurry was aged at 5 - 15 °C for another 80 - 90 minutes. The slurry was filtered, and the wet cake was washed with ethyl acetate (2L x 3). The wet cake was dried under vacuum at 40 - 50 °C for 8 hours to give 2.65 - 2.76 kg of (Z)-6-fluoro-3-((l -methyl-lH-l ,2,4-triazol-3- yl)methylene)-4-nitroisobenzofuran-l(3H)-one (3) as a yellow solid (2.66 kg, yield: 75.3 %, purity: 98.6 - 98.8 % by HPLC). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 291 (M+l)+. Ή-ΝΜΡ (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 3.94 (s, 3H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 8.10 (s, 1H), 8.40-8.42 (dd, Jx = 6.4 Hz, J2 = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.58-8.61 (dd, Jx = 8.8 Hz, J2 = 2.4 Hz, 1H).
Example 2
Methyl 5- enzoate (4)
Example 2A
[0054] (¾-6-Fluoro-3-((l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-taazol-3-yl)m (3) (177 g, 0.6 mol, 1.0 eq.), and HC1 (2 N in methanol, 3 L, 6 mol, 10 eq.) were charged into a 5 L 3-neck flask equipped with mechanical stirrer, thermometer, and nitrogen inlet/outlet. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 25 hours. The reaction mixture was monitored by HPLC, indicating 0.8 % compound (3) remained. The reaction mixture was concentrated under vacuum at 40 °C to dryness, and methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l -methyl- lH-l,2,4-triazole-3-yl)acetyl)-3-nitrobenzoate hydrochloride (4) was obtained as a yellow solid (201 g, yield: 93.4 %). It was used for the next step without further purification. LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 323 (M+l)+ ¾-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J6) δ (ppm): 3.89 (s, 3H), 3.92 (s, 3H), 4.60 (s, 2H), 7.85 (s, 1H), 8.25-8.28 (dd, Jx = 8.4 Hz, J2 = 2.8 Hz, 2H), 8.52-8.54 (dd, Jx = 8.4 Hz, J2 = 2.8 Hz, 2H).
Example 2B
An alternative workup procedure to that illustrated in Example 2A follows. Instead of evaporating the reaction mixture to dryness, it was condensed to 2 volumes, followed by solvent exchange with 12 volumes of THF, and then 12 volumes of heptane. The slurry mixture was concentrated to 2 volumes and filtered to give the product. As such, 1.8 kilograms of (Z)-6-fluoro-3-((l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3- yl)methylene)-4-nitroisobenzofuran-l(3H)-one (3) gave 2.15 kilograms (yield 96.4 %) of the product methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l -methyl- lH-l,2,4-triazole-3-yl)acetyl)-3-nitrobenzoate hydrochloride (4).
Example 3
Methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4- tetrahydroquinoline-5 -carboxylate (5)
Example 3A
To a suspension of methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)acetyl)-3-nitrobenzoate (4) (5 g, 15.5 mmol, leq.) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (3.6 g, 29 mmol, 1.87 eq.) in a mixture of solvents tetrahydrofuran (30 mL) and MeOH (5 mL) was added titanium(III) chloride (20 % w/w solution in 2N Hydrochloric acid) (80 mL, 6 eq.) dropwise with stirring at room temperature. The reaction mixture was allowed to stir at 30~50°C for 2 hours. The mixture was then diluted with water (160 mL), and the resulting solution was extracted with ethyl acetate (100 mL x 4). The combined organic layers were washed with saturated NaHC03 (50 mL x 3) and aqueous NaHS03 (100 mL x 3), dried by Na2S04, and concentrated to dryness. This afforded a crude solid, which was washed with petroleum ether (120 mL) to obtain the title compound as a yellow solid (5.9 g, yield: 95 %, purity: 97 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 399 (M+l)+. ^-NMR (400 MHz, CDCla) δ (ppm): 3.58 (s, 3H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 4.16-4.19 (d, J2=13.2 Hz, 1H), 4.88 (s, 1H), 5.37-5.40 (d, J2=13.2 Hz, 1H), 6.47-6.53 (m, 2H) , 6.97-7.01 (m, 2H), 7.37-7.41 (m, 2H), 7.80 (s, 1H).
Example 3B
An alternative workup procedure to that illustrated in Example 3A follows. After the completion of the reaction, the mixture was extracted with isopropyl acetate (20 volumes x 4) without water dilution. The product was isolated by solvent exchange of isopropyl acetate with heptanes followed by re-slurry with MTBE and filtration. As such, 3 kilograms of methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5- yl)acetyl)-3-nitrobenzoate (4) afforded 2.822 kilograms of the title compound (5) (yield 81 %).
Example 3C
To a stirred solution of methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)acetyl)-3- nitrobenzoate (4) (580 mg, 2 mmol) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (488 mg, 4 mmol) in methanol (0.75 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (4.5 mL) was added concentrated HC1 solution (w/w 37 %, 6 mL), then reductive powdered Fe (672 mg, 12 mmol) was added slowly to the reaction system. After the addition was complete, the resulting mixture was heated to 60 °C and kept at this temperature for 3 hours. After the disappearance of the starting material (4) as monitored by LC-MS, the reaction mixture was partitioned between ethyl acetate (30 mL) and water (30 mL) and the aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (20 mL x 3). The combined organic phase was dried with Na2S04, concentrated in vacuo and purified by column chromatography (ethyl acetate: petroleum ether = 1 : 1) to give the title compound (5) as a pale yellow solid (300 mg, yield 40 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 399 (M+l)+. LH-NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ (ppm): 3.58 (s, 3H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 4.17 (d, 1H), 4.87 (s, 1H), 5.38 (d, 1H), 6.50 (dd, 2H), 6.99 (dd, 2H), 7.38 (dd, 2H), 7.80 (s, 1H).
Example 3D
To a stirred solution of methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)acetyl)-3- nitrobenzoate (4) (580 mg, 2 mmol) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (488 mg, 4 mmol) in methanol (0.75 mL) and tetrahydrofuran (4.5 mL) was added SnCl2 (2.28 g, 12 mmol) and concentrated HC1 (w/w 37 %, 6 mL), the resulting mixture was reacted at 45 °C for 3 hours, until LC-MS indicating the disappearance of the starting material (4) and about 50 % formation of the product. The mixture was then partitioned between ethyl acetate (30 mL) and water (30 mL) and the aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (20 mL x 3). The combined organic phase was dried with Na2S04, concentrated in vacuo and purified by column chromatography (ethyl acetate: petroleum ether = 1 : 1) to give the title compound (5) as a pale yellow solid (10 mg, yield 1.3 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 399 (M+l)+. LH-NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ (ppm): 3.58 (s, 3H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 4.17 (d, 1H), 4.87 (s, 1H), 5.38 (d, 1H), 6.50 (dd, 2H), 6.99 (dd, 2H), 7.38 (dd, 2H), 7.80 (s, 1H).
Example 3E
A solution of methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)acetyl)-3-nitrobenzoate (4) (580 mg, 2 mmol) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (488 mg, 4 mmol) in methanol (20 mL) and acetic acid (1 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 24 hours under hydrogen (1 barr) in the presence of a catalytic amount of 10 % Pd/C (212 mg, 0.2 mmol). After the reaction was complete, the catalyst was removed by filtration through a pad of Celite, the solvent was removed in vacuo, and the residue was purified by column chromatography (ethyl acetate: petroleum ether = 1 : 1) to give the title compound (5) as a pale yellow solid (63 mg, yield 8 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 399 (M+l)+ . 1HNMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 3.56 (s, 3H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 7.02 (dd, 2H), 7.21 (dd, 2H), 7.90 (s, 1H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 8.26 (dd, 1H), 8.56 (dd, 1H).
Example 4
5-Fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-
Methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l -methyl-lH-l ,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4- tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (5) (150 g, 0.38 mol, 1.0 eq.) and methanol (1.7 L) were charged into a 3 L 3-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, thermometer, and nitrogen inlet/outlet. The resulted suspension was stirred at room temperature for 15 minutes. Hydrazine hydrate (85 % of purity, 78.1 g, 1.33 mol, 3.5 eq.) was charged dropwise into the above reaction mixture within 30 minutes at ambient temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction was monitored by HPLC, showing about 2 % of compound (5) left. The obtained slurry was filtered. The wet cake was suspended in methanol (2 L) and stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. The above slurry was filtered, and the wet cake was washed with methanol (0.5 L). The wet cake was then dried in vacuum at 45 - 55 °C for 12 hours. This afforded the title compound as a pale yellow solid (112 g, yield: 78.1 %, purity: 95.98 % by HPLC). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 381 (M+l)+. ^-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-J6) δ (ppm): 3.66 (s, 3H), 4.97-5.04 (m, 2H), 6.91-6.94 (dd, Jx = 2.4, J2 = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 7.06-7.09 (dd, Jx = 2.4, J2 = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.14-7.18 (m, 3H), 7.47-7.51 (m, 2H), 7.72 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 12.35 (s, 1H).
Example 55 -Amino-7-flu in- 1 (2H)-one
To a solution of 6-fluoro-3-((l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methylene)-4-nitroiso-benzofuran- l(3H)-one (3) (4.0 g, 135 mmol) in THF (100 mL) was added hydrazine monohydrate (85 %) (6 mL) at room temperature under nitrogen atmosphere. The mixture was stirred for 2 hours, then acetic acid (6 mL) was added and the mixture was heated to and kept at 60 °C for 18 hours. The resulting mixture was diluted with water (100 mL) and extracted with ethyl acetate (100 mL x 3). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2S04 and evaporated to dryness to afford the title compound as a yellow solid (1.6 g, yield 42 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 275(M+1)+.
Example 6
(£')-7-fluoro-5-(4-fluorobenzylideneamino)-4-((l -methyl- IH- 1 ,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methyl)phthalazin- 1 (2H)- one
(7)
To a suspended of 5-amino-7-fluoro-4-((l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl) phthalazin- l(2H)-one (7) (1.6 g, 5.8 mmol) in acetonitrile (50 mL) was added 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (2.2 g, 17.5 mmol). The mixture was stirred under reflux under nitrogen for 48 hours. The precipitate was filtered and washed with a mixture of solvents (ethyl acetate/hexane, 1 :1, 10 mL). After drying in vacuum, it afforded the title compound as a yellow solid (1.2 g, yield 52 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 381(M+1)+.
Example 7
5-Fluoro-8 4-fluorophenyl)-9 l-methyl H-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2H^yrido[4,3,2-
(8) (1 )
To a suspension of (£')-7-fluoro-5-(4-fluorobenzylideneamino)-4-((l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5- yl)methyl)phthalazin-l(2H)-one (8) (2.0 g, 5.3 mmol) in THF (80 mL) was added cesium carbonate (3.4 g, 10.6 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at 55 °C for 4 hours and cooled down to room temperature. The mixture was diluted with water (50 ml) and extracted with ethyl acetate (50 mL x 3). The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous Na2S04 and evaporated to dryness to afford the title compound as a white solid (1.6 g, yield 80 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 381(M+1)+. ^-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO- ) δ (ppm): 3.66 (s, 3H), 4.97-5.04 (m, 2H), 6.91-6.94 (dd, Jx = 2.4, J2 = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 7.06-7.09 (dd, Ji = 2.4, J2 = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.14-7.18 (m, 3H), 7.47-7.51 (m, 2H), 7.72 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 12.35 (s, 1H).
Example 8
(£)-Methyl 5-fluoro-2-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)acryloyl)-3-nitrobenzoate
(9)
To a stirred solution of methyl 5-fluoro-2-(2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)acetyl)-3- nitrobenzoate (4) (580mg, 2 mmol) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (488 mg, 4 mmol) in dimethylsulfoxide (2 mL) was added L-proline (230 mg, 2 mmol). The resulting mixture was kept with stirring at 45 °C for 48 hours. The reaction system was then partitioned between ethyl acetate (50 mL) and water (30 mL), and the organic phase was washed with water (20 mL x 3), dried with Na2S04, concentrated in vacuo, and purified by column chromatography (ethyl acetate: petroleum ether = 1 :3) to give the title compound (9) as a pale yellow foam (340 mg, yield 40 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 429 (M+l)+. ^-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-dg); δ (ppm): 3.56 (s, 3H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 7.02 (dd, 2H), 7.21 (dd, 2H), 7.90 (s, IH), 8.08 (s, IH), 8.26 (dd, IH), 8.56 (dd, IH).
Example 9
Methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)- 1 -hydroxy-3-( 1 -methyl- IH- 1 ,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo- 1 ,2,3,4- tetrahydroquinoline-5 -carboxylate (10)
To a solution of (£)-Methyl 5-fluoro-2-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5- yl)acryloyl)-3-nitrobenzoate (9) (200 mg, 0.467 mmol) in methanol (20 mL) was added 10 % Pd/C (24 mg). After the addition, the mixture was stirred under H2 (1 atm) at room temperature for 0.5 h. The reaction system was then filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by chromatography (ethyl acetate: petroleum ether = 1 :1) to give the title compound (10) (110 mg, yield 57 %) as an off-white foam. LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 415 (M+H)+. ¾-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 3.53 (s, 3H), 3.73 (s, 3H), 5.08 (d, 2H), 5.27 (d, 2H), 6.95 (dd, IH), 7.08 (dd, 2H), 7.15 (dd, IH), 7.42 (dd, 2H), 7.77 (s, IH), 9.92 (s, IH). Example 10
Methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4-
(10) (5)
To a stirred solution of methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-l-hydroxy-3-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4- triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l, 2,3, 4-tetrahydroquinoline-5 -carboxylate (10) (41.4 mg, 0.1 mmol) in methanol (5 mL) was added concentrated HCl solution (w/w 37 %, 1 mL) and reductive powdered Fe (56 mg, 1 mmol). The reaction mixture was refluxed for 3 hours. After the disappearance of compound (10) as monitored by LC-MS, the reaction system was partitioned between ethyl acetate (20 mL) and water (20 mL) and then the aqueous phase was extracted with ethyl acetate (10 mL x 3). The combined organic phase was dried with Na2S04, concentrated in vacuo and purified by column chromatography (ethyl acetate: petroleum ether = 1 :1) to give the title compound (5) as a pale yellow solid (12 mg, yield 30 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 399 (M+l)+. ¾-NMR (400 MHz, CDC13) δ (ppm): 3.58 (s, 3H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 4.17 (d, 1H), 4.87 (s, 1H), 5.38 (d, 1H), 6.50 (dd, 2H), 6.99 (dd, 2H), 7.38 (dd, 2H), 7.80 (s, 1H).
Example 11
Methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4-
To a solution of (£)-Methyl 5-fluoro-2-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5- yl)acryloyl)-3-nitrobenzoate (9) (214 mg, 0.5 mmol) in methanol (5 mL) was added concentrated HCl solution (w/w 37 %, 1 mL), then reductive Fe powder (140 mg, 2.5 mmol) was added slowly to the reaction system. After the addition was complete the resulting mixture was refluxed for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was then filtered, concentrated, neutralized with saturated NaHC03 (20 mL), and extracted with ethyl acetate (10 mL x 3). The residue was purified by chromatography (ethyl acetate: petroleum ether = 1 : 1) to give the title compound (5) (30 mg, yield 15 %) as an off-white foam. LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 399 (M+H)+. ^-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 3.56 (s, 3H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 7.02 (dd, 2H), 7.21 (dd, 2H), 7.90 (s, 1H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 8.26 (dd, 1H), 8.56 (dd, 1H).
Example 12
(8R,9S)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-me
Je]phthalazin-3(7H)-one (la) and (8S,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-
(1) (la) (lb)
A chiral resolution of 5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9- dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-Je]phthalazin-3(7H)-one (1) (52.5 g) was carried out on a super-fluid chromatography (SFC) unit using a CHIRALPAK IA column and C02/methanol/diethylamine
(80/30/0.1) as a mobile phase. This afforded two enantiomers with retention times of 7.9 minute (23.6 g, recovery 90 %, > 98 % ee) and 9.5 minute (20.4 g, recovery 78 %, > 98 % ee) as analyzed with a CHIRALPAK IA 0.46 cm x 15 cm column and C02/methanol/diethylamine (80/30/0.1) as a mobile phase at a flow rate of 2 g/minute.
Example 13
(2R,3R)-methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4- tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (6a) and (2S,3S)-methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH-
(5) (6a) (6b)
Example 13A
The chiral resolution of compound (5) was carried out on a SFC unit with a CHIRALPAK®IC 3 cm (I.D.) x 25 cm, 5 μηι column, using C02/MeOH (80/20) as a mobile phase at a flow rate of 65 g/ minute while maintaining the column temperature at 35 °C and with a detection UV wavelength of 254 nm. As such, a racemate of compound (5) (5 g) in methanol solution was resolved, which resulted in two enantiomers with a retention times of 2.35 minute (2.2 g, 88 % recovery, >98 % ee) and 4.25 minute (2.3 g, 92 % recovery, >98 % ee), respectively when analyzed using CHIRALPAK®IC 0.46 cm x 15 cm column and CO2/MeOH(80/20) as a mobile phase at a flow rate of 2 mL/ minute.
Example 13B
The chiral resolution of compound (5) was carried out on a SFC unit with a CHIRALPAK®IC 5cm (I.D.) x 25 cm, 5 μηι column, using C02/MeOH (75/25) as a mobile phase at a flow rate of 200 mL/ minute while maintaining the column temperature at 40 °C and with a detection UV wavelength of 255 nm. As such, a racemate of compound (5) (1.25 kg) in methanol solution was resolved, which resulted in two enantiomers in about 83 % yield and 97.4 % purity.
Example 13C
Alternatively, the separation can also be achieved on a Simulated Moving Bed (SMB) unit with a CHIRALPAK®IC column and acetonitrile as a mobile phase. The retention times for the two enantiomers are 3.3 and 4.1 minutes, respectively. In certain embodiments, the productivity can be greater than 6 kg Feed/day/kg CSP.
Example 14
(8R,9S)-5-fluoro-8 4-fluorophenyl)-9<l-me
Je]phthalazin-3(7H)-one (la) and (8S,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5- (lb)
Example 14A
To a solution of (2R,3R)-methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)- 4-oxo-l,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (6a) or (2S,3S)-methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l- methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (6b) (400 mg, 1.0 mmol) in ethanol (8.0 mL) was added hydrazine monohydrate (85 %, 2.0 mL), and the solution stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The resulting solution was then concentrated to a volume of 2 mL and filtered, and the resultant cake washed with ethanol (1 mL). After drying in vacuum at 50°C, this afforded the title compound as a white solid (209 mg, yield 55 %). LC-MS (ESI) m/z: 381(M+1)+. ^-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-dg): δ (ppm): 3.681 (s, 3H), 4.99-5.06 (m, 2H), 6.92-6.96 (m, 1H), 7.08-7.11 (m, 1H), 7.16-7.21 (t, J= 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.49-7.53 (m, 2H), 7.75 (s, 1H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 12.35 (s, 1H).
Example 14B
To a solution of (2R,3R)-methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)- 4-oxo-l,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (6a) or (2S,3S)-methyl 7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(l- methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-4-oxo-l,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-5-carboxylate (6b) (446 g) in acetonitrile (10 volume) was added hydrazine monohydrate (2.9 eq.), and the solution stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The resulting solution was then concentrated to a volume of 2 mL and filtered. The crude product was re-slurried with water (3~5 volumes) at 15-16 °C. After drying in vacuum at 50 °C, this affords the title compound as a white solid (329 g, yield 77%, 99.93% purity). LC-MS (ESI) m/z:
381(M+1)+; ¾-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ (ppm): 3.681 (s, 3H), 4.99-5.06 (m, 2H), 6.92-6.96 (m, 1H), 7.08-7.11 (m, 1H), 7.16-7.21 (t, J= 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.49-7.53 (m, 2H), 7.75 (s, 1H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 12.35 (s, 1H).
References
- Talazoparib tosylate
- BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. (28 July 2011). "BioMarin Announces Second Quarter 2011 Financial Results". prnewswire.com.
- "BioMarin Initiates Phase 3 BMN 673 Trial for Metastatic gBRCA Breast Cancer". Benzinga.
- A Study Evaluating Talazoparib (BMN 673), a PARP Inhibitor, in Advanced and/or Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients With BRCA Mutation (EMBRACA Study)
- BMN 673 trials
External links
- Talazoparib. Chemspider.com structure etc
Patent Submitted Granted
PROCESSES OF SYNTHESIZING DIHYDROPYRIDOPHTHALAZINONE DERIVATIVES [US2014323725]2014-06-022014-10-30
CRYSTALLINE (8S,9R)-5-FLUORO-8-(4-FLUOROPHENYL)-9-(1-METHYL-1H-1,2,4-TRIAZOL-5-YL)-8,9-DIHYDRO-2H-PYRIDO[4,3,2-DE]PHTHALAZIN-3(7H)-ONE TOSYLATE SALT [US2014228369]2014-04-142014-08-14
Crystalline (8S,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3(7H)-one tosylate salt [US8735392]2011-10-202014-05-27
DIHYDROPYRIDOPHTHALAZINONE INHIBITORS OF POLY(ADP-RIBOSE)POLYMERASE (PARP) [US8012976]2010-02-112011-09-06
DIHYDROPYRIDOPHTHALAZINONE INHIBITORS OF POLY(ADP-RIBOSE)POLYMERASE (PARP) FOR USE IN TREATMENT OF DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH A PTEN DEFICIENCY [US2014066429]2013-08-212014-03-06
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR TREATMENT OF CANCER AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE [US2013184342]2013-03-132013-07-18
| WO2012054698A1 | Oct 20, 2011 | Apr 26, 2012 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Crystalline (8s,9r)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1h-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2h-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3(7h)-one tosylate salt |
| WO2015069851A1 | Nov 6, 2014 | May 14, 2015 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Triazole intermediates useful in the synthesis of protected n-alkyltriazolecarbaldehydes |
| US8420650 | Mar 31, 2011 | Apr 16, 2013 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Dihydropyridophthalazinone inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) |
| US8541403 | Feb 3, 2011 | Sep 24, 2013 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Dihydropyridophthalazinone inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) for use in treatment of diseases associated with a PTEN deficiency |
| US8735392 | Oct 20, 2011 | May 27, 2014 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Crystalline (8S,9R)-5-fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-2H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3(7H)-one tosylate salt |
| US8765945 | Feb 8, 2011 | Jul 1, 2014 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Processes of synthesizing dihydropyridophthalazinone derivatives |
| US8999987 | Mar 6, 2013 | Apr 7, 2015 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Dihydropyridophthalazinone inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) |
| US9018201 | Aug 21, 2013 | Apr 28, 2015 | Biomarin Pharmaceuticial Inc. | Dihydropyridophthalazinone inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) for use in treatment of diseases associated with a PTEN deficiency |
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
(8S,9R)-5-Fluoro-8-(4-fluorophenyl)-9-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)-2,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3H-pyrido[4,3,2-de]phthalazin-3-one
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C19H14F2N6O |
| Molar mass | 380.35 g/mol |
SEE/////http://orgspectroscopyint.blogspot.in/2016/02/talazoparib.html
https://newdrugapprovals.org/2016/02/08/talazoparib/
/////////////BMN 673, talazoparib, phase 3, BMN673, BMN673, BMN-673, LT673, LT 673, LT-673, Poly ADP ribose polymerase 2 inhibitor, Poly ADP ribose polymerase 1 inhibitor, cancer, MDV-3800 , MDV 3800
Cn1c(ncn1)[C@H]2c3c4c(cc(cc4N[C@@H]2c5ccc(cc5)F)F)c(=O)[nH]n3
O=C1NN=C2C3=C1C=C(F)C=C3N[C@H](C4=CC=C(F)C=C4)[C@H]2C5=NC=NN5C