
Avoralstat, BCX4161,
CAS 918407-35-9
UNII: UX17773O15
UNII: UX17773O15
513.5513, C28-H27-N5-O5
2-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, 3-(2-(((4-(aminoiminomethyl)phenyl)amino)carbonyl)-4-ethenyl-5-methoxyphenyl)-6-(((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)carbonyl)-
3-(2-((4-Carbamimidoylphenyl)carbamoyl)-4-ethenyl-5-methoxyphenyl)-6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid
Hereditary angioedema (HAE)
Kallikrein inhibitor
BioCryst Pharmaceuticals

BioCryst is also investigating second-generation plasma kallikrein inhibitors to avoralstat, for treating HAE (in February 2016, this program was listed as being in preclinical development).
Prevent acute attacks in patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE); Treat hereditary angioedema (HAE)
U.S. - Fast Track (Treat hereditary angioedema (HAE));
U.S. - Orphan Drug (Prevent acute attacks in patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE))
U.S. - Orphan Drug (Prevent acute attacks in patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE))
26 Feb 2016Clinical trials in Hereditary angioedema (Prevention) in USA (PO, Hard-gelatin capsule) before February 2016
24 Feb 2016Discontinued - Phase-III for Hereditary angioedema (Prevention) in France (PO, Soft-gelatin capsule)
24 Feb 2016Discontinued - Phase-III for Hereditary angioedema (Prevention) in Germany (PO, Soft-gelatin capsule)

| Conditions | Interventions | Phases | Recruitment | Sponsor/Collaborators |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hereditary Angioedema|HAE | Drug: BCX4161|Drug: Placebo | Phase 2|Phase 3 | Recruiting | BioCryst Pharmaceuticals |
| Hereditary Angioedema | Drug: BCX4161|Drug: Placebo | Phase 2 | Completed | BioCryst Pharmaceuticals |
| Hereditary Angioedema | Drug: BCX4161 | Phase 1 | Completed | BioCryst Pharmaceuticals |
| Hereditary Angioedema | Drug: BCX4161 | Phase 1 | Completed | BioCryst Pharmaceuticals |
Avoralstat, also known as BCX-4161, is a potent and orally active Kallikrein inhibitor and Bradykinin inhibitor. Avoralstat may be potentially useful for treatment for Hereditary angioedema. Avoralstat inhibits plasma kallikrein and suppresses bradykinin production. Bradykinin is the mediator of acute swelling attacks in HAE patients.

Selective inhibitor of plasma kallikrein that subsequently suppresses bradykinin production
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a serious and potentially life-threatening rare genetic illness, caused by mutations in the C1-esterase inhibitor (C1 INH) gene, located on chromosome 11q. HAE is inherited as an autosomal dominant condition, although one quarter of diagnosed cases arise from a new mutation. HAE has been classed as an orphan disease in Europe, with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 50,000. Individuals with HAE experience recurrent acute attacks of painful subcutaneous or submucosal edema of the face, larynx, gastrointestinal tract, limbs or genitalia which, if untreated, may last up to 5 days. Attacks vary in frequency, severity and location and can be life-threatening. Laryngeal attacks, with the potential for asphyxiation, pose the greatest risk. Abdominal attacks are especially painful, and often result in exploratory procedures or unnecessary surgery. Facial and peripheral attacks are disfiguring and debilitating.
HAE has a number of subtypes. HAE type I is defined by C1 INH gene mutations which produce low levels of C1 -inhibitor, whereas HAE type II is defined by mutations which produce normal levels of ineffective C1 protein. HAE type III has separate pathogenesis, being caused by mutations in the F12 gene which codes for the serine protease known as Factor XII. Diagnostic criteria for distinguishing the subtypes of HAE, and distinguishing HAE from other angioedemas, can be found in Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2008; 100(Suppl 2): S30-S40 and J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 114: 629-37, incorporated herin by reference.
Current treatments for HAE fall into two main types. Older non-specific treatments including androgens and antifibrinolytics are associated with significant side effects, particularly in females. Newer treatments are based on an understanding of the molecular pathology of the disease, namely that C1 INH is the most important inhibitor of kallikrein in human plasma and that C1 INH deficiency leads to unopposed activation of the kallikrein-bradykinin cascade, with bradykinin the most important mediator of the locally increased vascular permeability that is the hallmark of an attack.
Approved therapies include purified plasma-derived C1 INH (Cinryze®, Berinert), the recombinant peptide kallikrein inhibitor ecallantide (Kalbitor®), and the bradykinin receptor B2 inhibitor iticabant (Firazyr®). All of the currently available targeted therapies are administered by intravenous or subcutaneous injection. There is currently no specific targeted oral chronic therapy for HAE.
There are many delivery routes for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Generally, the oral route of administration is favored. Oral administration provides a number of advantages, such as, but not limited to, patient convenience, flexibility of timing of administration, location of administration and non-invasiveness. Oral administration also provides more prolonged drug exposure compared with intermittent intravenous infusion, which may be important for drugs with schedule-dependent efficacy. For example, a drug with a short half-life can achieve a greater exposure time by either continuous infusion or by continuous oral dosing. The use of oral therapy further has the potential to reduce the cost of healthcare resources for inpatient and ambulatory patient care services.
In the pharmaceutical arts, it is known that a number of APIs cannot be administered effectively by the oral route. The main reasons why these compounds cannot be administered by the oral route are: a) rapid enzymatic and metabolic degradation; b) chemical and/or biological instability; c) low solubility in aqueous medium; and/or d) limited permeability in the gastrointestinal tract. For such compounds, non-oral routes of delivery, such as parenteral administration, mainly via intramuscular or subcutaneous injections, may be developed. However, non-oral administration poses a disadvantage for the patient as well as healthcare providers, and for this reason, it is important to develop alternative routes of administration for such compounds, such as oral routes of administration.
While the oral route of administration is the most convenient for the patient and the most economical, designing formulations for administration by the oral route involves many complications. Several methods are available to predict the ease by which an API may be formulated into a formulation suitable for administration by the oral route. Such methods include, but are not limited to, and Lipinski rule (also referred to as the Rule of Five) and the Biopharmaceutical Drug Disposition Classification System (BDDCS).
The BDDCS divides APIs into four classifications, depending on their solubility and permeability. Class I APIs have high solubility and high permeability; Class II APIs have low solubility and high permeability; Class III APIs have high solubility and low permeability; and Class IV APIs have low solubility and low permeability. APIs in higher classes in the BDDCS face greater challenges in formulating into an effective, pharmaceutically acceptable product than those in lower classes. Of the four classes, APIs falling into Class IV are the most difficult to formulate into a formulation for administration by the oral route that is capable of delivering an effective amount of the API as problems of both solubility and permeability must be addressed (note the BDDCS does not inherently address chemical stability). The role of BDDCS in drug development is described generally in L.Z. Benet J Pharm Sci. 2013, 102(1), 34-42.
Lipinski's rule (described in Lipinski et al. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 46 (1-3): 3-26) states, in general, that in order to develop a successful formulation for administration by the oral route, an API can have no more than one violation of the following criteria:
i) not more than 5 hydrogen bond donors (nitrogen or oxygen atoms with one or more hydrogen atoms)
ii) not more than 10 hydrogen bond acceptors (nitrogen or oxygen atoms) iii) a molecular mass less than 500 daltons
iv) an octanol-water partition coefficient log P not greater than 5.
J. Zhang et al. Medicinal Chemistry, 2006, 2, 545-553, describes a number of small molecule amidine compounds which have activity as inhibitors of kallikrein. The molecules described in this document fall into Class IV of the BDDCS as described above. The compounds are poorly soluble in aqueous and physiological fluids, and are poorly permeable as demonstrated by oral dosing in rats and in vitro experiments with Caco-2 cells.
Furthermore, 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, one of the compounds described in Zhang et al., is a Class IV API and violates criteria iii) and iv) as set forth in the Lipinski Rule.
Furthermore, the compounds described in Zhang et al., including 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, exhibit poor stability with respect to oxidation in air, to light
(photodegradation) and in aqueous and physiological fluids, as well as to elevated temperatures.
Therefore, the compounds described by Zhang et al. including, but not limited to, 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, not only exhibit poor solubility and permeability characteristics, but also poor stability characteristics. As a result, such compounds are predicted to be especially difficult to formulate into an effective, orally deliverable
pharmaceutical composition that is capable of delivering an effective amount of the compound to a subject.
Polymorphism, the occurrence of different crystal forms, is a property of some molecules. A single molecule may give rise to a variety of polymorphs having distinct crystal structures and physical properties, such as, but not limited to, melting point, thermal behaviors (e.g. measured by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), or differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), x-ray diffraction pattern, infrared absorption fingerprint, and solid state NMR spectrum. One or more of these techniques may be used to distinguish different polymorphic forms of a compound.
Discovering new polymorphic forms and solvates of a pharmaceutical product can provide alternate forms of the compound that display a number of desirable and advantageous properties, such as, but not limited to, ease of handling, ease of processing, ease of formulation, storage stability, and/or ease of purification. Further, new polymorphic forms and solvates of a pharmaceutically useful compound or salts thereof may further provide for improved pharmaceutical products, by providing compounds that are more soluble in a set of pharmaceutical excipients. Still further, the provision of new polymorphic forms and solvates of a pharmaceutically useful compound or salts thereof enlarges the repertoire of compounds that a formulation scientist has available for formulation optimization, for example by providing a pharmaceutical product with different properties, such as, but not limited to, improved processing characteristics, improved handling characteristics, improved solubility profiles, improved dissolution profile and/or improved shelf-life. Therefore, there is a need for additional polymorphs of pharmaceutically useful compounds, such as, but not limited to, 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6- (cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid and the compounds disclosed herein.
In one aspect, the present invention provides an oral formulation that is capable of delivering an effective amount of the amidine compounds described by Zhang et al. to a subject. In particular, the present invention provides an oral formulation that is capable of delivering an effective amount of 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid to a subject. In one specific aspect, the 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid is present in a particular crystal form designated Form A. In light of the art suggesting the difficulties in formulating such an oral formulation, this result was unexpected.
As described herein, the amidine compounds described in Zhang et al., including, but not limited to, 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6- (cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (specifically including particular crystal Form A), may now be conveniently used in oral administration and further used in oral administration for the treatment of a number of diseases and conditions in a subject, such as, but not limited to, HAE as described herein.
Avoralstat & next generation kallikrein inhibitors for HAE
Avoralstat

May 16 is HAE awareness day
See BioCryst’s video regarding HAE to learn more
See BioCryst’s video regarding HAE to learn more
Avoralstat is being developed as an oral prophylactic treatment for patients suffering from Hereditary Angioedema (HAE). Avoralstat inhibits plasma kallikrein and suppresses bradykinin production. Bradykinin is the mediator of acute swelling attacks in HAE patients.
In May 2014 BioCryst, announced that the OPuS-1 (OralProphylaxiS-1) Phase 2a proof of concept clinical trial met its primary efficacy endpoint, several secondary endpoints and all other objectives established for the trial. OpuS-1 enrolled 24 HAE patients with a history of HAE attack frequency of at least 1 per week. Treatment with avoralstat demonstrated a statistically significant mean attack rate reduction of 0.45 attacks per week versus placebo, p<0.001. The mean attack rate per week was 0.82 on BCX4161 treatment, compared to 1.27 on placebo.
In December 2014, BioCryst initiated enrollment in OPuS-2 (Oral ProphylaxiS-2). OPuS-2 is a blinded, randomized, 12-week, three-arm, parallel cohort design trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of two different dose regimens of avoralstat administered three-times daily, 300 mg and 500 mg, compared with placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint for the trial will be the mean angioedema attack rate, which will be reported for each avoralstat dose group compared to placebo. The trial is being conducted in the U.S., Canada and Europe. On October 8, 2015, announced that it has completed enrollment of approximately 100 HAE patients with a history of moderately frequent to very frequent attacks in OPuS-2. BioCryst expects to report the OPuS-2 trial results in early 2016.
PATENT
WO200234711
PATENT
PATENT
Examples
Example 1 - Synthesis of 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl- phenyll-6-(cvclopropylmethyl-carbarnoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid
The synthesis of the above compound and intermediates is described below. In this section, the following abbreviations are used:

The synthesis of starting material, (4-(benzyloxy)-2-formyl-5-methoxyphenyl)boronic acid (1f) is described in Scheme 1.
f 0HCY ° ΒΓΥΥ°

Preparation of 6-bromobenzofdl[1,3ldioxole-5-carbaldehvde (1b)

1a 1b
To a mixture of piperonal (1a) (498 g, 3.32 mol) in glacial acetic acid (1000 mL) was added a solution of bromine (200 mL, 3.89 mol) in glacial acetic acid (500 mL) over a period of 30 min and stirred at room temperature for 24h. The reaction mixture was poured into water (2000 mL) and the solid that separated was collected by filtration. The solid was dissolved in boiling ethanol (4000 mL) and cooled to room temperature. The solid obtained on cooling was collected by filtration to furnish 6-bromobenzo[d][1 ,3]dioxole-5-carbaldehyde (lb) (365 g, 48 %) as a white solid, MP 126 °C; HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 10.06 (s, 1 H), 7.42 (s,1 H), 7.29 (s, 1 H), 6.20 (d, J=12.3, 2H); IR (KBr) 3434, 2866, 1673,1489, 1413, 259, 1112, 1031 , 925 cm"1; Analysis calculated for CeH5BrO3.O 25H C, 41.15; H, 2.37; Found: C, 41.07; H, 2.11.
Preparation of 2-bromo-5-hvdroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde (1c)

1c
A solution of potassium tert-butoxide (397 g, 3.36 mol) in DMSO (1.5 L) was heated at 50 °C for 30 min. Methanol (1.5 L) was added to it and continued heating at 50 °C for additional 30 min. To the hot reaction mixture was added 6-bromo-benzo[d][1,3]dioxole-5-carbaldehyde (1 b) (350g, 1.53 mol) and continued heating at 50 °C for 30 min. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and quenched with water (2.3 L) and sodium hydroxide (61.2 g, 1.53 mol). The reaction mixture was washed with ether (2 x 1.5 L), acidified to pH 2 using cone. HCI and extracted with ethyl acetate ( 1 L). The ethyl acetate layers were combined and concentrated under vacuum to dryness. The residue obtained was treated with water (1.5 L) and ethyl acetate (1 L). The solid obtained was collected by filtration to furnish 2-bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde (1c) (97 g, 27.5% as a first crop). The layers from the filtrate were separated and aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (200 ml_). The ethyl acetate layers were combined dried over MgS04 and concentrated under vacuum to dryness to furnish 2-bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde (1c) (192 g, 54.4%, second crop) as an orange solid, MP 108 °C; 'HNMR (300MHz, DMSO-cfe): S 10.00 (s, 1 H), 9.92 (s,1 H), 7.27 (s, 1 H), 7.26 (s, 1 H), 3.93 (s, 3H); IR (KBr) 3477, 2967, 2917,
2837, 2767, 2740, 1657, 1595, 1428, 1270, 1210, 1164, 1022 cm"'; Analysis calculated for C8H7Br03.H20: C, 38.58; H, 3.64: Found: C, 38.60; H, 3.60.
Preparation of 5-(benzyloxy)-2-bromo-4-methoxybenzaldehvde ( d)

To a solution 2-bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde (1c) (120 g, 520 mmol) in DMF (1000 mL) was added potassium carbonate (79 g, 572 mmol) and benzyl bromide (68 mL, 572 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight and quenched with water (3000 mL). The solid obtained was collected by filtration, washed with ether and dried under vacuum to furnish 5-(benzyloxy)-2-bromo-4-methoxybenzaldehyde (1d) (113.19 g, 67.9%) as a white solid, MP 144 °C;1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-c/6): δ 10.06 (s, 1H), 7.47-7.34 (m, 7H), 5.17 (s, 2H), 3.92 (s, 3H); IR (KBr) 2898, 2851 , 1673, 1592, 1502, 1437, 1402, 1264, 1210, 1158, 1017, 754 cm"1; Analysis calculated for C 5H13Br03: C, 56.10; H, 4.08; Found: C, 55.44; H, 4.08.
Preparation of 1-(benzyloxy)-4-bromo-5-(diethoxymethyl)-2-methoxybenzene (1e)
15 046578
146

1d 1e
To a solution of 5-(benzyloxy)-2-bromo-4-methoxybenzaldehyde (1d) (100 g, 311 mmol) in
ethanol (1500 mL) was added triethyl orthoformate (103 mL, 622 mmol), ammonium nitrate
(7.5 g, 93.3 mmol) and stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was
treated with ether (1200 mL) and stirred for 15 min before filtration. The filtrate was
concentrated under vacuum to dryness to give 1-(benzyloxy)-4-bromo-5-(diethoxymethyl)-2-methoxybenzene (1e) (134 g) as a brown syrup; The product was used in the next step
without further purification; 1H N R (300 MHz, DMSO-cf6) δ 7.45 - 7.37 (m, 4H), 7.36 - 7.33
(m, 1 H), 7.17 - 7.14 (m, 1 H), 7.10 (s, 1 H), 5.10 (s, 2H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.58 - 3.33 (m, 5H),
1.13 - 1.07 (m, 6H); IR (KBr) 2974, 2879, 1601 , 1503, 1377, 1260, 1163, 1060 cm"1;
Analysis calculated for C19H23Br04: C, 57.73; H, 5.86; Found: C, 57.21 ; H, 5.94.
acid (1fi

To a solution of 1-(benzyloxy)-4-bromo-5-(diethoxymethyl)-2-methoxybenzene (1e) (120 g,
300 mmol) in dry ether (1000 mL) at -78 °C was added n-butyllithium (1.6 M solution in
hexanes, 244 mL, 390 mmol) over a period of 30 min and further stirred at -78 °C for 30 min.
A solution of tri-n-butylborate (110 mL, 405 mmol) in dry ether (300 mL) was added to this
solution at -78 °C over a period of 30 min. The reaction mixture was further stirred for 2 h at -78 °C and warmed to 0 °C. The reaction mixture was quenched with 3N HCI (300 mL) at 0
°C and heated at reflux for 1 h. After cooling to room temperature, the solid obtained was
collected by filtration washed with water (250 mL) dried in vaccum to afford (4-(benzyloxy)-2-formyl-5-methoxyphenyl)boronic acid (1f) (30.85 gm, 37.6% as a white solid. The organic
layer from above filtrate was extracted with 1.5 N NaOH (3 x 200 mL). The combined basic
extracts were acidified with cone. HCI (pH about 4). The solid obtained was collected by
filtration, washed with water and dried under vacuum to furnish a second crop of (4-(benzyloxy)-2-formyl-5-methoxyphenyl)boronic acid (1f) (22.3 g, 26%) as a light orange solid
MP 158 °C; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cfe) δ 10.08 (s, 1 H), 7.52 (s, 1 H), 7.48 - 7.33 (m, 5H),
7.24 (s, 1H), 5.18 (s, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6/D20) δ 10.06 (s, 1H),
7.52 (s, 1H), 7.49 - 7.32 (m, 5H), 7.23 (s, 1 H), 5.18 (s, 2H), 3.89 (s, 3H); MS (ES+) 309.1 (M+Na); IR (KBr) 3335, 2937, 1647, 1545, 1388, 1348, 1268, 1146, 1095 cm-1; Analysis calculated for C15H15BO5.0.25H2O: C, 62.00; H, 5.38; Found: C, 61.77; H, 5.19.
Synthesis of methyl-6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl¾-3-ftrifluoromethylsulfonyloxyVpicolinate
The synthesis of the intermediate methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl sulfonyloxy)picolinate (2h) is described in Scheme 2.

Preparation of 2-bromo-3-hvdroxy-6-methylpyridine (2b)
H3C N Br
2a 2b
To a solution of 3-hydroxy-6-methylpyridine (2a) (3000 g, 27.5 mol) in pyridine (24 L) cooled to 15 °C was added a solution of bromine (4.83 kg, 1.55 L, 30.2 mol) in pyridine (3 L) over a period of 50 min maintaining the internal temperature between 20 to 25 DC. After stirring for 19 h at room temperature the solvent was removed under vacuum and the residue was triturated with water. The solid separated was collected by filtration, washed with water and dried under vacuum to give 2-bromo-3-hydroxy-6-methylpyridine (2b) (3502 g, 67.7 %) as a light brown solid which was used as such without further purification; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.43 (s, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.08 (d, J
MS (ES+) 188.35, 186.36 (M+1).
(2c)
2b 2c
A mixture of 2-bromo-3-hydroxy-6-methylpyridine (2b) (3000 g, 15.96 mol), anhydrous potassium carbonate (3308 g, 23.94 mol), and iodomethane (2.491 kg, 1.09 L, 17.556 mol) in 30 L of acetone was heated at 40 °C overnight. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and filtered through Celite. Evaporation of the solvent followed by silica gel chromatography (Hexane: ethyl acetate = 7:3) afforded the desired compound, 2-bromo-3-methoxy-6-methylpyridine (2c) which was used as such for the next step; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cfe) δ 7.42 (dd, J = 8.3, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.29 - 7.19 (m, 1H), 3.84 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 3H), 2.37 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 3H).

2c
2d
To a solution of 2-bromo-3-methoxy-6-methylpyridine (2c) (310 g, 1.53 mol) in 6000 mL of water at 60 °C was added KMnO, (725 g, 4.59 mol) in small portions over a 90 min period with vigorous mechanical stirring. A dark purple solution resulted. This solution was kept at 90 °C for a further 3 h and filtered through Celite while still hot to give a colourless filtrate.
After cooling, the aqueous solution was acidified to pH 1-2 by adding 6 N HCI. The white solid obtained was collected by filtration to give on drying 6-bromo-5-methoxy-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid (2d) (302g, 85%) of product, which was used as such in the next reaction without further purification. An analytical sample was obtained by recrystallization from methanol to give 6-bromo-5-methoxy-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-tfe) δ 7.40 - 7.28 (m, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1 H), 3.83 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 3H).
Preparation of 6-bromo-N-(cvclopropylmethyl)-5-methoxypicolinamide (2e)

To a solution of 6-bromo-5-methoxy-2-pyridinecarboxylic acid (2d) (12 g, 52 mol) in pyridine (70 mL) was added EDCI (11.5 g, 59 mmol) and cyclopropylmethylamine (3.6 g, 52 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight and then concentrated under vacuum. The reaction mixture was diluted with water (100 mL) and ethyl acetate (100 mL). The organic layer was separated and the water layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 100 mL). The organic layers were combined and washed with water (2 x 50 mL), brine (500 mL), dried over magnesium sulphate, filtered and concentrated under vacuum to furnish 10.43g of crude product. The crude product was converted into a slurry (silica gel 20 g) and purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel 230 g, eluting with 0-100% ethyl acetate in hexane) to yield compound 6-bromo-N-(cyclopropylmethyl)-5-methoxypicolinamide (2e) (8.02 g, 54%) as off white solid, mp 67-70 °C; 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.51 (t, J = 5.8, 1 H), 8.02 (d, J = 8.4, 1 H), 7.65 (d, J = 8.5, 1 H), 3.96 (s, 3H), 3.14 (t, J = 6.5, 2H), 1.11 -0.99 (m, 1 H), 0.47 - 0.36 (m, 2H), 0.27 - 0.20 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 307.0, 309.0 (100%
M+Na)
Preparation of methyl 6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-methoxypicolinate (2f)

To a solution of 6-bromo-N-(cyclopropylmethyl)-5-methoxypicolinamide (2e) (7.5 g, 27.6 mol) in methanol (300 mL) in a 2-L stainless steel bomb was added Pd(OAc)2(750 mg), 1 ,1-bis(diphenylphosphino)-ferrocene (750 mg), and triethylamine (3.9 mL, 27.6 mmol). The reaction mixture was vacuum flushed and charged with CO gas to 150 psi. The reaction mixture was and heated with stirring at 150°C overnight and cooled to room temperature. The catalyst was filtered through a pad of celite, and concentrated to dryness to furnish crude product. The crude was purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel 150 g,
eluting with, 0%, 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 50% ethyl acetate/hexanes (250 mL each) as eluents to give methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-3-methoxypicolinate (2f) (6.29 g, 86.1 %) as a salmon coloured solid, MP 107 °C; 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cfe) δ 8.28 (t, J = 6.0, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.8, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.8, 1 H), 3.68 (s, 3H), 3.64 (s, 3H), 2.90 (t, J = 6.5, 2H), 0.89 - 0.68 (m, 1 H), 0.26 - 0.09 (m, 2H), 0.08 - 0.00 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 287.1 (M+Na); IR (KBr) 3316, 2921 , 1730, 1659, 1534, 1472, 1432, 1315, 1272, 1228, 1189, 1099, 1003, 929, 846, 680 cm"1; Analysis calculated for C13H16 204: C, 59.08; H, 6.10; N, 10.60; Found: C, 58.70; H, 5.97; N, 10.23.
Preparation of 6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl 3-hvdroxypicolinic acid (2q)

2f 2g
Aluminium chloride method:
To a solution of methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-methoxypicolinate (2f) (0.16 mmol) in dichloromethane (840 mL) was added AICI3 (193 g, 1.5 mol). The reaction mixture was heated at reflux for 12 h under nitrogen. After slowly adding ~2L of 1 N HCI, the organic layer was separated. The aqueous layer was re-extracted several times with ethyl acetate/DME. The combined organic layer was washed with brine, dried (MgSO.4), and evaporated in vacuo to furnish crude 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-hydroxypicolinic acid. To a solution of 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-hydroxypicolinic acid was added a solution of acetyl chloride (1 10 mL) in methanol (1.1 L). The reaction mixture was stirred for 12 h at room temperature and then concentrated to dryness in vacuo. After co-evaporating once with methanol, the compound was purified by flash-column chromatography (silica gel, 500 g, eluted with chloroform and 3% methanol in chloroform) to furnish 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-hydroxypicolinic acid (2g).
Boron tribromide method:
To a stirring solution of methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-ethoxypicolinate (2f) (58.0 g, 208 mmol) was added BBr3 (79 mL, 834 mmol) in CH2CI2 (1.3 L) at 0-5 °C. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 18h. The reaction mixture was evaporated to dryness and anhydrous methanol (1 L) was added to the light yellowish solid residue. Insoluble solid was collected by filtration (36 g). Mother liquor was evaporated and co-evaporated with MeOH (2 x 200 mL). The insoluble solid (36 g) was treated with MeOH (500 mL) and acetyl chloride (50 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 18 h (at this point reaction mixture was clear). The mixture was evaporated to dryness and diluted with water and extracted with EtOAc. White solid that separated out from EtOAc layer was collected by filtration, washed with water (2 x 20 mL), dried in vacuo at 50 °C to afford 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-hydroxypicolinic acid (2g) (5.36 g, 10 %) as a white solid, MP 92-95 °C. 1HNMR (DMSO-cfe) δ 11.04 (s, 1 H, exchangeable with D20), 8.37 (t, J = 6.0, 1 H, exchangeable with D20), 8.12 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 7.57 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1 H), 3.90 (m, 3 H), 3.15 (m, 2 H), 1.04 ( m, 1 H), 0.41 (m, 2 H), 0.24 (m, 2 H). IR (KBr): 3346, 3205, 1684 cm"1; MS (ES+): 251.1 (M+1); Analysis calculated for C12H14N2O4.0.1 H2O: C, 57.18; H, 5.67; N, 11.14; Found: C, 57.11 ; H, 5.61; N, 11.09.
Preparation of methyl-6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy) picolinate (2h

To a solution of 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-hydroxypicolinic acid (2g) (28 mmol) in DMF (200 mL) were added triethylamine (12 mL, 84 mmol) and N-phenyl-bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) (12 g, 34 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred for 1.5 h at room temperature and then poured into ice. After diluting with water and extracting with ethyl acetate, the aqueous phase was re-extracted, and then the combined organic layer was washed with water and concentrated under vacuum to give methyl-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy)picolinate (2h), which was used in the next step without purification.
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCI3) δ 8.50 (d, J = 8.6, 1 H), 8.07 (s, 1 H), 7.88 (d, J = 8.6, 1 H), 4.09 (d, J = 12.6, 3H), 3.48 - 3.24 (m, 2H), 1.18 - 1.01 (m, 1 H), 0.69 - 0.44 (m, 2H), 0.42 - 0.20 (m, 2H). MS (ES*): 405.17, 100%, M+Na.
Synthesis of 3-f2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyll-6-(cvclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid:
The synthesis of 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (3i) is described as shown in Scheme 3.

3-f4-Benzyloxy-2-formyl-5-methoxy-phenylV6-(cvcloDroDvlmethvl-carbarnovn-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (3a)
5 046578
153

3a
To a solution of methyl-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy)
picolinate (2h) (24.3g, 63 mmol) in DME (225 mL) were added water (25 mL), (4- (benzyloxy)-2-formyl-5-methoxyphenyl)boronic acid (1f) (27.3 g, 95 mmol), NaHC03(15.9 g,
5 189 mmol), and bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(ll) chloride (0.885 g). The reaction
mixture was stirred at 70°C overnight under nitrogen. After extracting with ethyl acetate, the organic layer was washed with water and brine and dried (MgSO^), and then concentrated
under vacuum. The compound was purified by flash-column chromatography (silica gel, 300 g, eluting with 10%, 20%, 30% and 40% ethyl acetate in hexane) to furnish 3-(4-benzyloxy- 10 2-formyl-5-methoxy-phenyl)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid
methyl ester (3a) (25 g, 83%) as off white solid, MP 48-50°C: 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cfe) δ 9.61(s, 1 H), 8.40 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H), 8.14 (t, J= 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.87 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1 H), 7.58
(s, 1H), 7.54-7.30 (m, 5H), 6.71 (s, 1 H), 5.24 (s, 2H), 3.93 (s, 3H), 3.70 (s, 3H), 3.45-3.34 (m,
2H), 1.19-1.05 (m, 1 H), 0.64-0.54 (m, 2H), 0.37-0.30 (m, 2H); IR ( Br) 1735, 1678, 1594,
15 1513, 1437, 1283, 1217, 1141, 1092 cm"1; MS (ES+) 497.29 (M+Na); Analysis calculated for
C27H2eN206: C, 68.34; H, 5.52; N, 5.90; Found; C, 68.16; H, 5.62; N, 5.80.
2-(6-(Cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-vn-4-methoxy-5- vinylbenzoic acid (3b)

To a solution of 3-(4-benzyloxy-2-formyl-5-methoxy-phenyl)-6-(cyclopropylmethyl- carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid methyl ester (3a) (24g, 50.6 mmol) in acetonitrile (50
mL), 2-methyl-2-propanol (350 mL), and water (125 mL) were added sodium dihydrogen
phosphate (12.5 g) and 2-methyl-2-butene (55 mL, 519 mmol). The reaction mixture was cooled in an ice bath and then sodium chlorite (28 g) was added. After stirring for 1 h, the reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate and washed with water. The aqueous layer was re-extracted and then the combined organic layers were dried (MgS04). The solvent was evaporated in vacuo to furnish 5-(benzyloxy)-2-(6- ((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxybenzoic acid (3b) (29 g) which was used for the next step. MS (ES+): 513.24, (M+Na(; (ES ): 489.26, M-1.
Methyl 3-(4-(benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxytoarbonyltohenyl)-6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamovnpicolinate (3c)

To a mixture of 5-(benzyloxy)-2-(6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-2-(methoxy-carbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxybenzoic acid (3b) (31 g, 63.2 mmol), and triethylamine (17.7 mL, 126.4 mmol) in dichloromethane (300 mL), was added MEM-chloride (9.03 mL, 79 mmol), and stirred at room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was diluted with water and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water and dried over MgS04, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel, 40 g) to furnish methyl 3-(4-(benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)picolinate (3c) (32.8 g, 89%) as a thick gum; H NMR (300 MHz, CDCI3) δ 8.35 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 8.15 (t, J = 5.7 Hz, 1 H), 7.78 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (s, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (ddd, J = 7.5, 14.8, 22.4 Hz, 3H), 6.66 (s, 1 H), 5.37-5.13 (m, 4H), 3.90 (s, 3H), 3.69 (s, 3H), 3.60-3.49 (m, 2H), 3.49 (s, 2H), 3.39 (dd, J = 4.4, 8.4 Hz, 2H), 3.34 (s, 3H), 1.19-1.00 (m, 1H), 0.57 (q, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H), 0.38-0.25 (m, 2H). MS (ES+): 601.24 (M+Na); (ES"): 577.27 (M-1);1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cfe) δ 8.69 (t, 7 = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.41 (m, 5H), 6.92 (s, 1 H), 5.20 (m, 4H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 3.57 (s, 3H), 3.44 (m, 2H), 3:33 (m, 2H), 3.21 (m, 5H), 1.14 (m, 1H), 0.44 (m, 2H), 0.27 (m, 2H). IR (KBr):
1732, 1671 cm"1. MS (ES+): 601.1(M+Na); Analysis calculated for C31H 2Oe: C, 64.35; H, 5.92; N, 4.84; Found: C, 64.27; H, 6.04; N, 4.79.
Methyl 6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(4-hvdroxy-5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy¾methoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)picolinate (3d)

3c 3d
To a solution of methyl 3-(4-(benzyloxy)-5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)-carbonyl)phenyl)-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)picolinate (3c) (32.8 g, 56.68 mmol) in ethanol (650 mL) was added 10% Pd/C (4 g) and hydrogenated at 45 psi for 5 h. The catalyst was removed by filtration through Celite and the filtrate was concentrated under vacuum to yield methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)picolinate (3d) (31.87 g, 86%), which was pure enough to be used as such for the next step. An analytical sample of methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy) methoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)picolinate (3d) was obtained by purification of 350 mg of above crude using flash column chromatography (silica gel, eluting with ethyl acetate in hexane) to afford methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)carbonyl)-phenyl)picolinate (3d) as a clear gum; 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.74 (s, 1 H), 8.68 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 8.18 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (s, 1H), 6.83 (s, 1H), 5.19 (s, 2H), 3.77 (m, 3H), 3.58 (s, 3H), 3.44 (m, 2H), 3.34 (m, 2H), 3.21 (m, 5H), 1.04 (m, 1 H), 0.44 (m, 2H), 0.27 (m, 2H); IR (KBr): 1731 , 1664 cm'1. MS (ES*): 489.0 (M+1); Analysis calculated for C^e^O,,: C, 59.01; H, 5.78; N, 5.73; Found: C, 58.92; H, 6.15; N, 5.29.
6-(Cvclopropylmethylcarbamovn-3-(5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy^methoxy)-carbonyl)-4- (trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy)phenyl)picolinate (3e)

To a solution of methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-(((2- methoxyethoxy) methoxy)carbonyl)phenyl)picolinate (3d) (14.3 g, 29.3 mmol) in dichloromethane (150 mL) were added pyridine (12 mL, 146 mmol) and triflic anhydride (7.5 mL g, 44 mmol). After stirring overnight at room temperature under N2. the reaction mixture was poured into ice water and then extracted twice with dichloromethane. After washing the combined organic extracts with water and drying (MgS0 ), the solvent was evaporated in vacuo. The compound was purified by flash chromatography over silica gel column using ethyl acetate: hexane to afford methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(5-methoxy-2-(((2- methoxyethoxy)methoxy)-carbonyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy)phenyl)picolinate (3e) (1 g, 93%); H NMR (300 MHz, CDCy a 8.41 (d, J = 8.0, 1H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 8.03 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.0, 1 H), 6.82 (s, 1H), 5.32 (q, J = 6.1, 2H), 3.97 (s, 3H), 3.74 (s, 3H), 3.67 - 3.57 (m, 2H), 3.55 - 3.45 (m, 2H), 3.41 (dd, J = 8.2, 14.5, 2H), 3.34 (s, 3H), 1.36 - 1.17 (m, 1H), 0.58 (d, J = 7.1 , 2H), 0.33 (d, J = 5.1 , 2H).
Methyl 6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(5-methoxy-2-f((2-methoxyethoxy)- methoxy)carbonvn-4-vinylphenyl)picolinate (3f)

To a solution of methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(5-methoxy-2-(((2- methoxyethoxy)methoxy)carbonyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy)phenyl)picolinate (3e) (37.4
g, 60.30 mmol) and potassium vinyltrifluoroborate (16.87 g, 120.6 mmol) in DMF (450 mL) and water (45 mL) was bubbled N2 for 5 min. To this mixture was added NaHC03 (20.26 g, 241.2 mmol) and dichloro-bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium (II) (6.34 g, 9.0 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at 70 °C for 20 h under N2(reaction progress was checked by 1H N R because product and starting material had same Rf in TLC). The reaction mixture was cooled down to room temperature and diluted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was separated, washed with water, brine, dried ( gS04) and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under vacuum to yield crude methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-3-(5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)carbonyl)-4-vinylphenyl)-picolinate (3f). The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel, 1 kg, eluting with 0-100% ethyl acetate in hexane) to afford methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy) carbonyl)-4-vinylphenyl)picolinate [31) (26.54 g, 88%) as an amber gum; H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-c¾ δ 8.70 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 8.12 (s, 1 H), 8.00 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 6.98 (m, 2H), 5.94 (dd, J = 1.2, 17.8 Hz, 1H), 5.43 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 1 H), 5.21 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 2H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.64 (s, 3H), 3.48 (d, J = 3.1 Hz, 2H), 3.35 (m, 5H), 3.22 (m, 2H), 1.11 (s, 1H), 0.44 (dt, J = 4.9, 5.5 Hz, 2H), 0.28 (q, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H). IR (KBr); 1732, 1670 cm"1. MS (ES+) 499.1 (M+1).
2-(6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzolc acid (3g)

A mixture of methyl 6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-3-(5-methoxy-2-(((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy) carbonyl)-4-vinylphenyl)picolinate (3f) (27.4 mmol) in DME (160 mL) and 6N HCI (40 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 6 h or till TLC showed complete conversion. The solvent was removed under vacuum. The residue obtained was suspended in water, the solid separated out was collected by filtration, washed with water and dried under vacuum to give 2-(6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (3g) (7.0 g, 63%) as a white
solid MP 40 - 42 °C; H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de) δ 8.69 (t, J= 6.0 Hz, 1H, NH), 8.20 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H), 8.09 (s, 1 H), 7.95 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.97 (dd, J= 18.0, 11.3 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (s, 1H), 5.92 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1H), 5.38 (d, J= 11.1 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.63 (s, 3H), 3.27-3.17 (m, 2H), 1.15-1.05 (m, 1 H), 0.48-0.40 (m, 2H), 0.31-0.24 (m, 2H); IR (KBr): 3084, 1728, 1650, 1533, 1212, 1143 cm-1; MS (ES+) 433.26 (M+Na); (ES-): 409.28 (M-1); Analysis calculated for θ22Η22Ν2Ο6.0.25Η2Ο; C, 63.68; H, 5.47; N, 6.75; Found C, 63.75; H, 5.56; N, 6.65
Methyl-3-(2-(4-carbamimidoylprienylcarbamoyl)-5-metrioxy-4-vinylphenyl)-6- (cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)picolinate (3h)

To a solution of 2-(6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (3g) (2.35 g, 5.7 mmol) and 4-aminobenzimidamide dihydrochloride (3j) (1.79 g, 8.6 mmol) in DMF (20 mL) and pyridine (30 mL) at 0 °C was added EDCI (1.65 g, 8.6 mmol) and allowed to warm to room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was quenched with 6N HCI (60 mL) and extracted with chloroform (3 x 60 mL). The organic layer was dried over MgS04, filtered and purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel, 110 g, eluting with 0 to 100% chloroform in CMA 80 in CMA 50) yielding methyl-3-(2-(4-carbamimidoylphenyl-carbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)picolinate (3h) (2.2 g, 65%) as a white solid MP 266 °C; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-c/6) δ 10.78 (s, 1 H), 9.26 (s, 2H), 9.03 (s, 2H), 8.67 (t, J = 6.1 , 1 H), 8.22 (d, J = 8.0, 1 H), 8.06 (d, J = 8.0, 1 H), 7.96 (s, 1 H), 7.89 - 7.74 (m, 4H), 7.13 - 6.96 (m, 2H), 6.07 (d, J = 17.7, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.4, 1 H), 3.91 (s, 3H), 3.61 (s, 3H), 3.20 (s, 2H), 1.09 (dd, J = 4.7, 8.2, 1H), 0.43 (dt, J = 4.9, 5.4, 2H), 0.34 - 0.21 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 528.1 (M+1); Analysis calculated for 
C, 58.93; H, 5.63; N,11.85; Found: C, 58.75; H, 5.65; N, 11.92.
C, 58.93; H, 5.63; N,11.85; Found: C, 58.75; H, 5.65; N, 11.92.
46578
159
3-r2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy -vinyl-phenyll-6-(cvclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (3i)

3h 3i
To a solution of methyl-3-(2-(4-carbamirriidoylphenylcarbarnoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)picolinate (3h) (1 g, 1.9 mmol) in methanol (10 mL) and THF
(10 mL) was added 2 N NaOH (10 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 3 h, and concentrated in vacuo to remove methanol and THF. The aqueous layer was acidified with 6N HCI to pH 6-7 and the solid obtained was collected by filtration
washed with water and ether to furnish on drying 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid
(3i)(0.775 g, 80%) as the hydrochloride salt as an off white solid.
1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.67 (s, 1 H), 9.11 (s, 2H), 8.97 (s, 2H), 8.74 (s, 1 H), 7.90
(d, J = 7.8, 1 H), 7.80 (s, 1 H), 7.72 - 7.58 (m, 4H), 6.99 (dd, J = 11.3, 17.7, 1 H), 6.78 (s, 1H),
5.95 (d, J = 17.2, 1H), 5.38 (d, J = 11.9, 1H), 3.82 (s, 3H), 3.18 (s, 2H), 1.06 (s, 1 H), 0.43 (d,
J = 7.9, 2H), 0.25 (d, J = 4.7, 2H); MS (ES+) 514.0 (M+1 ); Analysis calculated for
C2eH27N5O5.HCI.H2O: C, 59.21; H, 5.32; N, 12.33; Found: C, 59.43; H, 5.21; N, 12.06.
Example 1A- Preparation of 3-f2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyll-6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride in Form
C

The jacket of a 10 L glass reactor was set to -5 °C. To the reactor was charged 2-(6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (6d) prepared in Step (11) of Example 1 (500 g, 1.22 mol), 4-amino-benzamidine-2HCI (280 g, 1.34 mol), and 2-propanol (4.05 kg). The mixture was cooled to 0.3 °C, and pyridine (210 g, 2.62 mol) followed by EDCI HCI (310 g, 1.61 mol) was added. The mixture was stirred at -1.1 to -0.3 °C for 22 hrs followed by addition of the second portion of EDCI HCI (58 g, 0.30 mol). The temperature of jacket was set to 14.0 °C, and the mixture was stirred for 89 hrs. The precipitate was filtered, and washed with 1.32 kg of 2-propanol.
The wet product (8a) was recharged to the reactor followed by addition of acetonitrile (1.6 kg) and water (0.57 kg). The mixture was heated to 46 °C. Smopex-234 (21 g) and Acticarbone 2SW (10 g) were added and the mixture was stirred at this temperature for 1 hr. The solution was filtered, and filtrate was returned back to the reactor. The jacket of the reactor was set to -5 °C, and the mixture was cooled to -0.2 "C. NaOH solution (256 g 46% NaOH, 2.95 mol, in 960 g water) was added in 25 min keeping the temperature <3 °C. The mixture was stirred at 0.2-2.0 °C for 1 hr 40 min and then quenched with cone, acetic acid (40 g, 0.66 mol). Diluted acetic acid (80 g, 1.33 mol AcOH in 1000 g water) was added during 1 hr 20 min (temperature 1.7-3.0 °C), followed by 1250 g water (30 min). The
suspension was stirred at 0-3.0 "for 1 hr, and filtered at 0-5 °C (ice mantle around the filter). The reactor and product (8d) was rinsed with 3.5 kg water.
The wet product (8d) was recharged to the reactor followed by 0.65 kg water and 1.69 kg acetonitrile. The mixture was heated to 57-60 °C, and stirred at this temperature for 14.5 hrs. The mixture was cooled to -2.2 °C (Tjackel= -5 °C), and a solution of NaOH (163 g 46%, 1.87 mol, in 580 g water) was added during 15 min. The temperature rose to -0.4 °C. Hydrochloric acid (407 g 37% HCI, 4 mol) was added in 10 min, the temperature rose to 7.5 °C. The suspension was agitated at -3 - 0 °C for 19 hrs. The product was filtered and the filter cake was rinsed with 2.87 kg water, compressed and pulled dry. The wet product (1.30 kg) was dried at 40-43 °C and 50 mbar for 11 hrs to furnish 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6- (cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (7b) (484 g) as Form C.
Example-1 B: Preparation of 3-f2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyll-6-(cvclopropylmethylcarbartiovQpyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride in Form A
The procedure was carried out in an identical manner to Example 1 A, with the exception that after the final filtration the filter cake was rinsed with 2.87 kg methyl ierf-butyl ether instead of 2.87 kg water, and pulled dry. The product was dried at 40-43 °C and 50 mbar to furnish 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (7b) as Form A.
PATENT
Methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)picolinate (compound 6a) is (I) (pages 85 and 86). Avoralstat hydrochloride (compound of formula XVIII) is (II) (claim 40, page 109). A Markush structures is presented (claim 1, page 99).
The synthesis of (II) via intermediate (I) is described (example 1, pages 80-93).
A synthesis of the compound 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoyl-phenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinyl-phenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (Compound 3i) is described in Schemes A-C.
O y OHCk n Br^ ^OCH3
B Brr22,, AAccOOHH Y^ V"" \ \ tt--BBuuOOKK
OHC^^^O " Br^\^0 MeOH " OHC
1a 1b 66%

1d 95% 1 e
1f
Scheme A



3h 31
Scheme C
Examples. In this section, the following abbreviations are used:



Example-1 : Preparation of 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (7b)

7b
Step (1): Preparation of 6-Bromobenzo 1 ,3]dioxole-5-carbaldehyde (1 b):

1b
A solution of bromine (33.0 kg, 206.49 mol) in acetic acid (27.5 L) was added slowly to a solution of piperonal (1a) (29.9 kg, 199.16 mol) in acetic acid (105 L) at room
temperature over a period of 50 min and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 14.2 h. Additional solution of bromine (33 kg, 206.49 mol) in acetic acid (27.5 L) was added slowly to the reaction mixture over a period of 2 h and the reaction mixture was stirred for 22 h. The reaction mixture was quenched by addition of ice water (500 L) with stirring over a period of 6 h and continued stirring for additional 1.25 h. The mixture was allowed to settle and most of the supernatant liquid was decanted to a waste container using nitrogen pressure. Water (600 L) was added to the solid, stirred, mixture was allowed to settle and then most of the supernatant liquid was decanted to a waste container using nitrogen pressure. Water (100 L) was added to the decanted mixture, stirred for 15 min and the solid obtained was collected by filtration using a centrifuge. The solid was washed with water (2 x 100 L) and air-dried in a tray drier for 3.75 h to afford the crude product 1 b (52 kg). The crude product (51.2 kg) was stirred in n-hexane (178 L) for 3 h, collected by filtration, washed with n-hexane (25 L) and dried to afford 6-bromobenzo[1 ,3]dioxole-5-carbaldehyde (1b) (40.1 1 kg, 87.9%) as a light brown solid. MP: 109-112°C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCI3) δ 10.21 (s, 1 H), 7.37 (s, 1 H), 7.07 (s, 1 H), 6.10 (s, 2H); HNMR (DMSO-cf6): δ 10.06 (s, 1 H), 7.42 (s, 1 H), 7.29 (s, 1 H), 6.20 (d, J =12.3 Hz, 2H)
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 1.
Average yield of isolated 1 b from step-1 is 78 - 88%.
Step (2): Preparation of 2-Bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzaldehyde (1c)

A solution of potassium terf-butoxide (10.7 kg, 95.36 mol) in DMSO (49 L) was stirred at 50 °C for 30 min. Methanol (49 L) was added slowly over a period of 4.25 h and stirred at 50 °C for 30 min. 6-Bromobenzo[1 ,3]dioxole-5-carbaldehyde (1 b) (9.91 kg, 43.27 mol) was added to the reaction mixture in small portions over a period of 45 min and stirred at 50 °C for 1 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and split into two equal portions. Each portion was quenched with water (50.9 L) and basified with 50% aqueous NaOH solution (2.4 L). Each portion was extracted with MTBE (4 x 36 L) to remove impurities. The aqueous layer was acidified with cone. HCI to pH ~ 3 to obtain
product as a yellow solid. The solid was collected by filtration using a centrifuge, washed with water (2 x 35 L) and air-dried to afford 2-Bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzaldehyde (1c) (4.37 kg, 40.7%, contains 7 % water); Mp: 100-102°C; 1HNMR (300MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 10.00 (s, 1 H), 9.92 (s,1 H), 7.27 (s, 1 H), 7.26 (s, 1 H), 3.93 (s, 3H).
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 2.
Average yield of isolated product 2-Bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzaldehyde (1c) from step-2 is 40-50%.
Step (3): 5-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-2-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-[1 ,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-y benzaldehyde (4a)

2-Bromo-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzaldehyde (1c) [1.3 kg (93%, 7% water content), 5.25 mol] was dissolved in toluene (13 L) in a reaction flask equipped with a Dean Stark apparatus. The solution was heated at reflux with stirring to distil off about 25% of the toluene along with water (90 ml_). The solution was cooled to 90 °C then
bis(pinacolato)diboron (1.5 kg, 5.82 mol), KOAc (772.6 g, 7.87 mol) and Pd(PPh3) (24.3 g, 0.02 mol) were added and the reaction mixture was heated at reflux for 10h. After confirming the completion of reaction by TLC (mobile phase: 100% DCM), the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and was kept standing overnight. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite and the celite cake was washed with toluene (4 L). The filtrate of this batch was mixed with the filtrate of another batch (batch size 1.3 kg obtained from an identical reaction). The mixed filtrate was washed with water (17.5 L), brine (17.5 L), dried over Na2S04, filtered and the solution was passed through a pad of silica gel (2 kg, mesh size 230-400). The silica gel pad was washed with toluene. The combined filtrate and washing was concentrated under reduced pressure and the residual crude product was stirred with n-hexane (23 L) for 1 h to obtain a solid product. The solid was collected by filtration, washed with n-hexane (5 L) and dried to afford 5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-2-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-[1 ,3,2]dioxaborolan-2-yl)benzaldehyde (4a) (2.47 kg, 84.6%). H NMR (300 MHz, CDCI3) δ 10.54 (s, 1 H), 7.57 (s, 1 H), 7.33 (s, 1 H), 5.89 (s, 1 H), 4.01 (s, 3H), 1.37 (s, 12H); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.35 (s, 1 H), 9.95 (s, 1 H), 7.33 (s, 1 H), 7.23 (s, 1 H), 3.87 (s, 3H), 1.33 (s, 12H); MS (ES+) 301.1 (M+Na); 579.1 (2M+Na); Analysis calculated for C14H19B05: C, 60.46; H, 6.89; Found: C, 60.60; H, 6.87
The average yield of 5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-2-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-[1 ,3,2]dioxa-borolan-2-yl)benzaldehyde (4a) from step (3) is 78 - 90%.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 3.
Step (4): Preparation of 3-Bromo-2,6-dimethylpyridine (5b)

2,6-lutidine (5a) (115 kg, 1073.3 mol) was added into pre-chilled oleum (20-23%, 1015 kg, 2276.7 mol) at 0 °C over a period of 4.5 h (temperature r6ached 14 °C during the addition). Bromine (88.18 kg, 1103.6 mol) was then added at 5-10 °C over a period of 1 h. The reaction mixture was slowly heated to 150 °C over a period of 12h. TLC analysis indicated about 40-50% conversion to product and the formation of a dimer by-product (5%). The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and then additional bromine (88.18 kg, 1103.6 mol) was added slowly. The reaction mixture was slowly heated to maintain a temperature of 65-75 °C over a period of 15h. TLC analysis indicated a 65-70 % conversion to product and the formation of 5% dimer by product. The reaction mixture was quenched by addition of water (500L) while maintaining the reaction temperature below 20 °C. The mixture was basified with 6.6 M NaOH (3800 L) while maintain the temperature at < 40 °C. EtOAc (220 L) was added and the mixture was stirred for 1 h then allowed to settle over a period of 2 h. The layers were separated and the aqueous layer was treated with NaOH (10 kg) in water (10 L) and extracted with EtOAc (160 L). The organic extracts were combined washed with brine (100 L), dried over Na2S04 (50.0 kg), filtered and the solvent was evaporated under atmospheric pressure. The residue was vacuum distilled and the desired product 3-bromo-2,6-dimethylpyridine (5b) was collected at 58-60 °C, 2 mmHg (98.45 kg, 49.2 %) as a colorless liquid.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 4.
Step (5): Preparation of 3-Bromopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (5c)
5b 5c
To a stirred solution of 3-bromo-2,6-dimethylpyridine (5b) (98 kg, 5326 mol) in water (1310 L) was added KMn0 (225 kg, 1423.6 mol) in 5 equal portions in 1 h intervals at 70 °C. After stirring for 1 h at 70 °C, additional KMn04 (225 Kg, 1423.6 mol) was added in 5 equal portion in 1 h intervals at 90 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred for 12 h at 90 °C. The suspension was filtered hot through celite to obtain a clear solution. The solvent was distilled off to remove about 30% of the total volume. The remaining concentrated solution was chilled to 0 °C and made acidic (to pH 3-4) by the addition of cone. HCI (120 L). The white precipitate obtained was collected by filtration and dried at 70 °C to afford 3-bromopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (5c) as a white solid (109 kg, 84%).
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 5.
Step (6): Preparation of Dimethyl 3-Bromopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate (5d)

To a stirred solution of 3-bromopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (5c) (20.0 kg, 81.29 mol) in methanol (100 L) was added cone. H2S04 (4.4 L) over a period of 30 min. The reaction mixture was heated to 65 °C and maintained at that temperature for 5 h (the reaction was monitored by TLC analysis to determine completion of reaction). The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature basified by careful addition of aqueous NaHC03 solution (prepared from 10 kg NaHC03 in 120 L of water) and further diluted with water (120 L). The white solid obtained was collected by filtration, washed with plenty of water and then oven-dried at 40 °C to obtain dimethyl 3-bromopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate (5d) (9.2 kg, 41.3%) as a white solid; 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cf6) δ 8.47 (d, J = 8.4, 1 H), 8.08 (dd, J = 4.5, 8.4, 1 H), 3.95 (s, 3H), 3.91 (s, 3H); MS (ES+) 570.6 (2M+Na); Analysis calculated for C9H8BrN04: C, 39.44; H, 2.94; Br, 29.15 N, 5. 1 ;
Found: C, 39.52; H, 2.92; Br, 29.28; N, 5.03.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 6.
6582
Step (7): Preparation of Methyl 3-bromo-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylate (

To a stirred solution of dimethyl 3-bromopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate (5d) (27 kg, 98.52 mol) in ierf-butanol (135 L) was added at room temperature cyclopropylmethanamine (7.83 kg, 110.1 mol). The reaction mixture was heated at 65 °C for 17 h. The progress of reaction was monitored by TLC and HPLC (HPLC analysis showed the formation of 74% of the product 5e after 17 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and then cone. HCI (2.7 L) was added slowly and the mixture was stirred for 15 min. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain the crude product. The crude product was dissolved in hot /-PrOH (54 L) filtered through a celite pad. The filtrate was cooled with stirring to 10 °C to obtain a white precipitate. The solid obtained was collected by filtration, washed with cold
i-PrOH (13 kg), n-hexane (15 L) and dried to provide pure methyl 3-bromo-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylate (5e) (15.7 kg, 50.9%). The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure and the crude product can be purified by silica gel column chromatography eluting with tert-butanol in hexanes to furnish additional 10% methyl 3-bromo-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylate (5e). HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cf6) δ 8.83 (t, J = 5.9, 1 H), 8.47 - 8.41 (m, 1 H), 8.06 (d, J = 8.4, 1 H), 3.96 (s, 3H), 3.16 (t, J = 6.5, 2H), 1.14 - 0.99 (m, 1 H), 0.42 (m, 2H), 0.30 -0.19 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 337.0 (M+23), 650.8 (2M+23); Analysis calculated for
C12H13BrN203: C, 46.03; H, 4.18; N, 8.95; Br, 25.52; Found: C, 46.15; H, 4.17; N, 8.72; Br, 25.26.
The average isolated yield for step (7) is 50% to 60%.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 7.
Step (8): Preparation of methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)picolinate (6a)
2

6a
THF (37.5 L) was charged to a 100 L reactor followed by ethyl 3-bromo-6- (cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylate (5e) (2.5 kg, 7.98 mol) under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction mixture was degassed twice by applying alternate vacuum and nitrogen. 5-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-2-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-[1 ,3,2]dioxa-borolan-2-yl)benzaldehyde (4a) (2.88 kg, 10.36 mol) was added, followed by the addition of PPh3 (53.13 g, 0.20 mol), PdCI2(PPh3)2 (120.4 g, 0.17 mol) and a solution of Na2C03(2.12 kg, 20.00 mol) in demineralized water (10.0 L) under nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction mixture was degassed again two times by applying alternate vacuum and nitrogen. The reaction mixture was heated at reflux for 6.5 h, cooled to room temperature and filtered through a Celite bed. Water (75 L) was added to the filtrate and the product was extracted with ethyl acetate (75 L). The aqueous layer was back extracted with ethyl acetate (2 χ 60 L). The combined ethyl acetate extract was divided into two equal portions and each portion was washed with brine (37 L), dried over Na2S04, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give crude methyl 6- ((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)picolinate (6a) as a reddish viscous material (-4.5 Kg) which was used as such for the next step without further purification. An analytical sample was prepared by purification of a small sample by flash column chromatography (silica gel, eluting with 0-100% ethyl acetate in hexane) to furnish methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-picolinate (6a) as an off-white solid; HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.89 (s, 1 H), 9.52 (s, 1 H), 8.79 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1 H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 8.09 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.34 (s, 1 H), 6.90 (s, 1 H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.62 (s, 3H), 3.22 (m, 2H), 1.16 -1.02 (m, 1 H), 0.49 - 0.38 (m, 2H), 0.32 - 0.22 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 791.0 (2M+Na), (ES-) 382.7 (M-1), 767.3 (2M-1); Analysis calculated for C20H20N2O6.0.25 H20: C, 61.77; H, 5.31 ; N, 7.20; Found: C, 61.54; H, 5.13; N, 7.05.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 8.
46582
Step (9): Preparation of methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-5-methoxy-4-(((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)oxy)phenyl)picolinate (6b)

6a 6b
A solution of methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)picolinate (6a) (2.11 kg, estimated about 3.83 mol from step-8) in dichloromethane (16.0 L) and pyridine (1.4 L, 17.4 mol) cooled to -10°C and maintained at that temperature for 1 h was added a solution of triflic anhydride (980.0 ml_, 5.8 mol) in dichloromethane (6.0 L) drop wise over a period of 3 h at -10 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at -5°C for 1.3 h, quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3(10.4 L) and stirred for 30 mins. The organic layer was separated, washed successively with saturated aqueous NaHC03 (10.4 L), 1 HCI (2 x 16.6 L), water (13.2 L), brine (13.2 L), dried over MgS04, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product. The crude product was stirred with 15% ethyl acetate in n-hexane (7.0 L) for 1 h. The solid obtained was collected by filtration washed with 15% ethyl acetate in n-hexane (3.0 L). The solid was stirred again with 15% ethyl acetate in n-hexane (7.0 L) for 1 h, was collected by filtration and washed with 15% ethyl acetate in n-hexane (3.0 L). The solid was stirred again with 15% ethyl acetate in n-hexane (8.0 L) for 1 h, collected by filtration washed with 15% ethyl acetate in n-hexane (3.0 L). The solid was dried to afford methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-5-methoxy-4-(((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)-oxy)phenyl)picolinate (6b) as a light brown solid (1.7 kg, 86% yield, for combined steps 8 & 9). Average isolated yield for combined steps 8 and 9 was 70% to 86%; Ή NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-cf6): δ 9.64 (s, 1 H), 8.78 (t, J = 6.1 , 1 H), 8.29 (d, J = 8.0, 1 H), 8.16 (d, J = 8.0, 1 H), 8.03 (s, 1H), 7.39 (s, 1 H), 4.00 (s, 3H), 3.63 (s, 3H), 3.22 (m, 2H), 1.11 (m, 1 H), 0.52 - 0.39 (m, 2H), 0.28 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 538.9 (M+Na). The process is also illustrated in Fig. 9.
Step (10): Preparation of methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)picolinate (6c)

A solution of methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-5-methoxy-4- (((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)oxy)phenyl)picolinate (6b) (12 kg, 23.24 mol) in DME (106 L) was charged into reactor under nitrogen. The reaction mixture was degassed twice by applying alternate vacuum and nitrogen. Potassium trifluoro(vinyl)borate (3.9 kg, 29.1 1 mol), PdCI2(PPh3)2 (815 g, 1.13 mol), KHC03 (4.65 g, 46.44 mol) and demineralized water (12 L) was then added under a N2 atmosphere. The reaction mixture was degassed by applying alternate vacuum and nitrogen. The reaction mixture was heated at reflux for 5 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and then filtered through a Celite bed. Demineralized water (118 L) was added to the filtrate followed by ethyl acetate (124 L). The mixture was stirred for 20 min and then the organic layer was separated. The aqueous layer was back-extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 95 L). The combined organic extract was washed with brine (95 L), dried over Na2S04, and filtered. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to give the crude product. The crude product was purified by column chromatography (silica gel, 120 kg, 230-400 mesh size, eluting with ethyl acetate in n-hexane) to obtain methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)picolinate (6c) (6 kg, 72%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCI3): δ (ppm) 9.64 (s, 1 H), 8.35 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 8.06-8.03 (m, 2H), 7.78(d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.02-6.92 (m, 1 H), 6.61 (s, 1 H), 5.86 (d, J = 17.7 Hz, 1 H), 5.38 (d, J = 1 1.4 Hz, 1 H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.67 (s, 3H), 3.35-3.29 (m, 2H),1.08-1.03 (m, 1H), 0.55-0.49 (m, 2H), 0.29-0.2 4(m, 2H). 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) 6 9.68 (s, 1 H), 8.77 (t, J = 6.1 , 1 H), 8.35 - 8.21 (m, 1 H), 8.16 - 8.01 (m, 2H), 7.14 -6.87 (m, 2H), 6.01 (dd, J = 1.2, 17.8, 1 H), 5.45 (dd, J = 1.1 , 1 1.3, 1 H), 3.91 (s, 3H), 3.64 (s, 3H), 3.23 (m, 2H), 1.21 - 1.01 (m, 1H), 0.51 - 0.40 (m, 2H), 0.34 - 0.20 (m, 2H). MS
(ES+) 417.0 (M+Na); Analysis calculated for C22H22N205: C, 66.99; H, 5.62; N, 7.10;
Found: C, 66.75; H, 5.52; N, 7.06.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 10.
Step (1 1): Preparation of 2-(6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-2- (methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (6d)

To a stirred solution of methyl 6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-3-(2-formyl-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)picolinate (6c) (1.57 kg, 3.80 mol) in acetonitrile (15.4 L) was added ferf-butyl alcohol (22.2 L), demineralized water (3.2 L) and sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate (323.74 g, 2.346 mol). The reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and added 2-methyl-2-butene (5.3 L, 50.0 mol) and stirred at 0 °C for 30 min. A solution of 80% sodium chlorite (1.36 kg, 12.0 mol) in demineralized water (5.2 L) was added to the reaction mixture over a period of 2.5 h at 0 °C [temperature rises to 7 °C during the addition]. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 2 h, diluted with water (40 L) and ethyl acetate (24 L). After stirring the mixture, it was allowed to settle and the organic layer was separated. The aqueous layer was back-extracted with ethyl acetate (2 x 20 L) then acidified with 5.9 % aqueous acetic acid (2 L) and extracted once with ethyl acetate (10 L). The organic extracts were combined washed with water (2 x 20 L), a solution of acetic acid (125 mL) in water (20.0 L), brine (2 χ 20 L), dried over Na2S04, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure (vapor temperature below 40 °C). The residue obtained was dissolved in acetone (7 L) (residue didn't dissolve completely). The solution was poured slowly into a reactor containing stirred n-hexane (70.0 L) to precipitate the solid product and the mixture was stirred for 2 h. The solid obtained was collected by filtration, washed with 10% acetone in n-hexane (6.3 L), AJ-hexane (6.3 L), dried to afford 2-(6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4- methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (6d) as an off-white solid (1.29 Kg, yield: 79.0%). Average isolated yield for step 1 1 is 74% to 84%. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 12.50 (brs, 1 H), 8.69(t, J= 6.0 Hz, 1 H, NH), 8.20 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1 H), 8.09 (s, 1 H), 7.95 (d, J= 8.1 Hz, 1 H), 6.97 (dd, J= 18.0, 1 1.3 Hz, 1 H), 6.88 (s, 1 H), 5.92 (d, J= 7.9 Hz, 1 H), 5.38 (d, J= 1 1.1 Hz, 1 H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.63 (s, 3H), 3.27-3.17 (m, 2H), 1.15-1.05 (m, 1 H), 0.48-0.40 (m, 2H), 0.31-0.24 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 433.26, (M+Na); (ES-) 409.28 (M-1). The process is also illustrated in Fig. 1 1.
Step (12): Preparation of Methyl 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylate methanesulfonate (7a

Pyridine (3.8 L, 47.17 mol) and EDCI (5.31 kg, 27.66 mol) were sequentially added to a cooled solution (0 °C) of 2-(6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (6d) (9 kg, 21.92 mol) and 4-aminobenzamidine dihydrochloride (5.13 kg, 24.65 mol) in /-PrOH (90 L). The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 2 h. TLC analysis indicated incomplete reaction. Additional EDCI (1.08 kg, 5.6 mol) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 8 h. The reaction was still incomplete as indicated by TLC analysis, additional EDCI (0.54 kg, 2.8 mol) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 5 h. TLC analysis indicated there was trace amount of unreacted starting material remaining. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and a solution of
methanesulfonic acid (MSA) (9.13 kg, 95 mol) in MeOH (38.7 L) was added to the cooled mixture over a period of 4 h. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 15 h. The product was collected by filtration, washed with a mixture of /'-PrOH and MeOH (4:1 , 45 L). The wet cake was slurried in a mixture of /-PrOH and MeOH (2:1 , 135 L) stirred for 1 h and the product was collected by filtration and washed with a mixture of /'-PrOH and MeOH (4:1 , 46.8 L). The product was dried in
2015/046582
a vacuum oven at 45 °C to afford methyl 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylate methanesulfonate (7a) as a pink-colored solid (12.71 kg, 93%). Average isolated yield for this step: >90%.
1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-c/6) δ 10.71 (s, 1 H), 9.16 (s, 2H), 8.80 (s, 2H), 8.68 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1 H), 8.22 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1 H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.84 - 7.72 (m, 4H), 7.12 - 6.97 (m, 2H), 6.04 (dd, J = 17.8, 1.3 Hz, 1 H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.6 Hz, 1H), 3.91 (s, 3H), 3.60 (s, 3H), 3.25 - 3.16 (m, 2H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 1.10 - 1.01 (m, 1 H), 0.48 - 0.37 (m, 2H), 0.30 - 0.22 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 528.0 (M+1); Analysis calculated for
C29H29N5O5.CH3SO3H.2H2O. C, 54.62; H, 5.65; N, 10.62; S, 4.86; Found: C, 54.95; H, 5.55; N, 10.61 ; S, 4.87.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 12.
Step (13): Preparation of 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-rnethoxy-4- vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrate

(3i) ,a 3i
A pre-cooled (0-5 °C) aq. NaOH solution [prepared from solid NaOH (4 kg, 100 mol) in water (86 L)] was added to a suspension of methyl 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethyl-carbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylate methanesulfonate (7a) (28.7 kg, 46 mol) in acetonitrile (86 L) cooled to 0 to 5 °C over a period of 25 mins. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 to 5 °C for 2.5 h (TLC analysis showed the reaction was complete). The reaction mixture was filtered through a sparkler filter, washed with a mixture of 1 :1 CH3CN / H20 ( 57.4 L). Acetic acid (3.2 L, 55.9 mol) in water (56 L) was added to the filtrate at room temperature over a period of 25 mins and the resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2.5 h. The solid product obtained was collected by filtration, washed with a 1 :4 mixture of CH3CN / H20 (57.5 L). The solid was dried at 45°C in a vacuum oven to afford 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6- (cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrate (3i) as an off-white solid (12,77 kg, 54.1%). Average yield for this step is 50% to 75%. Mp: >200°C; H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 13.49 (s, 1 H), 8.94 (bs, 4H), 8.56 (t, 1 H), 7.82 - 7.71 (m, 2H), 7.67 -7.56 (m, 4H), 7.51 (d, J = 7.8, 1 H), 6.98 (dd, J = 11.3, 17.8, 1 H), 6.68 (s, 1 H), 5.92 (d, J = 16.6, 1 H), 5.36 (d, J = 12.4, 1 H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.16 (m, 2H), 1.05 (m, 1 H), 0.43 (m, 2H), 0.24 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 514.1 (M+1), 536.1 (M+Na), (ES-) 512.1 ; Analysis calculated for C28H27N5O5.3H2O: C, 59.25; H, 5.86; N, 12.34; Found C, 59.50; H,
5.75; N, 12.05. If needed this material can be crystallized from a mixture of acetone and water.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 13.
Step 14: Preparation of 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (7b

A pre-cooled (5-8 °C) aqueous NaOH solution (prepared from solid NaOH (1.97 kg, 49.25 mol) in demineralized water (41 L) was added to a pre-cooled (0-5 °C) suspension of (3i) (13.8 kg, 26.9 mol) in acetonitrile (41 L). The reaction mixture was stirred at 0-5 °C for 30 min (until the reaction mixture becomes homogeneous). The reaction mixture was filtered through a sparkler filter washed with 50% acetonitrile in demineralized water (4.4 L). The filtrate was charged into a reactor and cooled to 0-5 °C. Aqueous HCI [prepared from cone. HCI (9.3 L) in demineralized water (36 L)] was added slowly with stirring to keep the reaction temperature at or below 15 °C, the resulting mixture was stirred at 10-15 °C for 13 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0-5 °C and stirred for 1 h. The solid obtained was collected by filtration and washed with demineralized water (36 L). The solid product was suspended in water (69 L) stirred for 30 mins and collected by filtration washed twice with water (20 L each). The solid product was dried in a vacuum oven at 45°C to afford 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-
(cyclopropylmethyl carbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (7b) (1 1.21 Kg, 75.77%). Mp: >200°C; 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-ci6): δ 12.98 (br s, 1 H), 10.86 (s, 1 H), 9.24 (s, 3H), 9.04 (s, 2H), 8.22 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.96 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 2H), 7.78 (s, 4H), 7.09-6.99 (m, 2H), 6.07 (d, J = 17.7 Hz, 1 H), 5.45(d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1 H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.26-3.24 (m, 2H), 1.09 (m, 1 H), 0.47 (m, 2H), 0.28 (m, 2H).
Average isolated yield for this step varies from 63% to 80%.
The process is also illustrated in Fig. 14.
Example-2: Preparation of 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid sulfate salt (8b)

6d 8a
To a solution of 2-(6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (6d) (2.35 g, 5.7 mmol) and 4-aminobenzamidine dihydrochloride (1.79 g, 8.6 mmol) in DMF (20 mL) and pyridine (30 ml_) at 0 °C was added EDCI (1.65 g, 8.6 mmol) and allowed to warm to room temperature overnight. The
reaction mixture was quenched with 6N HCI (60 mL) and extracted with chloroform (3 x 60 mL). The organic layer was dried over MgS04, filtered and concentrated in vacuum. The residue obtained was purified by flash column chromatography (silica gel, 110 g, eluting with 0 to 100% chloroform in CMA 80 and 0-100% chloroform in CMA 50) to furnish methyl 3-(2-((4-carbamimidoylphenyl)carbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)-6-((cyclopropylmethyl)-carbamoyl)picolinate hydrochloride (8a) (2.2 g, 65%) as a white solid; MP 266 °C; 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.78 (s, 1 H), 9.26 (s, 2H), 9.03 (s, 2H), 8.67 (t, J = 6.1 , 1 H), 8.22 (d, J = 8.0, 1 H), 8.06 (d, J = 8.0, 1 H), 7.96 (s, 1 H), 7.89 -7.74 (m, 4H), 7.13 - 6.96 (m, 2H), 6.07 (d, J = 17.7, 1 H), 5.45 (d, J = 12.4, 1 H), 3.91 (s, 3H), 3.61 (s, 3H), 3.20 (s, 2H), 1.09 (dd, J = 4.7, 8.2, 1 H), 0.43 (dt, J = 4.9, 5.4, 2H), 0.34 - 0.21 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 528.1 (M+1); Analysis calculated for C29H29N505 (H20)1 5 (HCI): C, 58.93; H, 5.63; N, 1 1.85; Found: C, 58.75; H, 5.65; N, 1 1.92.
Step-2: preparation of 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid sulfate salt (8b)

8a 8b j0 a solution of methyl 3-(2-((4-carbamimidoylphenyl)carbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)-6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)picolinate hydrochloride (8a) (1.128 g, 2 mmol) in acetonitrile (5 ml), was added 1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide (5.00 ml, 5.00 mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 2 h, TLC [CMA80/CMA50 (7/3)] shows reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was neutralized with a solution of sulfuric acid (0.483 ml, 9.00 mmol) in water (5 mL) and stirred for 10 min at room temperature. To this cold water (5 ml) was added and stirred at room temperature until product crystallized out. Cold water (5 mL) was added to the slurry and stir for additional 20 min, additional cold water (5 mL) was added prior to filtration of solid. The solid obtained was collected by filtration washed with water (5 mL and 2.5 mL), dried under vacuum overnight to afford 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-
(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid sulfate salt (8b) (1.103 g, 90 % yield) as a white solid; MP 221.7 °C; H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.30 - 10.91 (bs, 1 H, D20 exchangeable), 10.69 (bs, 1 H, D20 exchangeable), 9.24 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 1 H), 9.16 (s, 2H, D2O exchangeable), 8.78 (s, 2H, D2O exchangeable), 8.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 8.04 - 7.91 (m, 2H), 7.84 - 7.67 (m, 4H), 7.13 - 6.94 (m, 2H), 6.03 (dd, J = 17.8, 1 .4 Hz, 1 H), 5.51 - 5.37 (m, 1 H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.24 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 1.16 - 1.01 (m, 1 H), 0.52 - 0.41 (m, 2H), 0.32 - 0.22 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 514.0 (M+1); Analysis calculated for: C28H27N605 1.0H2SO4 1.5H20: C, 52.66; H, 5.05; N, 10.97; S, 5.02; Found: C, 52.81 ; H, 4.95; N, 10.94; S, 4.64.
Example-3: Preparation of 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid methane s

To a solution of methyl 3-(2-((4-carbamimidoylphenyl)carbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl)-6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)picolinate hydrochloride (8a) (1.128 g, 2 mmol) in acetonitrile (5 ml) was added 1 N aqueous sodium hydroxide (5.00 ml, 5.00 mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 2 h, TLC [CMA80/CMA50 (7/3)] shows reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was neutralized with methanesulfonic acid (0.584 ml, 9.00 mmol) and stirred for 1 h at room temperature. Cold water (5.00 ml) was added to the reaction mixture and stirred at room temperature until product crystallized out. To the slurry was added water (5 ml) of water stirred for additional 20 min, followed by the addition of water (5 ml) prior to filtration. The solid obtained was collected by filtration washed with water (5 ml and 2.5 ml), dried under vacuum to afford 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6- (cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid methane sulfonate salt (8c)
(1 .138 g, 1.867 mmol, 93 % yield) as a white solid; MP 221.2 °C; 1 H NMR (300 MHz,
DMSO-d6) δ 12.89 (s, 1 H, D2O exchangeable), 10.69 (s, 1 H, D2O exchangeable), 9.24
(t, J = 6.0 Hz, 1 H), 9.16 (s, 2H,), 8.85 (s, 2H), 8.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1 H), 8.06 - 7.91 (m, 2H), 7.86 - 7.70 (m, 4H), 7.15 - 6.96 (m, 2H), 6.03 (dd, J = 17.8, 1.4 Hz, 1 H), 5.52 - 5.35 (m, 1 H), 3.88 (s, 3H), 3.25 (t, J = 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.34 (s, 3H), 1.17 - 1.01 (m, 1 H), 0.53 -0.43 (m, 2H), 0.32 - 0.23 (m, 2H); MS (ES+) 514.0 (M+1); Analysis calculated for:
CzeH^NsOsCHsSOsH 1.5H20: C, 54.71 ; H, 5.38; N, 11.00; S, 5.04; Found: C, 54.80; H, 5.14; N, 10.94; S, 4.90.
Example-4: Preparation of 3-[2-(4-Carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (7b) in Form C (Compound XX)

The jacket of a 10 L glass reactor was set to -5 °C. To the reactor was charged 2-(6-((cyclopropylmethyl)carbamoyl)-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-pyridin-3-yl)-4-methoxy-5-vinylbenzoic acid (6d) prepared in Step (11) of Example 1 (500 g, 1.22 mol), 4-amino-benzamidine-2HCI (280 g, 1.34 mol), and 2-propanol (4.05 kg). The mixture was cooled
46582
to 0.3 °C, and pyridine (210 g, 2.62 mol) followed by EDCI HCI (310 g, 1.61 mol) was added. The mixture was stirred at -1.1 - -0.3 °C for 22 hrs followed by addition of the second portion of EDCI HCI (58 g, 0.30 mol). The temperature of jacket was set to 14.0 °C, and the mixture was stirred for 89 hrs. The precipitate was filtered, and washed with 1.32 kg of 2-propanol.
The wet product (8a) was recharged to the reactor followed by addition of acetonitrile (1 .6 kg) and 0.57 kg water. The mixture was heated to 46 °C. 21 g of Smopex-234 and 10 g Acticarbone 2SW were added and the mixture was stirred at this temperature for 1 hr. The solution was filtered, and filtrate was returned back to the reactor. The jacket of the reactor was set to -5 °C, and the mixture was cooled to -0.2 °C. NaOH solution (256 g 46% NaOH, 2.95 mol, in 960 g water) was added in 25 min keeping the temperature <3 °C. The mixture was stirred at 0.2-2.0 °C for 1 hr 40 min and then quenched with cone, acetic acid (40 g, 0.66 mol). Diluted acetic acid (80 g, 1.33 mol AcOH in 1000 g water) was added during 1 hr 20 min (temperature 1.7-3.0 °C), followed by 1250 g water (30 min). The suspension was stirred at 0-3.0 °for 1 hr, and filtered at 0-5 °C (ice mantle around the filter). The reactor and product (8d) was rinsed with 3.5 kg water.
The wet product (8d) was recharged to the reactor followed by 0.65 kg water and 1.69 kg acetonitrile. The mixture was heated to 57-60 °C, and stirred at this temperature for 14.5 hrs. The mixture was cooled to -2.2 °C (Tjacke,= -5 °C), and a solution of NaOH (163 g 46%, 1.87 mol, in 580 g water) was added during 15 min. The temperature rose to -0.4 °C. Hydrochloric acid (407 g 37% HCI, 4 mol) was added in 10 min, the temperature rose to 7.5 °C. The suspension was agitated at -3 - 0 °C for 19 hrs. The product was filtered and the filter cake was rinsed with 2.87 kg water, compressed and pulled dry. The wet product (1.30 kg) was dried at 40-43 °C and 50 mbar for 1 17 hrs to furnish 3-[2-(4-carbamimidoylphenylcarbamoyl)-5-methoxy-4-vinylphenyl]-6-(cyclopropylmethylcarbamoyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (7b) (484 g) as Form C (Compound XX).
/////avoralstat, BCX4161, Fast Track, Treat hereditary angioedema (HAE), Orphan Drug, PRECLINICAL
COc1cc(c(cc1C=C)C(=O)Nc2ccc(cc2)C(=N)N)c3cc(ncc3C(=O)O)C(=O)NCC4CC4
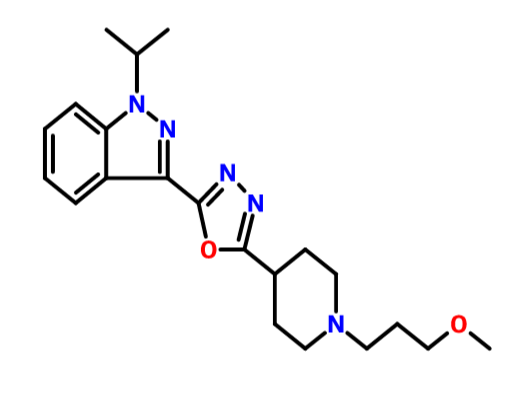
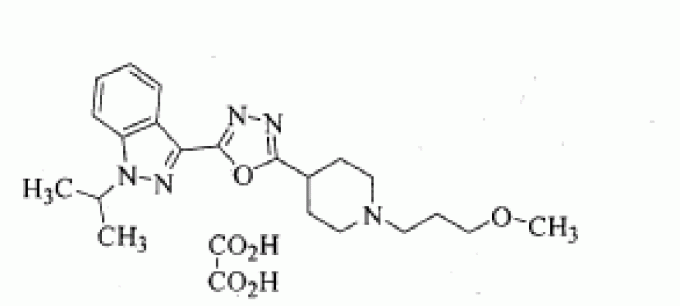

 SUVEN Life Sciences Ltd
SUVEN Life Sciences Ltd












 TAJ KRISHNA
TAJ KRISHNA
