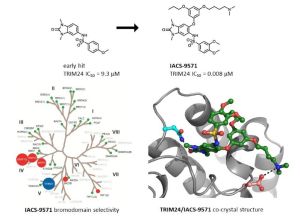
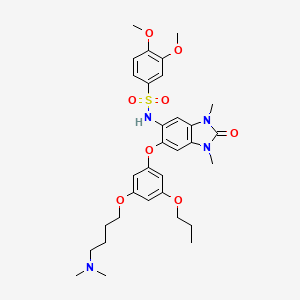
IACS-9571
TRIM24/BRPF1 bromodomain inhibitor
IACS-9571; IACS 9571; IACS9571.
| Molecular Formula: | C32H42N4O8S |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 642.76288 g/mol |
|---|
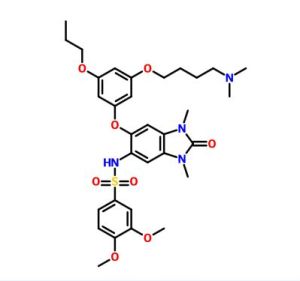
N-[6-[3-[4-(dimethylamino)butoxy]-5-propoxyphenoxy]-1,3-dimethyl-2-oxobenzimidazol-5-yl]-3,4-dimethoxybenzenesulfonamide
BOARD OF REGENTS, UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS SYSTEM
IACS-9571
is a potent and selective inhibitor TRIM24 and BRPF1. The bromodomain
containing proteins TRIM24 (Tripartite motif containing protein 24) and
BRPF1 (bromodomain and PHD finger containing protein 1) are involved in
the epigenetic regulation of gene expression and have been implicated in
human cancer. Overexpression of TRIM24 correlates with poor patient
prognosis and BRPF1 is a scaffolding protein required for the assembly
of histone acetyltransferase complexes, where the gene of MOZ (monocytic
leukemia zinc finger protein) was first identified as a recurrent
fusion partner in leukemia patients (8p11 chromosomal rearrangements).
IACS-9571 has low nanomolar affinities for TRIM24 and BRPF1 (ITC Kd = 31
nM and 14 nM, respectively). With its excellent cellular potency (EC50 =
50 nM) and favorable pharmacokinetic properties (F = 29%), IACS-9571 is
a high-quality chemical probe for the evaluation of TRIM24 and/or BRPF1
bromodomain function in vitro and in vivo. (J Med Chem. 2015 Jun 10.
[Epub ahead of print] )

PAPER
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00405
Structure-Guided Design of IACS-9571, a Selective High-Affinity Dual TRIM24-BRPF1 Bromodomain Inhibitor
Wylie S. Palmer*†, Guillaume Poncet-Montange‡, Gang Liu†, Alessia Petrocchi†, Naphtali Reyna†, Govindan Subramanian†, Jay Theroff†, Anne Yau†, Maria Kost-Alimova†, Jennifer P. Bardenhagen†, Elisabetta Leo†, Hannah E. Shepard†, Trang N. Tieu†, Xi Shi†, Yanai Zhan†, Shuping Zhao†, Michelle C. Barton§, Giulio Draetta†, Carlo Toniatti†, Philip Jones†, Mary Geck Do†, and Jannik N. Andersen†
†Institute for Applied Cancer Science, and ‡Core for Biomolecular Structure and Function, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 1881 East Road, Unit 1956, Houston, Texas 77054, United States
§ Department of Epigenetics and Molecular Carcinogenesis,
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center,
1515 Holcombe Boulevard
, Houston, Texas 77030,
United States
J. Med. Chem., 2016, 59 (4), pp 1440–1454
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00405
Publication Date (Web): June 10, 2015
Copyright © 2015 American Chemical Society

The
bromodomain containing proteins TRIM24 (tripartite motif containing
protein 24) and BRPF1 (bromodomain and PHD finger containing protein 1)
are involved in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression and have
been implicated in human cancer. Overexpression of TRIM24 correlates
with poor patient prognosis, and BRPF1 is a scaffolding protein required
for the assembly of histone acetyltransferase complexes, where the gene
of MOZ (monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein) was first identified as
a recurrent fusion partner in leukemia patients (8p11 chromosomal
rearrangements). Here, we present the structure guided development of a
series of N,N-dimethylbenzimidazolone bromodomain
inhibitors through the iterative use of X-ray cocrystal structures. A
unique binding mode enabled the design of a potent and selective
inhibitor 8i (IACS-9571) with low nanomolar affinities for TRIM24 and BRPF1 (ITC Kd = 31 nM and ITC Kd = 14 nM, respectively). With its excellent cellular potency (EC50 = 50 nM) and favorable pharmacokinetic properties (F = 29%), 8i is a high-quality chemical probe for the evaluation of TRIM24 and/or BRPF1 bromodomain function in vitro and in vivo.
TFA
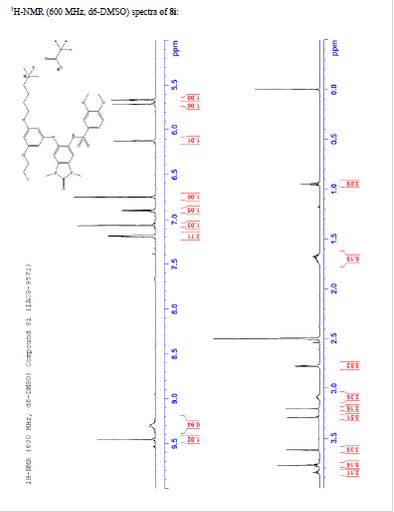
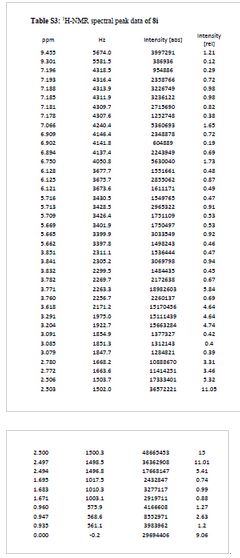
salt of 8i (106 mg, 57%) as a white solid. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ
9.46 (s, 1H), 9.30 (br-s, 1H), 7.19 (m, 2H), 7.07 (s, 1H), 6.90 (d, J =
9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.75 (s, 1H), 6.13 (t, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.71 (t, J = 2.0
Hz, 1H), 5.67 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 3.77 (m,
5H), 3.62 (s, 3H), 3.29 (s, 3H), 3.20 (s, 3H), 3.12–3.05 (m, 2H), 2.78
(d, J = 4.7 Hz, 6H), 1.77–1.63 (m, 6H), 0.95 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H). 13C
NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 160.0, 159.3, 154.1, 152.0, 148.4,
143.9, 131.8, 128.2, 126.0, 121.9, 120.5, 110.4, 109.4, 106.4, 100.6,
95.9, 95.8, 95.2, 68.9, 66.7, 56.3, 55.6, 55.4, 42.1, 27.1, 27.0, 25.6,
21.9, 20.7, 10.4. MS (ESI) m/z 644 [M + H]+.
NMR
ABSTRACT
251st ACS National Meeting & Exposition
13–17 March 2016
San Diego, United States
MEDI 5
Discovery
and development of a potent dual TRIM24/BRPF1 bromodomain inhibitor,
IACS -9571, using structure- based drug design Wylie S. Palmer 1 ,
wpalmer@mdanderson.org, Guillaume Poncet -Montagne 1 , Gang Liu 1 ,
Alessia Petrocchi 1 , N aphtali Reyna 1 , Govindan Subramanian 1 , Jay
Theroff 1 , Maria Kost -Alimova 1 , Jennifer Bardenhagen 1 , Elisabetta
Leo 1 , Hannah Sheppard 1 , Trang Tieu 1 , Shi Xi 1 , Yanai Zhan 1 ,
Shuping Zhao 1 , Michelle Barton 2 , Giulio Draetta 1 , Carlo Toniatti 1
, Philip Jones 1 , Mary Ge ck Do 1 , Jannik Andersen 1 . (1) Institute
for Applied Cancer Science, The University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer
Center, Houston, Texas, United States (2) Department of Epigenetics and
Molecular Carcinogenesis, The University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer
Center, Houston, Texas, United States
Bromodomains are an
important class of chromatin remodeling proteins that recognize
acetylated lysine residues on histone tails. As epigenetic targets they
regulate gene transcription and offer a new way to treat diseas es,
particularly in inflammation and oncology. The bromodomain and extra-
terminal (BET) family has emerged as an important and druggable example
of this class of proteins with the successful entry of small- molecule
inhibitors into the clinic. Other families of bromodomains are only
starting to be explored, such as the Tripartite Motif -containing 24
protein (TRIM24) and bromodomain- PHD finger protein 1 (BRPF1). Both
proteins contain a dual PHD -bromo motif which have a role in
recognizing specific histone mar ks. TRIM24 recognizes the dual histone
marks of unmodified H3K4 and acetylated- H3K23 within the same histone
tail. TRIM24 is a potent co- activator of ER -alpha and overexpression
of TRIM24 has been linked to poor survival rates in breast cancer
patients.
This presentation will describe the structure guided
development of a series of N,N- dimethyl -benzimidazolones through the
iterative use of X -ray cocrystal structures. A unique binding mode
enabled the design of a potent and selective inhibitor (IACS -9571) with
low nanomolar affinities for TRIM24 and BRPF1 (ITC Kd = 31 nM and ITC
Kd = 14 nM, respectively). With its excellent cellular potency (EC 50 =
50 nM) and favorable pharmacokinetic properties, IACS -9571 is a high-
quality chemical probe for the evaluation of TRIM24 and/or BRPF1
bromodomain function in vitro and in vivo

PATENT
WO-2016033416-A1
Synthesis of Intermediates:
N-(6-bromo-l ,3-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-2,2,2- trifluoroacetamide (Intermediate 1):
Step 1 : 5-nitro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one:
To a 0 °C solution of 4-nitrobenzene- 1 ,2-diamine (44 g, 285 mmol) in 80 mL of DMF was added l, l'-carbonyldiimidazole
(70 g, 428 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 4 h, then
water (250 mL) was added. The resulting suspension was filtered, and the
collected solids were washed with water (200 mL) and dried to give 5-nitro-lH- benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one as a yellow solid (45 g, 88%). MS (ES+) C7H5N3O3 requires: 179, found: 180 [M+H]+.
Step 2: l,3-dimethyl-5-nitro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one:
To a solution of 5-nitro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (55 g, 309 mmol) in 150 mL of DMF was added K2CO3 (85 g, 618 mmol), the reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C, then iodomethane
(109 g, 772 mmol) was slowly added. The reaction mixture was stirred at
RT overnight, then water was added to the reaction mixture. The
resulting suspension was filtered and the collected solids were washed
with water (200 mL) and dried to give 1,3- dimethyl-5-nitro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one as a yellow solid (55 g, 86%). MS (ES+) C9H9N3O3 requires: 207, found: 208 [M+H] +.
Step 3: 5-amino-l,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one:
To a solution of l,3-dimethyl-5-nitro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (50 g, 240 mmol) in 200 mL of EtOAc under an inert atmosphere was added 10% palladium on activated carbon (5 g, 24 mmol). The reaction mixture was then charged with hydrogen
and stirred at RT under an ¾ atmosphere overnight. The reaction mixture
was filtered through a pad of celite then concentrated to give 5-amino-l,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)- one as a yellow solid (32 g, 68%). MS (ES+) C9H11N3O requires: 177, found: 178 [M+H]+.
Step 4: 5-amino-6-bromo-l ,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one:
To a 0 °C solution of 5-amino-l ,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (4 g, 22.6 mmol) in 25 mL of CHCI3 and 25 mL of AcOH was slowly added drop wise bromine (3.5 g, 22.6mmol). The mixture was stirred at RT for 30 min, then concentrated and purified by silica gel chromatography (1 : 1 EtOAc/ hexanes) to afford 5-amino-6-bromo-l ,3-dimethyl- lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one as a yellow solid (3.2 g, 69%). MS (ES+) C9HioBrN30 requires: 256, found: 257 [M+H]+.
Step 5: N-(6-bromo-l ,3-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-2,2,2- trifluoroacetamide:
To a 0 °C solution of 5-amino-6-bromo-l ,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol- 2(3H)-one (1.50 g, 5.9 mmol) in DCM (45 ml) was added DMAP (72 mg, 0.59 mmol), triethylamine (1.63 ml, 11.7 mmol) and trifluoroacetic anhydride
(0.91 ml, 6.4 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred for 2 h and
warmed to RT. The reaction mixture was then quenched with water and the
organic phase was washed with brine, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated to give N-(6-bromo-l,3-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-lH- benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide (Intermediate 1) as a yellow solid (2.20 g, 100%). MS (ES+) CiiH9BrF3N302 requires: 352, found 353 [M+H]+.
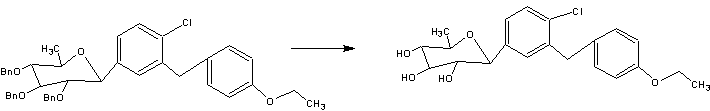
5-amino-6-(3-hydroxyphenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (Intermediate 2, Route A):
To a mixture of 5-amino-6-(3-(benzyloxy)phenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-lH- benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (400 mg, 1.07 mmol) in DCM (20 mL) at -78 °C was added tribromoborane (5.3 mL, 5.3 mmol). The mixture was warmed up to room temperature gradually, then quenched by methanol dropwise, concentrated, and purified by column chromatography (20-100% EtOAc/hexanes and then 0-40% methanol/EtOAc) to give 5- amino-6-(3-hydroxyphenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one as a solid (240 mg, 79%). MS (ES+) C15H15N3O3 requires: 285, found: 286 [M+H]+.
5-amino-6-(3-hydroxyphenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (Intermediate 2, Route B):
Step 2
Step 1: 3-[(ieri-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy]phenol:
A mixture of lH-imidazole (2.25 g, 33.1 mmol), ieri-butylchlorodimethylsilane (3.83 g, 25.4 mmol) and resorcinol
(5.6 g, 51 mmol) in THF (30 ml) was stirred at 80 °C for 5 h. The
resulting suspension of the cooled reaction mixture was filtered and the
collected filtrate was concentrated and purified by silica-gel
chromatography (20:80 to 0:100, EtOAc/hexanes) to give 3-((ieri-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy)phenol (2.78 g, 49%). MS (ES+) C12H20O2S1 requires: 224, found 225 [M+H]+.
Step 2: 5-amino-6-(3-((ier^butyldimethylsilyl)oxy)phenoxy)-l ,3-dimethyl-lH- benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one:
A mixture of 3-((ieri-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy)phenol (1.39 g, 6.20 mmol), quinolin-8-ol (79 mg, 0.55 mmol), copper(I) chloride (20 mg, 0.21 mmol), potassium phosphate (526 mg, 2.48 mmol) and 5-amino-6-bromo-l ,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol- 2(3H)-one (529 mg, 2.07 mmol) in diglyme (20 ml) in a 100 mL round-bottom flask was degassed under a nitrogen atmosphere and heated to 120 °C for 24 h. To the cooled reaction mixture was added silica gel, stirred for 2 min, then the mixture was filtered through a pad of silica
gel. The collected filtrate was concentrated and purified by column
chromatography (20:80 to 0: 100, EtOAc/hexanesthen 0: 100 to 40:60,
MeOH/EtOAc) to give 5-amino-6-(3- ((ieri-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy)phenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (521 mg, 63%). MS (ES+) C21H29N3O3S1 requires: 399, found 400 [M+H]+.
Step 3: 5-amino-6-(3-hydroxyphenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one:
To a 0 °C solution of 5-amino-6-(3-((ieri-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy)phenoxy)-l,3- dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (623 mg, 1.56 mmol) in THF was added a solution of ieira-butylammonium fluoride
(0.90 mL, 3.1 mmol) in THF, the reaction mixture was allowed to warm up
to RT and then stirred for 1-2 h. The reaction mixture was quenched
with 1 M hydrogen chloride
(0.10 mL, 3.1 mmol) and then partitioned between EtOAc and water. The
seperated organic layer was washed with water twice, then concentrated
and purified by column chromatography (20-80% EtOAc/hexanes and 0-40%
MeOH/DCM) to give 5-amino-6-(3-hydroxyphenoxy)-l ,3-dimethyl-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-one (120 mg, 27%) as a solid. MS (ES+) C15H15N3O3 requires: 285, found 286 [M+H]+.
EXAMPLE 10: N-(6-(3-(4-(dimethylamino)butoxy)-5-propoxyphenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-2-
oxo-2,3-dihydro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-3,4-dimethoxybenzenesulfonamide
2,2,2-

To a solution of N-(6-(3-(4-aminobutoxy)-5-propoxyphenoxy)-l
,3-dimethyl-2-
oxo-2,3-dihydro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-3,4-dimethoxybenzenesulfonamide
2,2,2- trifluoroacetate (180 mg, 0.247 mmol) in methanol (3.0 ml) was added triethylamine (0.034 ml, 0.25 mmol), acetic acid (0.028 ml, 0.49 mmol), formaldehyde (0.054 ml, 2.0 mmol), and sodium triacetoxyborohydride
(131 mg, 0.618 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room
temperature and checked by LCMS every 30 minutes. After 3 h the reaction
was complete by LCMS. The reaction was quenched with a few drops of TFA
and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by
prep-HPLC using a gradient of 20-60% ACN/water containing 0.1% TFA to
afford N-(6-(3-(4-(dimethylamino)butoxy)-5-
propoxyphenoxy)-l,3-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-5-yl)-3,4-
dimethoxybenzenesulfonamide 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (106 mg, 57%) as a white solid. MS (ES+) C32H42N4O8S requires: 642, found 643 [M+H]+.
¾ NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-ifc) δ 9.46 (s, 1H), 9.30 (br-s, 1H), 7.19 (m,
2H), 7.07 (s, 1H), 6.90 (d, 7 = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.75 (s, 1H), 6.13 (t, 7 =
2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.71 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 5.67 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.84
(t, 7 = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 3.77 (m, 5H), 3.62 (s, 3H), 3.29 (s, 3H), 3.20 (s,
3H), 3.12-3.05 (m, 2H), 2.78 (d, 7 = 4.7 Hz, 6H), 1.77-1.63 (m, 6H),
0.95 (t, 7 = 7.3 Hz, 3H)
References
1:
Palmer WS, Poncet-Montange G, Liu G, Petrocchi A, Reyna N, Subramanian
G, Theroff J, Yau A, Kost-Alimova M, Bardenhagen JP, Leo E, Shepard HE,
Tieu TN, Shi X, Zhan Y, Zhao S, Draetta G, Toniatti C, Jones P, Geck Do
M, Andersen JN. Structure-Guided Design of IACS-9571, a Selective
High-Affinity Dual TRIM24-BRPF1 Bromodomain Inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2015
Jun 10. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 26061247.
US-20160060260-A1
Institute for Applied Cancer Science, The University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, United States
 The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center | University of Texas System
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center | University of Texas System
 The new Institute for Applied Cancer Science will be located at the south campus of M.D.
The new Institute for Applied Cancer Science will be located at the south campus of M.D.
 Draetta arrived at MD Anderson in 2011 to direct the Institute for Applied Cancer Science. He oversees the moon shots platforms
Draetta arrived at MD Anderson in 2011 to direct the Institute for Applied Cancer Science. He oversees the moon shots platforms
Department
of Epigenetics and Molecular Carcinogenesis, The University of Texas,
MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, United States
 ///
///////IACS-9571,
TRIM24, BRPF1 bromodomain inhibitor, IACS-9571, IACS 9571, IACS9571,
BOARD OF REGENTS, UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS SYSTEM
CAS BASE 1800477-30-8
CAS OF 1:1 TRIFLUOROACETATE 1883598-69-3
c1(cc(cc(c1)OCCC)Oc3cc2N(C(N(c2cc3NS(=O)(=O)c4cc(c(cc4)OC)OC)C)=O)C)OCCCCN(C)C
CCCOC1=CC(=CC(=C1)OC2=C(C=C3C(=C2)N(C(=O)N3C)C)NS(=O)(=O)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)OC)OC)OCCCCN(C)C
TFA
salt of 8i (106 mg, 57%) as a white solid. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ
9.46 (s, 1H), 9.30 (br-s, 1H), 7.19 (m, 2H), 7.07 (s, 1H), 6.90 (d, J =
9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.75 (s, 1H), 6.13 (t, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 5.71 (t, J = 2.0
Hz, 1H), 5.67 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 3.84 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 2H), 3.77 (m,
5H), 3.62 (s, 3H), 3.29 (s, 3H), 3.20 (s, 3H), 3.12–3.05 (m, 2H), 2.78
(d, J = 4.7 Hz, 6H), 1.77–1.63 (m, 6H), 0.95 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H). 13C
NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 160.3, 160.0, 159.3, 154.1, 152.0, 148.4,
143.9, 131.8, 128.2, 126.0, 121.9, 120.5, 110.4, 109.4, 106.4, 100.6,
95.9, 95.8, 95.2, 68.9, 66.7, 56.3, 55.6, 55.4, 42.1, 27.1, 27.0, 25.6,
21.9, 20.7, 10.4. MS (ESI) m/z 644 [M + H]+.



























 CLICK ON IMAGE
CLICK ON IMAGE