Doravirine, MK-1439........... AN ANTIVIRAL
3-Chloro-5-({1-[(4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3-pyridinyl}oxy)benzonitrile
Benzonitrile, 3-chloro-5-[[1-[(4,5-dihydro-4-methyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinyl]oxy]-
3-chloro-5-({1-[(4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile
(3-Chloro-5-((1-((4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl)-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile)
1338225-97-0 CAS
MF C17H11ClF3N5O3
MW 425.7 Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp
MW 425.7 Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp
Merck Frosst Canada Ltd. INNOVATOR
Reverse transcriptase inhibitor
UNII:913P6LK81M
- Originator Merck & Co
- Class Antiretrovirals; Nitriles; Pyridones; Small molecules; Triazoles
- Mechanism of Action Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- Phase III HIV-1 infections
Most Recent Events
- 16 Jul 2016 No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in HIV-1-infections(Monotherapy, Treatment-naive) in Germany (PO, Tablet)
- 01 Jun 2016 Merck Sharp & Dohme completes a phase I pharmacokinetics trial in subjects requiring methadone maintenance therapy in USA (PO, Tablet) (NCT02715700)
- 01 May 2016 Merck completes a phase I trial in severe renal impairment in USA (NCT02641067)
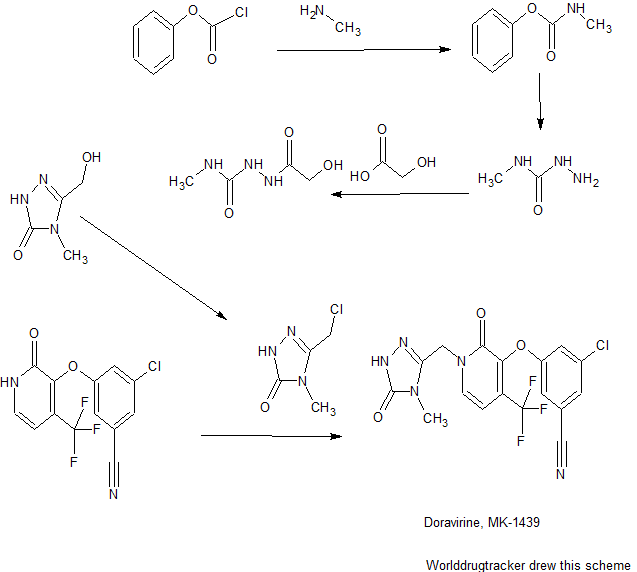
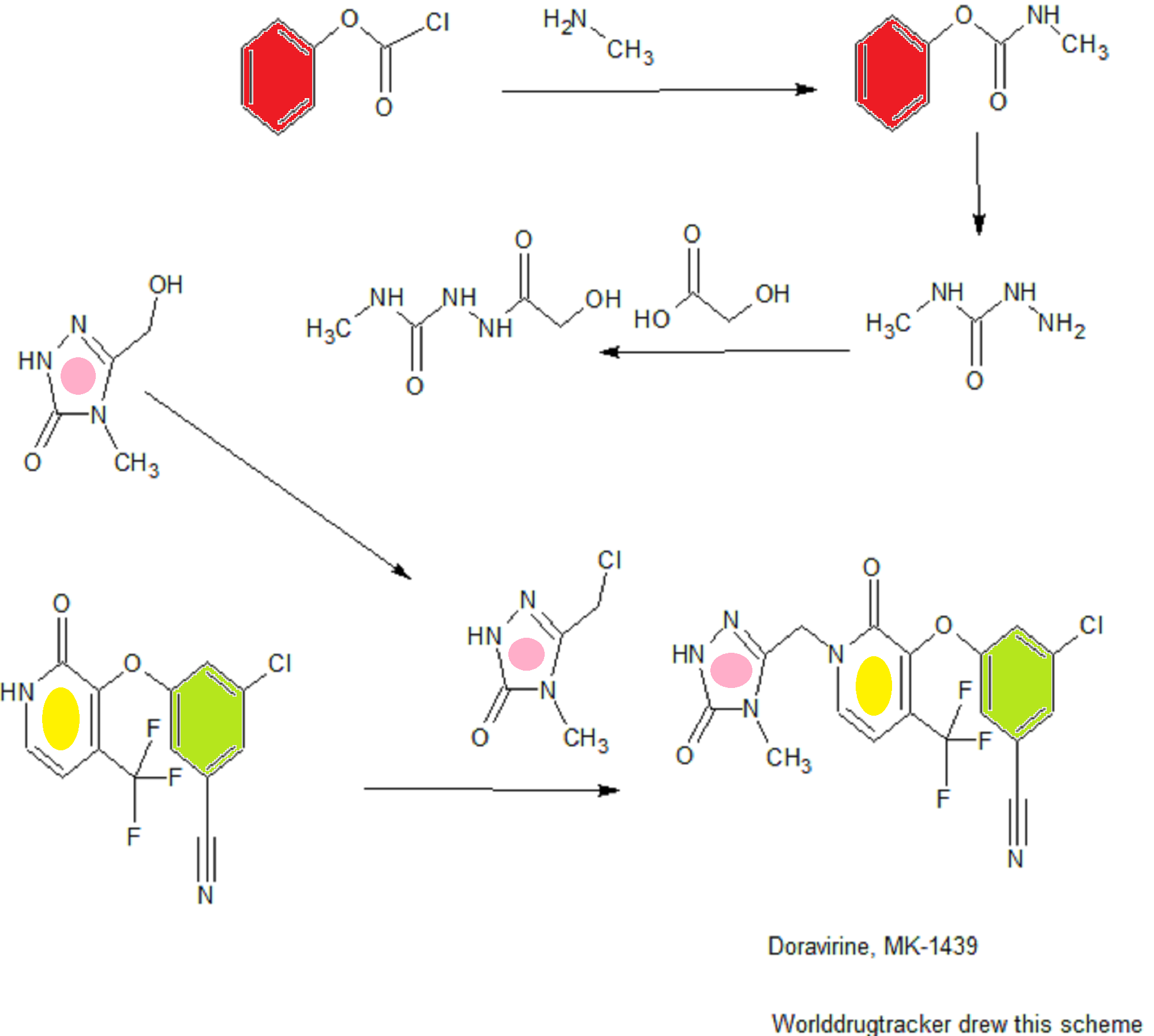
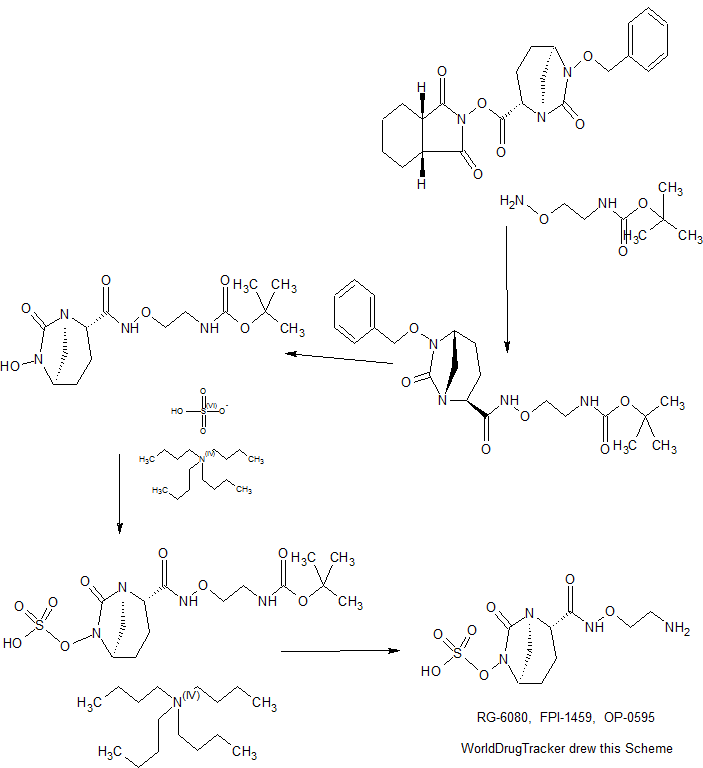
SYNTHESIS COMING.........
WO 2015084763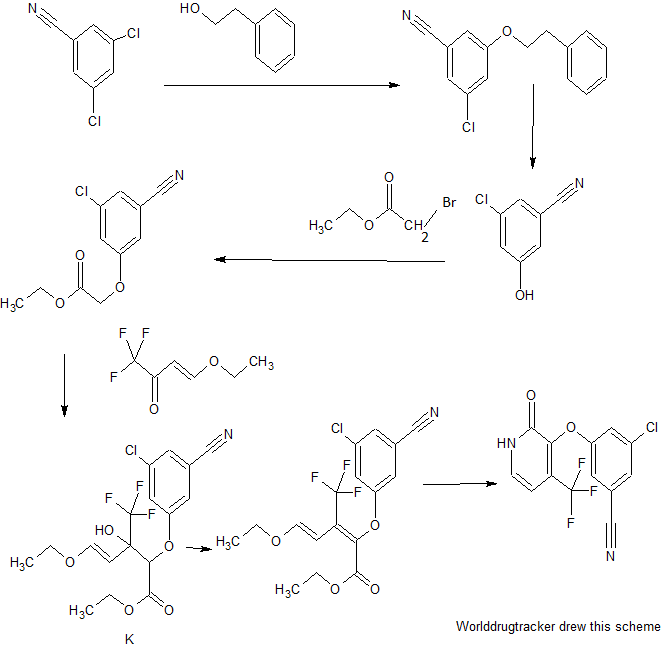
CONTD...........................
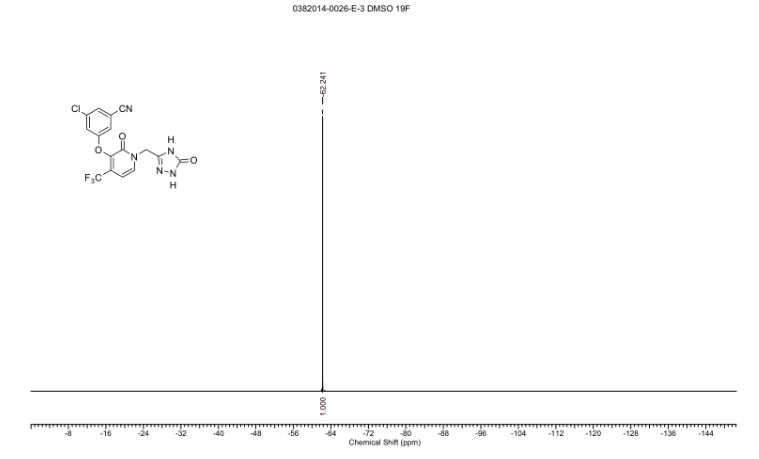
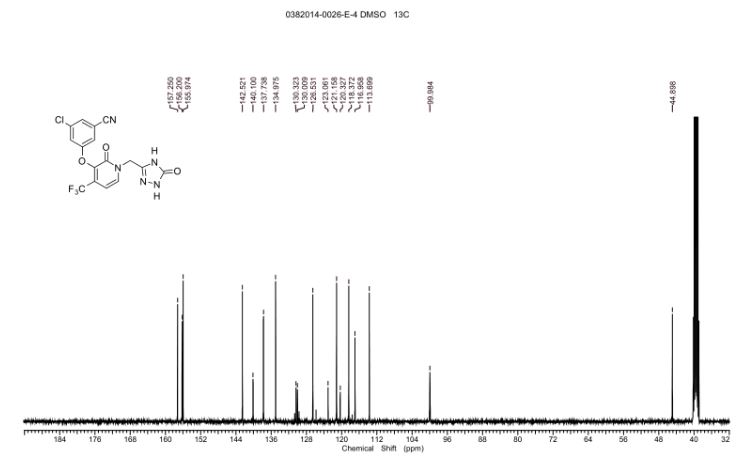
SPECTRAL DATA
19F DMSOD6
13C NMR DMSOD6
1H NMR DMSOD6
3-chloro-5-((2-oxo-1-((5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile.
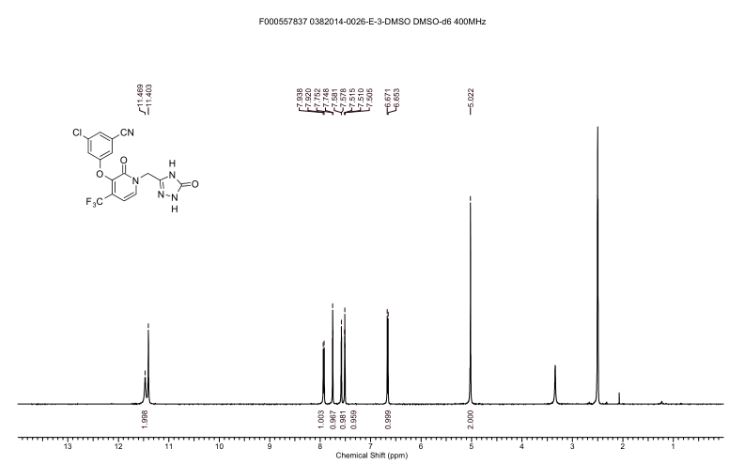
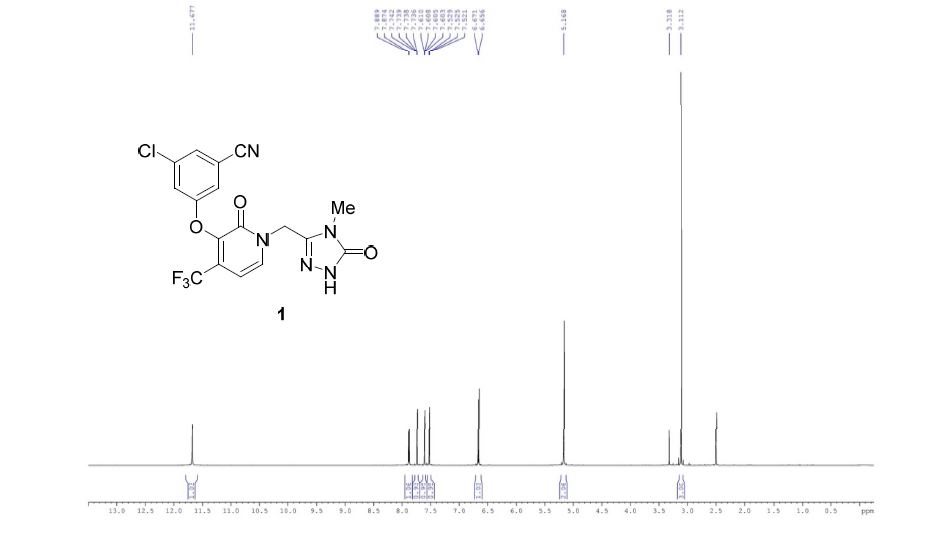
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.47 (br. s., 1H), 11.40 (s, 1H), 7.93 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.75 (t, J =1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (dd, J = 1.2, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.51 (t, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.66 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 5.02 (s, 2H)
13C NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 157.25, 156.20, 155.97, 142.52, 140.09 (q, JC-F = 2.0 Hz), 137.74,134.97, 130.17 (q, JC-F = 31.2 Hz), 126.53, 121.70 (q, JC-F = 274.7 Hz), 121.16, 118.37, 116.96, 113.70,99.96 (q, JC-F = 4.0 Hz), 44.90
19F NMR (376 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ -62.24 (s, 1F)
HRMS [M + H]+ for C16H10ClF3N5O3 calcd, 412.0419; found, 412.0415.
mp 148.46-156.11 °C
HRMS [M + H]+ for C16H10ClF3N5O3 calcd, 412.0419; found, 412.0415.
mp 148.46-156.11 °C
REF Org. Process Res. Dev., Article ASAP, DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00163
Doravirine (MK-1439) is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor under development by Merck & Co. for use in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. Doravirine demonstrated robust antiviral activity and good tolerability in a small clinical study of 7-day monotherapy reported at the 20th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections in March 2013. Doravirine appeared safe and generally well-tolerated with most adverse events being mild-to-moderate.[2][3]
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is the standard of care for the treatment of HIV infection. Typically, this protocol recommends the combination of two nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) with either a non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor or an integrase inhibitor.
NNRTI-based combinations have become first-line therapy mainly because of their demonstrated efficacies, convenient dosing regimen and relatively low toxicities. These inhibitors block the polymerase activity of the HIV reverse transcriptase by binding to an allosteric hydrophobic pocket adjacent to the active site. Efavirenz (1, ) is a first generation NNRTI that has been conveniently co-formulated with NRTIs tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and emtricitabine (FTC) as a once-a-day fixed-dose combination (Atripla®). Although recommended for the therapy of treatment-naïve patients, efavirenz suffers from neurocognitive side effects, teratogenicity and exacerbation of hyperlipidemia. Moreover, the low barrier to genetic resistance of first generation NNRTIs led to the emergence of resistant viruses bearing mutations K103N and Y181C in patients failing therapy.
Second generation NNRTIs etravirine (2) and rilpivirine (3) efficiently suppress the replication of the K103N resistant mutants as shown by an improved activity in cell culture assays . Etravirine (200 mg, bid) is approved for use in treatment-experienced adult patients with multi-drug resistance. With an improved pharmacokinetic profile, the close analog rilpivirine (25 mg, qd) was recently approved for use in treatment-naïve patients. Phase III data reveal that at the 96-week point, a rilpivirine/truvada® combination was better tolerated than efavirenz/truvada®. However, the virologic failure rate was twice as high for rilpivirine (14%) than it was for efavirenz (8%). For patients with viral load greater than 500,000 copies/mL, the response rate is 62% (rilpivirine) versus 81% (efavirenz). As a result, rilpivirine is not recommended for treating HIV patients with viral load >500,000 copies/mL. This difference in treatment durability could be explained by the much higher ratio of trough concentration over the antiviral activity for efavirenz versus rilpivirine.
Investigational next-generation, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), at the 21st Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI). Interim data demonstrating potent antiretroviral (ARV) activity for four doses (25, 50, 100 and 200 mg) of once-daily, oral doravirine in combination with tenofovir/emtricitabine in treatment-naïve, HIV-1 infected adults after 24 weeks of treatment were presented during a late-breaker oral session. Based on these findings as well as other data from the doravirine clinical program, Merck plans to initiate a Phase 3 clinical trial program for doravirine in combination with ARV therapy in the second half of 2014.
“Building on our long-standing commitment to the HIV community, Merck continues to evaluate new candidates we believe have the potential to make a meaningful difference in the lives of HIV patients,” said Daria Hazuda, Ph.D., vice president, Infectious Diseases, Merck Research Laboratories. “We look forward to advancing doravirine into Phase 3 clinical trials in the second half of 2014.”
Doravirine Clinical Data
This randomized, double-blind clinical trial examined the safety, tolerability and efficacy of once-daily doravirine (25, 50, 100 and 200 mg) in combination with once-daily tenofovir/emtricitabine versus efavirenz (600 mg), in treatment-naïve, HIV-1 infected patients. The primary efficacy analysis was percentage of patients achieving virologic response (< 40 copies/mL).
At 24 weeks, doravirine doses of 25, 50, 100, and 200 mg showed virologic response rates consistent with those observed for efavirenz at a dose of 600 mg. All treatment groups showed increased CD4 cell counts.
Proportion of Patients with Virologic
Response at 24 weeks (95% CI) |
Mean CD4 Change
from Baseline (95% CI) | |||||||
| Treatment* | Dose (mg) | n/N |
% <40
copies/mL |
cells/μL
| ||||
| Doravirine | 25 | 32/40 | 80.0 (64.6, 90.9) | 158 (119, 197) | ||||
| 50 | 32/42 | 76.2 (60.5, 87.9) | 116 (77, 155) | |||||
| 100 | 30/42 | 71.4 (55.4, 84.3) | 134 (100, 167) | |||||
| 200 | 32/41 | 78.0 (62.4, 89.4) | 141 (96, 186) | |||||
| Efavirenz | 600 | 27/42 | 64.3 (48.0, 78.4) | 121 (73, 169) | ||||
| Missing data approach: | Non-completer = Failure | Observed Failure | ||||||
*In combination with tenofovir/emtricitabine
| ||||||||
The incidence of drug-related adverse events was comparable among the doravirine-treated groups. The overall incidence of drug-related adverse events was lower in the doravirine-treated groups (n=166) than the efavirenz-treated group (n=42), 35 percent and 57 percent, respectively. The most common central nervous system (CNS) adverse events at week 8, the primary time point for evaluation of CNS adverse experiences, were dizziness [3.0% doravirine (overall) and 23.8% efavirenz], nightmare [1.2% doravirine (overall) and 9.5% efavirenz], abnormal dreams [9.0% doravirine (overall) and 7.1% efavirenz], and insomnia [5.4% doravirine (overall) and 7.1% efavirenz].
Based on the 24-week data from this dose-finding study, a single dose of 100 mg doravirine was chosen to be studied for the remainder of this study, up to 96 weeks.
About Doravirine
Doravirine, also known as MK-1439, is an investigational next-generation, NNRTI being evaluated by Merck for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. In preclinical studies, doravirine demonstrated potent antiviral activity against HIV-1 with a characteristic profile of resistance mutations selected in vitro compared with currently available NNRTIs. In early clinical studies, doravirine demonstrated a pharmacokinetic profile supportive of once-daily dosing and did not show a significant food effect.
Merck’s Commitment to HIV
For more than 25 years, Merck has been at the forefront of the response to the HIV epidemic, and has helped to make a difference through our proud legacy of commitment to innovation, collaborating with the community, and expanding global access to medicines. Merck is dedicated to applying our scientific expertise, resources and global reach to deliver healthcare solutions that support people living with HIV worldwide.

About Merck

Today's Merck is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. Merck is known as MSD outside the United States and Canada. Through our prescription medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies, and consumer care and animal health products, we work with customers and operate in more than 140 countries to deliver innovative health solutions. We also demonstrate our commitment to increasing access to healthcare through far-reaching policies, programs and partnerships. For more information, visit www.merck.com and connect with us on Twitter, Facebook and YouTube.
PATENT
The compound 3 -chloro-5-( { 1 - [(4-methyl-5 -oxo-4,5 -dihydro- 1 H- 1 ,2,4-triazol-3 - yl)methyl]-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile has the following chemical structure.
Anhydrous 3 -chloro-5-( { 1 - [(4-methyl-5 -oxo-4,5 -dihydro- 1 H- 1 ,2,4-triazol-3 -yl)methyl] -2-oxo-4- (trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile is known to exist in three crystalline forms - Form I, Form II and Form III. The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curve for crystalline anhydrous Form II shows an endotherm with an onset at 230.8° C, a peak maximum at 245.2°C, and an enthalpy change of 3.7 J/g, which is due to polymorphic conversion of anhydrous Form II to anhydrous Form I, and a second melting endotherm with an onset at 283.1°C, a peak maximum at 284.8°C, and an enthalpy change of 135.9 J/g, due to melting of Anhydrous Form I. Alternative production and the ability of this compound to inhibit HIV reverse transcriptase is illustrated in WO 201 1/120133 Al, published on October 6, 201 1, and US 201 1/0245296 Al, published on October 6, 201 1, both of which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety.
The process of the present invention offers greater efficiency, reduced waste, and lower cost of goods relative to the methods for making the subject compounds existing at the time of the invention. Particularly, the late stage cyanation and methylation steps are not required.
The following examples illustrate the invention. Unless specifically indicated otherwise, all reactants were either commercially available or can be made following procedures known in the art. The following abbreviations are used:
EXAMPLE 1
Step 1
1 2
3-(Chloromethyl)-l-(2-methoxypropan-2-yl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one (2): A
100 ml round bottom flask equipped with stir bar and a nitrogen inlet was charged with 1 (5 g, 33.9 mmol) and (lS)-(+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid (0.39 g, 1.694 mmol) at ambient temperature. After 2,2-dimethoxy propane (36.0 g, 339 mmol) was charged at ambient temperature, the resulting mixture was heated to 45°C. The resulting mixture was stirred under nitrogen at 45°C for 18 hours and monitored by HPLC for conversion of the starting material (< 5% by HPLC). After the reaction was completed, the batch was taken on to the next step without further workup or isolation. 'H NMR (CDCI3, 500 MHz): 4.45 (s, 2H), 3.35 (s, 3H), 3.21 (s, 3H), 1.83 (s, 6H).
Step 2
3-Fluoro-l-((l-(2-methoxypropan-2-yl)-4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3- yl)methyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2(lH)-one (3): A mixture of 2 (100 mg, 93.1% purity, 0.49 mmol), pyridone (1 17 mg, 97.6% purity, 0.49 mmol) and K2CO3 (82 mg, 0.59 mmol) in DMF (0.5 ml) was aged with stirring at ambient temperature for 3h. After the reaction was completed, the batch was taken on to the next step without further work up or isolation.
Step 3
3-Chloro-5-((l-((l-(2-methoxypropan-2-yl)-4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3- yl)methyl)-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile (4): To a mixture of compound 3 in DMF (reaction mixture from the previous step) was added 3-chloro-5- hydroxybenzonitrile (1.77 g, 1 1.5 mmol) at ambient temperature. The resulting mixture was then heated to 95-100°C and held for 20 hours.
Upon completion (typically 18-20 hours), the reaction was cooled to room temperature, diluted with ethyl acetate and washed with water. The aqueous cut was back extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layers were combined and then concentrated to an oil. MeOH (80 ml) was added and the resulting slurry was taken on to the next step. XH NMR (CDC13, 500 MHz): 7.60 (d, IH), 7.42 (s, IH), 7.23 (s, IH), 7.12 (s, IH), 6.56 (d, IH), 5.14 (s, 2H), 3.30 (s, 3H), 3.22 (s, 3H), 1.82 (s, 6H).
Step 4
4 5
3-Chloro-5-((l-((4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl)-2-oxo-4- (trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile (5): To a solution of 4 (5.74 g., 1 1.53 mmol) in MeOH (from previous step) was added concentrated hydrochloric acid (lml, 12.18 mmol) at ambient temperature. The resulting mixture was agitated for 1 hour at room temperature.
The resulting solids were collected by filtration and dried under a nitrogen sweep, providing 5 as a white solid (2.63 g, 46% yield): XH NMR (DMSO, 400 MHz): 1 1.74 (S, IH), 7.92 (d, IH), 7.76 (s, IH), 7.61 (s, IH), 7.54 (s, IH), 6.69 (d, IH), 5.15 (s, 2H), 3.10 (s, 3H)
EXAMPLE 2
Step 1
Phenyl methylcarbamate: 40% Aqueous methylamine (500 g, 6.44 mol) was charged to a 2 L vessel equipped with heat/cool jacket, overhead stirrer, temperature probe and nitrogen inlet. The solution was cooled to -5 °C. Phenyl chloroformate (500.0 g, 3.16 mol) was added over 2.5 h maintaining the reaction temperature between -5 and 0 °C. On complete addition the white slurry was stirred for lh at ~0 °C.
The slurry was filtered, washed with water (500 mL) and dried under 2 sweep overnight to afford 465g (96%> yield) of the desired product as a white crystalline solid; 1H NMR (CDCI3, 500 MHz): δ 7.35 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.19 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 4.95 (br s, 1H), 2.90 (d, J = 5 Hz, 3H).
Step 2
2-(2-Hydroxyacetyl)-N-methylhydrazinecarboxamide: Part A: Phenyl methylcarbamate (300 g, 1.95 mol) was charged to a 2 L vessel with cooling jacket, overhead stirrer, temperature probe, reflux condenser and nitrogen inlet. IPA (390 mL) was added at 23 °C. Hydrazine hydrate (119 g, 2.33 mol) was added and the slurry heated to 75 °C for 6 h.
Part B: On complete reaction (>99% conversion by HPLC), IPA (810 mL) and glycolic acid (222 g, 2.92 mol) were added and the mixture stirred at 83-85 °C for 10-12 h. The reaction mixture is initially a clear colorless solution. The mixture is seeded with product (0.5 g) after 4h at 83-85 °C. The slurry was slowly cooled to 20 °C over 2h and aged for lh.
The slurry was filtered and washed with IPA (600 mL). The cake was dried under 2 sweep to afford 241.8g (81% yield) of the desired product as a white crystalline solid: XH NMR (D20, 500 MHz): δ 4.11 (s, 2H), 2.60 (s, 3H).
Step 3
3-(Hydroxymethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one: 2-(2-Hydroxyacetyl)-N- methylhydrazinecarboxamide (130 g @ ~95wt%, 0.84 mol), w-propanol (130 mL) and water (130 mL) were charged to a 1 L vessel with jacket, overhead stirrer, temperature probe, reflux condenser and nitrogen inlet. Sodium hydroxide (pellets, 16.8 g, 0.42 mol) was added and the slurry warmed to reflux for 3h. The reaction mixture was cooled to 20 °C and the pH adjusted to 6.5 (+/- 0.5) using cone hydrochloric acid (28.3 mL, 0.34 mol). Water was azeotropically removed under vacuum at 40-50 °C by reducing the volume to -400 mL and maintaining that volume by the slow addition of n-propanol (780 mL). The final water content should be <3000 ug/mL. The resultant slurry (~ 400 mL) was cooled to 23 °C and heptane (390 ml) was added. The slurry was aged lh at 23 °C, cooled to 0 °C and aged 2h. The slurry was filtered, the cake washed with 1 :2 n-PrOH/heptane (100 mL) and dried to provide 125g (85% yield) of an off- white crystalline solid. The solid is ~73 wt% due to residual inorganics (NaCl): 'H NMR (CD3OD, 500 MHz): δ 3.30 (s, 3H), 4.46 (s, 2H).
Step 4
3-(Chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one (1): A mixture of 3- (Hydroxymethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one (54 g, at 73wt%, 307 mmol) in ethyl acetate (540 mL) was stirred at 45 °C. SOCI2 (26.9 mL, 369 mmol) was added over 30-45 min and aged at 50 °C for 2h. Monitor reaction progress by HPLC. On complete reaction (>99.5% by area at 210nm.), the warm suspension was filtered and the filter cake (mainly NaCl) was washed with ethyl acetate (108 mL). The combined filtrate and wash were concentrated at 50-60 °C under reduced pressure to approximately 150 mL. The resulting slurry was cooled to -10 °C and aged lh. The slurry was filtered and the filter cake washed with ethyl acetate (50 mL). The cake was dried under 2 sweep to afford 40. lg (86% yield) of the desired product as a bright yellow solid: 'H NMR (CD3OD, 500 MHz): δ 3.30 (s, 3H), 4.58 (s, 2H).
EXAMPLE 3
3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2(lH)-one (2): To a 250 ml round bottom flask equipped with overhead stirring and a nitrogen inlet was added a mixture of sulfuric acid (24.31 ml, 437 mmol) and water (20.00 ml). To this was added 2,3-difluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine (6.83 ml, 54.6 mmol) and the mixture was heated to 65 °C and stirred for 4 h. By this time the reaction was complete, and the mixture was cooled to room temperature. To the flask was slowly added 5M sodium hydroxide (43.7 ml, 218 mmol), maintaining room temperature with an ice bath. The title compound precipitates as a white solid during addition. Stirring was maintained for an additional lh after addition. At this time, the mixture was filtered, the filter cake washed with 20 mL water, and the resulting white solids dried under nitrogen. 3-fluoro-4- (trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2(lH)-one (2) was obtained as a white crystalline solid (9.4g, 51.9 mmol, 95 % yield): ¾ NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz): 12.97 (br s, 1H), 7.36 (d, 1H), 6.44 (m, 1H).
EXAMPLE 4
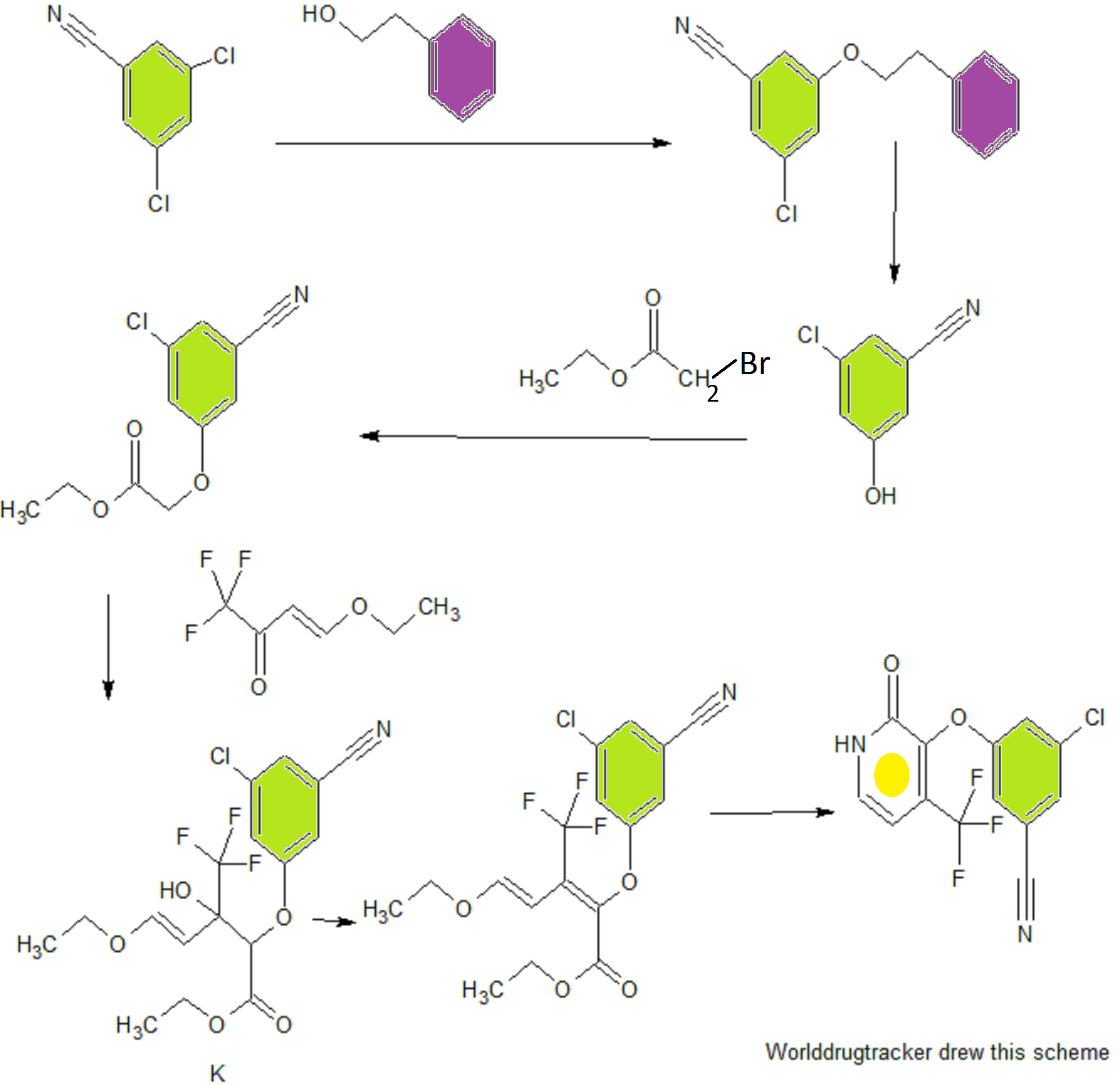
Step 1 - Ethyl Ester Synthesis Experimental Procedure;
Ethyl 2-(3-chloro-5-cyanophenoxy)acetate (A): A 1L round bottom flask equipped with overhead stirring was charged with 3-chloro-5-hydroxybenzonitrile (50.0 g, 98 wt% purity, 319 mmol) and 15% aqueous DMF (200 mL DMF + 35.5 mL FLO). To the resulting solution was added diisopropylethylamine (61.3 mL, 99.0% purity, 1.1 equiv) and ethyl 2-bromoacetate (35.7 g, 98% purity, 1.15 equiv) at ambient temperature. The resulting solution was warmed to 50°C under nitrogen and aged for 12 h. Upon completion of the reaction the batch was cooled to 0- 5°C. To the clear to slightly cloudy solution was added 5% seed (3.8g, 16.0 mmol). H20 (64.5mL) was added to the thin suspension via syringe pump over 3h while maintaining the temp at 0-5 °C. Additional FLO (200mL) was added over lh while maintaining the temp at 0-5 °C. The final DMF/FLO ratio is 1 : 1.5 (10 vol). The resulting slurry was typically aged lh at 0-5 °C. The batch was filtered and the cake slurry washed with 2: 1 DMF/water (150 mL, 3 vol), followed by water (200 mL, 4 vol). The wet cake was dried on the frit with suction under a nitrogen stream at 20-25 °C; note: heat must not be applied during drying as product mp is 42 °C. The cake is considered dry when H20 is <0.2%. Obtained 73.4 g ethyl ester as a light tan solid, 96% yield (corrected), 99.5 LCAP: XH NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz) δ = 7.29 (s, 1H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 7.06 (s, 1H), 4.67 (s, 2H), 4.32 (q, 2H), 1.35 (t, 3H) ppm. Step 2 - Pyridone Synthesis
Synthetic Scheme; batch
TEA, TFAA, 10 °C;
then MeOH, rt
[isolated solid, A] [PhMe exit stream, B]
[PhMe/MeOH solution, C] [PhMe/MeOH/NH3 solution, D] [isolated solid, E]
Experimental Procedures;
Aldol Condensation, Ester A to Diene C
(2E/Z,4E)-Ethyl 2-(3-chloro-5-cyanophenoxy)-5-ethoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)penta-2,4- dienoate (C): Ester A (25.01 g, 104.4 mmol, 1.00 equiv) was charged to toluene (113.43 g, 131 mL, 5.24 vol) and 4-ethoxy-l, l, l-trifluoro-3-buten-2-one (26.43 g, 157.2 mmol, 1.51 equiv) was added.
The flow reactor consisted of two feed solution inlets and an outlet to a receiving vessel. The flow reactor schematic is shown in Figure 1.
The ester solution was pumped to one flow reactor inlet. Potassium tert-pentoxide solution was pumped to the second reactor inlet. Trifluoroacetic anhydride was added continuously to the receiver vessel. Triethylamine was added continuously to the receiver vessel. The flow rates were: 13 mL/min ester solution, 7.8 mL/min potassium tert-pentoxide solution, 3.3 mL/min trifluoroacetic anhydride and 4.35 mL/min triethylamine.
Charged toluene (50 mL, 2 vol) and potassium trifluoroacetate (0.64 g, 4.21 mmol, 0.04 equiv) to the receiver vessel. The flow reactor was submerged in a -10 °C bath and the pumps were turned on. The batch temperature in the receiver vessel was maintained at 5 to 10 °C throughout the run using a dry ice/acetone bath. After 13.5 min the ester solution was consumed, the reactor was flushed with toluene (10 mL) and the pumps were turned off.
The resulting yellow slurry was warmed to room temperature and aged for 4.5 h. Charged methanol (160 mL) to afford a homogeneous solution which contained 81.20 area percent diene C by HPLC analysis.
The solution of diene C (573 mL) was used without purification in the subsequent reaction. Cyclization, Diene C to E
3-Chloro-5-((2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile (E): To a solution of diene C in PhMe/MeOH (573 mL; 40.69 g, 104.4 mmol theoretical C) was charged methanol (25 mL, 0.61 vol). Ammonia (32 g, 1.88 mol, 18 equiv based on theoretical C) was added and the solution was warmed to 60 °C. The reaction was aged at 60 °C for 18 h. The temperature was adjusted to 35-45 °C and the pressure was decreased maintain a productive distillation rate. The batch volume was reduced to -300 mL and methanol (325 mL, 8 vol) was charged in portions to maintain a batch volume between 250 and 350 mL. The heating was stopped and the system vented. The resulting slurry was cooled to room temperature and aged overnight.
The batch was filtered and the cake washed with methanol (3x, 45 mL). The wet cake was dried on the frit with suction under a nitrogen stream to afford 18.54 g of a white solid: XH NMR (DMSO-i/6, 500 MHz): δ 12.7 (br s, 1H), 7.73 (t, 1H, J= 1.5 Hz), 7.61-7.59 (m, 2H), 7.53 (t, 1H, J= 2.0 Hz), 6.48 (d, 1H, J= 7.0 Hz) ppm.
Step 3 - Chlorination, Alkylation and Isolation of 3-Chloro-5-({l-[(4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro- lH-l,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile
3-(Chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one: 3-(Hydroxymethyl)-4-methyl-lH- l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one (1.638 kg of 68wt%, 8.625 mol) and N-methylpyrrolidinone (8.9 L) was charged into a 30 L vessel. The suspension was aged for lOh at ambient temperature. The slurry was filtered through a 4L sintered glass funnel under 2 and the filter cake (mainly NaCl) was washed with NMP (2.23 L). The combined filtrate and wash had a water content of 5750 μg/mL. The solution was charged to a 75L flask equipped with a 2N NaOH scrubber to capture off-gasing vapors. Thionyl chloride (0.795 L, 10.89 mol) was added over lh and the temperature rose to 35 °C. HPLC analysis indicated that the reaction required an additional thionyl chloride charge (0.064 L, 0.878 mol) to bring to full conversion. The solution was warmed to 50 °C, placed under vacuum at 60 Torr (vented to a 2N NaOH scrubber), and gently sparged with subsurface N2 (4 L/min). The degassing continued for lOh until the sulfur dioxide content in the solution was <5 mg/mL as determined by quantitative GC/MS. The tan solution of 3-(chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one in NMP weighed 13.0 kg and was assayed at 9.63 wt% providing 1.256 kg (97% yield).
3-chloro-5-((l-((4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl)-2-oxo-4- (trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile: To a 75L flask was charged a 9.63wt% solution of 3-(chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one in NMP (1 1.6 kg, 7.55 mol), 3 -chloro-5 -((2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)- 1 ,2-dihydropyridin-3 -yl)oxy)benzonitrile (2.00 kg, 6.29 mol), NMP (3.8 L) and 2-methyl-2-butanol (6.0 L). To the resulting suspension was slowly added N,N-diisopropylethylamine (4.38 L, 25.2 mol) over 4h. The reaction was aged 18h at ambient temperature. The reaction is considered complete when HPLC indicates <1% 3 -chloro-5 -((2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile remaining. The tan solution was quenched with acetic acid (1.26 L, 22.0 mol) and aged at ambient temperature overnight. The tan solution was warmed to 70 °C. Water (2.52 L) was added and the batch was seed with anhydrate Form II (134 g). The thin suspension was aged lh at 70 °C. Additional water (14.3 L) was added evenly over 7 h. The slurry was aged 2h at 70 °C and then slowly cooled to 20 °C over 5 h. The slurry was filtered and washed with 2 : 1 NMP/water (6 L), followed by water washes (6 L x 2). The filter cake was dried over a 2 sweep to give 2.53 kg (85% yield - corrected) of a white solid that was confirmed to be crystalline Form II by X-ray powder detraction analysis.
PATENT
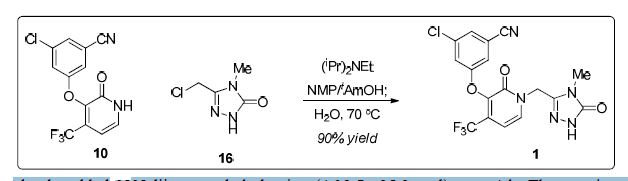
The following scheme is an example of Step 3A.

EXAMPLE 1

1
Step 1
c| 0. h CH3NH3 Me.NA0.Ph
H
Phenyl methylcarbamate: 40% Aqueous methylamine (500 g, 6.44 mol) was charged to a 2 L vessel equipped with heat/cool jacket, overhead stirrer, temperature probe and nitrogen inlet. The solution was cooled to -5 °C. Phenyl chloroformate (500.0 g, 3.16 mol) was added over 2.5 h maintaining the reaction temperature between -5 and 0 °C. On complete addition the white slurry was stirred for lh at ~0 °C.
The slurry was filtered, washed with water (500 mL) and dried under a nitrogen sweep overnight to afford 465g (96% yield) of the desired product as a white crystalline solid; XH NMR (CDCI3, 500 MHz): δ 7.35 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.19 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 4.95 (br s, 1H), 2.90 (d, J = 5 Hz, 3H).
Step 2

2-(2-Hydroxyacetyl)-N-methylhydrazinecarboxamide: Part A: Phenyl methylcarbamate (300 g, 1.95 mol) was charged to a 2 L vessel with cooling jacket, overhead stirrer, temperature probe, reflux condenser and nitrogen inlet. IPA (390 mL) was added at 23 °C. Hydrazine hydrate (119 g, 2.33 mol) was added and the slurry heated to 75 °C for 6 h.
Part B: On complete reaction (>99% conversion by HPLC), IPA (810 mL) and glycolic acid (222 g, 2.92 mol) were added and the mixture stirred at 83-85 °C for 10-12 h. The reaction mixture was initially a clear colorless solution. The mixture was seeded with product (0.5 g) after 4h at 83-85 °C. The slurry was slowly cooled to 20 °C over 2h and aged for lh. Seed was used to advance the crystallization, but the crystalline product can be precipitated and isolated without seed by allowing the solution to age at 83-85 °C for 4 hours.
The slurry was filtered and washed with IPA (600 mL). The cake was dried under a nitrogen sweep to afford 241.8g (81% yield) of the desired product as a white crystalline solid: XH NMR (D20, 500 MHz): δ 4.11 (s, 2H), 2.60 (s, 3H).
Step 3

3-(Hydroxymethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one: 2-(2-Hydroxyacetyl)-N-methylhydrazinecarboxamide (130 g @ ~95wt%, 0.84 mol), w-propanol (130 mL) and water (130 mL) were charged to a 1 L vessel with jacket, overhead stirrer, temperature probe, reflux condenser and nitrogen inlet. Sodium hydroxide (pellets, 16.8 g, 0.42 mol) was added and the slurry warmed to reflux for 3h. The reaction mixture was cooled to 20 °C and the pH adjusted to 6.5 (+/- 0.5) using concentrated hydrochloric acid (28.3 mL, 0.34 mol). Water was
azeotropically removed under vacuum at 40-50 °C by reducing the volume to -400 mL and maintaining that volume by the slow addition of n-propanol (780 mL). The final water content was <3000 ug/mL. The resultant slurry (~ 400 mL) was cooled to 23 °C and heptane (390 ml) was added. The slurry was aged lh at 23 °C, cooled to 0 °C and aged 2h. The slurry was filtered, the cake washed with 1 :2 n-PrOH/heptane (100 mL) and the filter cake was dried under a nitrogen sweep to provide 125g (85% yield) of an off-white crystalline solid. The solid was -73 wt% due to residual inorganics (NaCl): ¾ NMR (CD3OD, 500 MHz): δ 3.30 (s, 3H), 4.46 (s, 2H).
Step 4

3-(Chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one (1): A mixture of 3-(Hydroxymethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one (54 g, at 73wt%, 307 mmol) in ethyl acetate (540 mL) was stirred at 45 °C. SOCl2 (26.9 mL, 369 mmol) was added over 30-45 min and aged at 50 °C for 2h. The reaction progress was monitored by HPLC. On complete reaction (>99.5% by area at 210nm), the warm suspension was filtered and the filter cake (mainly NaCl) was washed with ethyl acetate (108 mL). The combined filtrate and wash were concentrated at 50-60 °C under reduced pressure to approximately 150 mL. The resulting slurry was cooled to - 10 °C and aged lh. The slurry was filtered and the filter cake washed with ethyl acetate (50 mL). The cake was dried under a nitrogen sweep to afford 40. lg (86% yield) of the desired product as a bright yellow solid: XH NMR (CD3OD, 500 MHz): δ 3.30 (s, 3H), 4.58 (s, 2H).
EXAMPLE 2



Step 1 - Ethyl Ester Synthesis
Experimental Procedure;

A
Ethyl 2-(3-chloro-5-cyanophenoxy)acetate (A): A 1L round bottom flask equipped with overhead stirring was charged with 3-chloro-5-hydroxybenzonitrile (50.0 g, 98 wt% purity, 319 mmol) and 15% aqueous DMF (200 mL DMF + 35.5 mL Η20). To the resulting solution was added diisopropylethylamine (61.3 mL, 99.0% purity, 1.1 equiv) and ethyl 2-bromoacetate (35.7 g, 98% purity, 1.15 equiv) at ambient temperature. The resulting solution was warmed to 50°C under nitrogen and aged for 12 h. Upon completion of the reaction the batch was cooled to 0-5°C. To the clear to slightly cloudy solution was added 5% seed (3.8g, 16.0 mmol). H20 (64.5mL) was added to the thin suspension via syringe pump over 3h while maintaining the temperature at 0-5 °C. Additional H20 (200mL) was added over lh while maintaining the temp at 0-5 °C. The final DMF/H20 ratio is 1 : 1.5. The resulting slurry was aged lh at 0-5 °C. The batch was filtered and the cake slurry washed with 2: 1 DMF/water (150 mL), followed by water (200 mL). The wet cake was dried on the frit with suction under a nitrogen stream at 20-25 °C. The cake is considered dry when H20 is <0.2%. Obtained 73.4 g ethyl ester as a light tan solid, 96% yield: XH NMR (CDC13, 400 MHz) δ = 7.29 (s, 1H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 7.06 (s, 1H), 4.67 (s, 2H), 4.32 (q, 2H), 1.35 (t, 3H) ppm. Seed was used to advance the crystallization, but the crystalline product can be precipitated and isolated without seed by allowing the solution to age at 0-5 °C for at least about 2 hours.
Step 2 - Pyridone Synthesis
Synthetic Scheme;

Experimental Procedures;
Aldol Condensation
(2E/Z,4E)-Ethyl 2-(3-chloro-5-cyanophenoxy)-5-ethoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)penta-2,4-dienoate (C): Ethyl 2-(3-chloro-5-cyanophenoxy)acetate (25.01 g, 104.4 mmol, 1.00 equiv) was charged to toluene (113.43 g, 131 mL) and 4-ethoxy-l, l,l-trifluoro-3-buten-2-one (26.43 g, 157.2 mmol, 1.51 equiv) was added.
The flow reactor consisted of two feed solution inlets and an outlet to a receiving vessel. The flow reactor schematic is shown in Figure 1.
The ester solution was pumped to one flow reactor inlet. Potassium tert-amylate solution was pumped to the second reactor inlet. Trifluoroacetic anhydride was added continuously to the receiver vessel. Triethylamine was added continuously to the receiver vessel.
The flow rates were: 13 mL/min ester solution, 7.8 mL/min potassium tert-amylate solution, 3.3 mL/min trifluoroacetic anhydride and 4.35 mL/min triethylamine.
Charged toluene (50 mL) and potassium trifluoroacetate (0.64 g, 4.21 mmol, 0.04 equiv) to the receiver vessel. The flow reactor was submerged in a -10 °C bath and the pumps were turned on. The batch temperature in the receiver vessel was maintained at 5 to 10 °C throughout the run using a dry ice/acetone bath. After 13.5 min the ester solution was consumed, the reactor was flushed with toluene (10 mL) and the pumps were turned off.
The resulting yellow slurry was warmed to room temperature and aged for 4.5 h. Charged methanol (160 mL) to afford a homogeneous solution which contained 81.20 LCAP diene .
The solution of diene (573 mL) was used without purification in the subsequent reaction.
Cyclization
3-Chloro-5-((2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile (E): To a solution of diene in PhMe/MeOH (573 mL; 40.69 g, 104.4 mmol theoretical) was charged methanol (25 mL). Ammonia (32 g, 1.88 mol, 18 equiv based on theoretical) was added and the solution was warmed to 60 °C. The reaction was aged at 60 °C for 18 h. The temperature was adjusted to 35-45 °C and the pressure was decreased to maintain a productive distillation rate. The batch volume was reduced to -300 mL and methanol (325 mL) was charged in portions to maintain a batch volume between 250 and 350 mL. The heating was stopped and the system vented. The resulting slurry was cooled to room temperature and aged overnight.
The batch was filtered and the cake washed with methanol (3x, 45 mL). The wet cake was dried on the frit with suction under a nitrogen stream to afford 18.54 g of a white solid: XH NMR (DMSO-ifc, 500 MHz): δ 12.7 (br s, 1H), 7.73 (t, 1H, J= 1.5 Hz), 7.61-7.59 (m, 2H), 7.53 (t, 1H, J= 2.0 Hz), 6.48 (d, 1H, J= 7.0 Hz) ppm.
Step 3 - Chlorination, Alkylation and Isolation of 3-Chloro-5-({l-[(4-methyl-5-oxo-' dihydro-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile

3-(Chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one: 3-(Hydroxymethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one (1.638 kg of 68wt%, 8.625 mol) and N-methylpyrrolidinone (8.9 L) was charged into a 30 L vessel. The suspension was aged for lOh at ambient temperature. The slurry was filtered through a 4L sintered glass funnel under 2 and the filter cake (mainly NaCl) was washed with NMP (2.23 L). The combined filtrate and wash had a water content of 5750 μg/mL. The solution was charged to a 75L flask equipped with a 2N NaOH scrubber to capture off-gasing vapors. Thionyl chloride (0.795 L, 10.89 mol) was added over lh and the temperature rose to 35 °C. HPLC analysis indicated that the reaction required an additional thionyl chloride charge (0.064 L, 0.878 mol) to bring to full conversion. The solution was warmed to 50 °C, placed under vacuum at 60 Torr (vented to a 2N NaOH scrubber), and gently sparged with subsurface nitrogen (4 L/min). The degassing continued for lOh until the sulfur dioxide content in the solution was <5 mg/mL as determined by quantitative GC/MS. The tan solution of 3-(chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one in NMP weighed 13.0 kg and was assayed at 9.63 wt% providing 1.256 kg (97% yield).
3-chloro-5-((l-((4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl)-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile: To a 75L flask was charged a 9.63wt% solution of 3-(chloromethyl)-4-methyl-lH-l,2,4-triazol-5(4H)-one in NMP (1 1.6 kg, 7.55 mol), 3-chloro-5-((2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile (2.00 kg, 6.29 mol), NMP (3.8 L) and 2-methyl-2-butanol (6.0 L). To the resulting suspension was slowly added N,N-diisopropylethylamine (4.38 L, 25.2 mol) over 4h. The reaction was aged 18h at ambient temperature. The reaction is considered complete when HPLC indicated <1% 3-chloro-5-((2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-l,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzonitrile remaining. The tan solution was quenched with acetic acid (1.26 L, 22.0 mol) and aged at ambient temperature overnight. The tan solution was warmed to 70 °C. Water (2.52 L) was added and the batch was seeded with anhydrate Form II (134 g)(procedures for making anhydrate Form II are described in WO2014/052171). The thin suspension was aged lh at 70 °C. Additional water (14.3 L) was added evenly over 7 h. The slurry was aged 2h at 70 °C and then slowly cooled to 20 °C over 5 h. The slurry was filtered and washed with 2 : 1 NMP/water (6 L), followed by water washes (6 L x 2). The filter cake was dried under N2 to give 2.53 kg (85% yield) of a white solid that was confirmed to be crystalline Form II of the title compound by X-ray powder detraction analysis.
EXAMPLE 3
Ethyl 2-(3-chloro-5-cyanophenoxy)acetate (A):


70%
Step 3
Three step one pot sequence
Steps 1 and 2:
To an oven dried 250mL round bottom flask was added sodium 2-methylpropan-2-olate (12.85 g, 134 mmol) and BHT (0.641 g, 2.91 mmol) then added DMF (30mL). After lOmin, a light yellow solution resulted. 2-Phenylethanol (7.66 ml, 63.9 mmol) was added and the solution exothermed to 35 °C. The light yellow solution was warmed to 55 °C and then a solution of 3,5-dichlorobenzonitrile (10 g, 58.1 mmol) in DMF (15mL) was added over 2h via syringe pump. The resulting red-orange suspension was aged at 55-60 °C. After 2h, HPLC showed >98% conversion to the sodium phenolate.
Step 3:
The suspension was cooled to 10 °C, then ethyl 2-bromoacetate (8.70 ml, 78 mmol) was added over lh while maintaining the temperature <20 °C. The resulting mixture was aged at ambient temperature. After lh, HPLC showed >99% conversion to the title compound.
Work-up and isolation:
To the suspension was added MTBE (50mL) and H20 (50mL) and the layers were separated. The organic layer was washed with 20% aq brine (25mL). The organic layer was assayed at 12.5g (90% yield). The organic layer was concentrated to -38 mL, diluted with hexanes (12.5mL) and then cooled to 5 °C. The solution was seeded with 0.28g (2 wt%) of crystalline ethyl 2-(3-chloro-5-cyanophenoxy)acetate and aged 0.5h at 5 °C to give a free flowing slurry. Hexane (175mL) was added to the slurry over lh at 0-5 °C. The slurry was filtered at 0-5 °C, washed with hexane (50 mL) and dried under a nitrogen sweep to give 9.8g (70% yield) of the title compound as a white crystalline solid. Seed was used to advance the crystallization, but the crystalline product can be precipitated and isolated without seed by allowing the solution to age at 0-5 °C for at least about 2 hours.
Paper
Discovery of MK-1439, an orally bioavailable non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor potent against a wide range of resistant mutant HIV viruses
Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2014, 24(3): 917
Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2014, 24(3): 917
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960894X13014546
The optimization of a novel series of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI) led to the identification of pyridone 36. In cell cultures, this new NNRTI shows a superior potency profile against a range of wild type and clinically relevant, resistant mutant HIV viruses. The overall favorable preclinical pharmacokinetic profile of 36 led to the prediction of a once daily low dose regimen in human. NNRTI 36, now known as MK-1439, is currently in clinical development for the treatment of HIV infection.


Scheme 1.
Reagents and conditions: (a) K2CO3, NMP, 120 °C; (b) KOH, tert-BuOH, 75 °C; (c) Zn(CN)2, Pd(PPh3)4, DMF, 100 °C.
Scheme 3.
Reagents and conditions: (a) K2CO3, DMF, −10 °C; (b) MeI or EtI, K2CO3, DMF.
36 IS DORAVIRINE
PATENT
WO 2011120133
http://www.google.com/patents/WO2011120133A1?cl=en
Scheme I depicts a method for preparing compounds of Formula I in which hydroxypyridine 1-1 is alkylated with chlorotriazolinone 1-2 to provide 1-3 which can be selectively alkylated with an alkyl halide (e.g., methyl iodide, ethyl iodide, etc.) to afford the desired 1-4. Scheme I
Scheme II depicts an alternative route to compounds of the present invention, wherein fluorohydroxypyridine II-l can be alkylated with chlorotriazolinone II-2 to provide the alkylated product II-3 which can be converted to the desired II-5 via nucleophilic aromatic substitution (S] fAr) using a suitable hydroxyarene II-4.
Scheme II
Hydroxypyridines of formula I-l (Scheme 1) can be prepared in accordance with Scheme III, wherein a SNAr reaction between pyridine III-l (such as commercially available 2- chloro-3-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine) and hydroxyarene H-4 can provide chloropyridine III-2, which can be hydrolyzed under basic conditions to the hydroxypyridine I-l. Scheme III
Another method for preparing hydroxypyridines of formula I-l is exemplified in Scheme IV, wherein S Ar coupling of commercially available 2-chloro-3-fluoro-4- nitropyridone-N-oxide IV-1 with a suitable hydroxyarene II-4 provides N-oxide IV-2, which can first be converted to dihalides IV-3 and then hydro lyzed to hydroxypyridine IV-4. Further derivatization of hydroxypyridine IV-4 is possible through transition metal-catalyzed coupling processes, such as Stille or boronic acid couplings using a PdLn catalyst (wherein L is a ligand such as triphenylphosphine, tri-tert-butylphosphine or xantphos) to form hydroxypyridines IV-5, or amination chemistry to form hydroxypyridines IV-6 in which R2 is N(RA)RB.
Scheme IV
IV-1
- - Scheme V depicts the introduction of substitution at the five-position of the hydroxypyridines via bromination, and subsequent transition metal-catalyzed chemistries, such as Stille or boronic acid couplings using PdLn in which L is as defined in Scheme IV to form hydroxypyridines V-3, or amination chemistry to form hydroxypyridines V-4 in which R3 is N(RA)RB.
Scheme V
As shown in Scheme IV, fiuorohydroxypyridines II-l (Scheme II) are available from the commercially available 3-fluoroypridines VI- 1 through N-oxide formation and rearrangement as described in Konno et al., Heterocycles 1986, vol. 24, p. 2169.
Scheme VI
The following examples serve only to illustrate the invention and its practice. The examples are not to be construed as limitations on the scope or spirit of the invention.
The term "room temperature" in the examples refers to the ambient temperature which was typically in the range of about 20°C to about 26°C.
EXAMPLE 1
3-Chloro-5-({ l-[(4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l ,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-2-oxo-4- (trifluoromethyl)-l ,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile (1-1)
Step 1(a):
A mixture of the 3-bromo-5-chlorophenol (3.74 g; 18.0 mmol), 2-chloro-3-fluoro- 4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine (3.00 g; 15.0 mmol) and 2CO3 (2.49 g; 18.0 mmol) in NMP (15 mL) was heated to 120°C for one hour, then cooled to room temperature. The mixture was then diluted with 250 mL EtOAc and washed with 3 x 250 mL 1 :1 H20:brine. The organic extracts were dried (Na2S04) and concentrated in vacuo. Purification by ISCO CombiFlash (120 g column; load with toluene; 100:0 to 0:100 hexanes:CH2Cl2 over 40 minutes) provided title compound (1-2) as a white solid. Repurification of the mixed fractions provided additional title compound. lH NMR (400 MHz, CDCI3): δ 8.55 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1 H); 7.64 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1 H);
7.30 (s, 1 H); 6.88 (s, 1 H); 6.77 (s, 1 H).
3-(3-bromo-5-chlorophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-ol (1-3)
To a suspension of 3-(3-bromo-5-chlorophenoxy)-2-chloro-4- (trifluoromethyl)pyridine (1-2; 3.48 g; 8.99 mmol) in lBuOH (36 mL) was added KOH (1.51 g; 27.0 mmol) and the mixture was heated to 75°C overnight, at which point a yellow oily solid had precipitated from solution, and LCMS analysis indicated complete conversion. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, and neutralized by the addition of -50 mL saturated aqueous NH4CI. The mixture was diluted with 50 mL H2O, then extracted with 2 x 100 mL EtOAc. The combined organic extracts were dried (Na2S04) and concentrated in vacuo. Purification by ISCO CombiFlash (120 g column; dry load; 100:0 to 90: 10 CH2Cl2:MeOH over 40 minutes) provided the title compound (1-3) as a fluffy white solid. lH NMR (400 MHz, DMSO): δ 12.69 (s, 1 H); 7.59 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1 H); 7.43 (t, J = 1.7 Hz, 1 H); 7.20 (t, J = 1.9 Hz, 1 H); 7.13 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1 H); 6.48 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1 H).
3-chloro-5-{[2-hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]oxy}benzonitrile (1-4)
To a suspension of 3-(3-bromo-5-chlorophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-ol (1-3; 3.25 g; 8.82 mmol) in NMP (29 mL) was added CuCN (7.90 g; 88 mmol) and the mixture was heated to 175°C for 5 hours, then cooled to room temperature slowly. With increased fumehood ventilation, 100 mL glacial AcOH was added, then 100 mL EtOAc and the mixture was filtered through Celite (EtOAc rinse). The filtrate was washed with 3 x 200 mL 1 : 1 H20:brine, then the organic extracts were dried (Na2S04) and concentrated in vacuo.
Purification by ISCO CombiFlash (120 g column; dry load; 100:0 to 90:10 CH2Cl2:MeOH over 40 minutes), then trituration of the derived solid with Et20 (to remove residual NMP which had co-eluted with the product) provided the title compound (1-4). lH NMR (400 MHz, DMSO): δ 12.71 (s, 1 H); 7.75 (s, 1 H); 7.63-7.57 (m, 2 H); 7.54 (s, 1 H); 6.49 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1 H).
Step 1(d): 5-(chloromethyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-l,2,4-triazol-3-one (1-5)
The title compound was prepared as described in the literature: Cowden, C. J.; Wilson, R. D.; Bishop, B. C; Cottrell, I. F.; Davies, A. J.; Dolling, U.-H. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 47, 8661.
3 -chloro-5 -( { 2-oxo- 1 - [(5 -oxo-4,5 -dihydro- 1 H- 1 ,2,4-triazol-3 -yl)methyl] - 4- (trifiuoromethyl)- 1 ,2-dihydropyridin-3 -yl } oxy)benzonitrile (1-6)
A suspension of the 3-chloro-5-{[2-hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3- yl]oxy}benzonitrile (1-4; 2.00 g; 6.36 mmol), 5-(chloromethyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-l,2,4-triazol-3- one (1-5; 0.849 g; 6.36 mmol) and K2CO3 (0.878 g; 6.36 mmol) in DMF (32 mL) was stirred for 2 hours at room temperature, at which point LCMS analysis indicated complete conversion. The mixture was diluted with 200 mL Me-THF and washed with 150 mL 1 : 1 : 1 H20:brine:saturated aqueous NH4CI, then further washed with 2 x 150 mL 1 : 1 H20:brine. The aqueous fractions were further extracted with 150 mL Me-THF, then the combined organic extracts were dried (Na2S04) and concentrated in vacuo. Purification by ISCO CombiFlash (80 g column; dry load; 100:0 to 90:10 EtOAc:EtOH over 25 minutes) provided the title compound (1-6) as a white solid. lH NMR (400 MHz, DMSO): δ 1 1.46 (s, 1 H); 1 1.39 (s, 1 H); 7.93 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H); 7.76 (s, 1 H); 7.58 (s, 1 H); 7.51 (s, 1 H); 6.67 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H); 5.02 (s, 2 H).
Step 1(f): 3 -chloro-5 -( { 1 - [(4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5 -dihydro- 1 H- 1 ,2,4-triazol-3 -yl)methyl] -2- oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)- 1 ,2-dihydropyridin-3 -yl } oxy)benzonitrile (1 -1 )
A solution of 3-chloro-5-({2-oxo-l -[(5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l,2,4-triazol-3- yl)methyl]- 4-(trifluoromethyl)-l ,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile (1-6; 2.37 g; 5.76 mmol) and K2CO3 (0.796 g; 5.76 mmol) in DMF (58 mL) was cooled to 0°C, then methyl iodide (0.360 mL; 5.76 mmol) was added. The mixture was allowed to warm to room
temperature, and stirred for 90 minutes, at which point LCMS analysis indicated >95%
conversion, and the desired product of -75% LCAP purity, with the remainder being unreacted starting material and 6/s-methylation products. The mixture was diluted with 200 mL Me-THF, and washed with 3 x 200 mL 1 : 1 H20:brine. The aqueous fractions were further extracted with 200 mL Me-THF, then the combined organic extracts were dried (Na2S04) and concentrated in vacuo. The resulting white solid was first triturated with 100 mL EtOAc, then with 50 mL THF, which provided (after drying) the title compound (1-1) of >95% LCAP. Purification to >99% LCAP is possible using Prep LCMS (Max-RP, 100 x 30 mm column; 30-60% CH3CN in 0.6% aqueous HCOOH over 8.3 min; 25 mL/min). lH NMR (400 MHz, DMSO): δ 1 1.69 (s, 1 H); 7.88 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H); 7.75 (s, 1 H); 7.62 (s, 1 H); 7.54 (s, 1 H); 6.67 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H); 5.17 (s, 2 H); 3.1 1 (s, 3 H). EXAMPLE 1A
3-Chloro-5-({ l-[(4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-lH-l ,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-2- (trifluoromethyl)-l ,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl}oxy)benzonitrile (1-1)
Step lA(a): 2-chloro-3-(3-chloro-5-iodophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine (1A-2)
A mixture of the 3-chloro-l-iodophenol (208 g; 816.0 mmol), 2-chloro-3-fluoro-
4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine (155 g; 777.0 mmol) and K2CO3 (161 g; 1 165.0 mmol) in NMP (1.5 L) was held at 60°C for 2.5 hours, and then left at room temperature for 2 days. The mixture was then re-heated to 60°C for 3 hours, then cooled to room temperature. The mixture was then diluted with 4 L EtOAc and washed with 2 L water + 1 L brine. The combined organics were then washed 2x with 500 mL half brine then 500 mL brine, dried over MgS04 and concentrated to afford crude 1A-2. lH NMR (500 MHz, DMSO) δ 8.67 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.98 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1 H), 7.63-7.62 (m, 1 H), 7.42-7.40 (m, 1 H), 7.22 (t, J = 2.1 Hz, 1 H).
Step lA(b): 2-chloro-3-(3-chloro-5-iodophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine (1A-3)
To a suspension of 3-(3-chloro-5-iodophenoxy)-2-chloro-4- (trifluoromethyl)pyridine (1A-2; 421 g, 970 mmol) in t-BuOH (1 L) was added KOH (272 g, 4850 mmol) and the mixture was heated to 75°C for 1 hour, at which point HPLC analysis indicated >95% conversion. The t-BuOH was evaporated and the mixture diluted with water (7mL/g, 2.4L) and then cooled to 0°C, after which 12N HC1 (~240mL) was added until pH 5. This mixture was then extracted with EtOAc (20mL/g, 6.5L), back extracted with EtOAc 1 x 5mL/g (1.5L), washed 1 x water:brine 1 : 1 (l OmL/g, 3.2L), 1 x brine (lOmL/g, 3.2L), dried over MgS04, filtered and concentrated to afford a crude proudct. The crude product was suspended in MTBE (2.25 L, 7mL/g), after which hexanes (1 L, 3 mL/g) was added to the suspension over ten minutes, and the mixturen was aged 30minutes at room temperature. The product was filtered on a Buchner, rinsed with MTBE hexanes 1 :2 (2 mL/g = 640 mL), then hexanes
(640mL), and dried on frit to afford 1A-3. lH NMR (400 MHz, acetone-d6): δ 11.52 (s, 1 H); 7.63 (d, J = 7.01 Hz, 1 H); 7.50-7.48 (m, 1 H); 7.34-7.32 (m, 1 H); 7.09-7.07 (m, 1 H); 6.48 (d, J = 7.01 Hz, 1 H).
Step lA(c): 3-chloro-5-{[2-hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl]oxy}benzonitrile (1-4)
A solution of 3-(3-chloro-5-iodophenoxy)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-ol (1A-3; 190 g; 457 mmol) in DMF (914 mL) was degassed for 20 minutes by bubbling N2, after which CuCN (73.7 g; 823 mmol) was added, and then the mixture was degassed an additional 5 minutes. The mixture was then heated to 120°C for 17 hours, then cooled to room temperature and partitioned between 6 L MeTHF and 2 L ammonium buffer (4:3: 1 = NH4CI
sat/water/NH-iOH 30%). The organic layer washed with 2 L buffer, 1 L buffer and 1 L brine then, dried over MgS04 and concentrated. The crude solid was then stirred in 2.2 L of refluxing
MeCN for 45 minutes, then cooled in a bath to room temperature over 1 hour, aged 30 minutes, then filtered and rinsed with cold MeCN (2 x 400mL). The solid was dried on frit under N2 atm for 60 hours to afford title compound 1-4. lH NMR (400 MHz, DMSO): δ 12.71 (s, 1 H); 7.75 (s, 1 H); 7.63-7.57 (m, 2 H); 7.54 (s, 1 H); 6.49 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1 H).
Steps lA(d) and lA(e)
The title compound 1-1 was then prepared from compound 1-4 using procedures similar to those described in Steps 1(d) and 1(e) set forth above in Example 1.
Patent
WO-2014052171
Crystalline anhydrous Form II of doravirine, useful for the treatment of HIV-1 and HIV-2 infections. The compound was originally claimed in WO2008076223. Also see WO2011120133. Merck & Co is developing doravirine (MK-1439), for the oral tablet treatment of HIV-1 infection. As of April 2014, the drug is in Phase 2 trials.
CLIPS
The next-generation non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) doravirine (formerly MK-1439) showed potent antiretroviral activity and good tolerability in combination with tenofovir/FTC (the drugs in Truvada) in a dose-finding study presented at the 21st Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) last week in Boston.
NNRTIs are generally well tolerated and well suited for first-line HIV treatment, but as a class they are susceptible to resistance. Pre-clinical studies showed that Merck's doravirine has a distinct resistance profile and remains active against HIV with common NNRTI resistance mutations including K103N and Y181C.
As reported at last year's CROI, doravirine reduced HIV viral load by about 1.3 log in a seven-day monotherapy study. Doravirine is processed by the CYP3A4 enzyme, but it is neither a CYP3A4 inducer nor inhibitor, so it is not expected to have major drug interaction concerns.
Javier Morales-Ramirez from Clinical Research Puerto Rico reported late-breaking findings from a phase 2b study evaluating the safety and efficacy of various doses of doravirine versus efavirenz (Sustiva) for initial antiretroviral therapy.
This study included 208 treatment-naive people living with HIV from North America, Europe and Asia. More than 90% were men, 74% were white, 20% were black and the median age was 35 years. At baseline, the median CD4 cell count was approximately 375 cells/mm3 and 13% had received an AIDS diagnosis. Study participants were stratified by whether their viral load was above (about 30%) or below 100,000 copies/ml; median HIV RNA was approximately 4.5 log10.
Morales-Ramirez reported 24-week results from part 1 of the study, which will continue for a total of 96 weeks. In this part, participants were randomly allocated into five equal-sized arms receiving doravirine at doses of 25, 50, 100 or 200mg once daily, or else efavirenz once daily, all in combination with tenofovir/FTC.
At 24 weeks, 76.4% of participants taking doravirine had viral load below 40 copies/ml compared with 64.3% of people taking efavirenz. Response rates were similar across doravirine doses (25mg: 80.0%; 50mg: 76.2%; 100mg: 71.4%; 200mg: 78.0%). More than 80% of participants in all treatment arms reached the less stringent virological response threshold of <200 copies/ml.
Both doravirine and efavirenz worked better for people with lower pre-treatment viral load in an ad hoc analysis. For people with <100,000 copies/ml at baseline, response rates (<40 copies/ml) ranged from 83 to 89% with doravirine compared with 74% with efavirenz. For those with >100,000 copies/ml, response rates ranged from 50 to 91% with doravirine vs 54% with efavirenz.
Median CD4 cell gains were 137 cells/mm3 for all doravirine arms combined and 121 cells/mm3 for the efavirenz arm.
Doravirine was generally safe and well tolerated. People taking doravirine were less than half as likely as people taking efavirenz to experience serious adverse events (3.0% across all doravirine arms vs 7.1% with efavirenz) or to stop treatment for this reason (2.4 vs 4.8%). Four people taking doravirine and two people taking efavirenz discontinued due to adverse events considered to be drug-related.
The most common side-effects were dizziness (3.6% with doravirine vs 23.8% with efavirenz), abnormal dreams (9.0 vs 7.1%), diarrhoea (4.8 vs 9.5%), nausea (7.8 vs 2.4%) and fatigue (6.6 vs 4.8%). Other central nervous system (CNS) adverse events of interest included insomnia (5.4 vs 7.1%), nightmares (1.2 vs 9.5%) and hallucinations (0.6 vs 2.4%). Overall, 20.5% of people taking doravirine reported at least one CNS side-effect, compared with 33.3% of people taking efavirenz.
People taking doravirine had more favourable lipid profiles and less frequent liver enzyme (ALT and AST) elevations compared with people taking efavirenz.
The researchers concluded that doravirine demonstrated potent antiretroviral activity in treatment-naive patients, a favourable safety and tolerability profile, and fewer drug-related adverse events compared with efavirenz.
Based on these findings, the 100mg once-daily dose was selected for future development and will be used in part 2 of this study, a dose-confirmation analysis that will enrol an additional 120 participants.
In the discussion following the presentation, Daniel Kuritzkes from Harvard Medical School noted that sometimes it takes longer for viral load to go down in people who start with a high level, so with further follow-up past 24 weeks doravirine may no longer look less effective in such individuals.
NNRTIs are generally well tolerated and well suited for first-line HIV treatment, but as a class they are susceptible to resistance. Pre-clinical studies showed that Merck's doravirine has a distinct resistance profile and remains active against HIV with common NNRTI resistance mutations including K103N and Y181C.
As reported at last year's CROI, doravirine reduced HIV viral load by about 1.3 log in a seven-day monotherapy study. Doravirine is processed by the CYP3A4 enzyme, but it is neither a CYP3A4 inducer nor inhibitor, so it is not expected to have major drug interaction concerns.
Javier Morales-Ramirez from Clinical Research Puerto Rico reported late-breaking findings from a phase 2b study evaluating the safety and efficacy of various doses of doravirine versus efavirenz (Sustiva) for initial antiretroviral therapy.
This study included 208 treatment-naive people living with HIV from North America, Europe and Asia. More than 90% were men, 74% were white, 20% were black and the median age was 35 years. At baseline, the median CD4 cell count was approximately 375 cells/mm3 and 13% had received an AIDS diagnosis. Study participants were stratified by whether their viral load was above (about 30%) or below 100,000 copies/ml; median HIV RNA was approximately 4.5 log10.
Morales-Ramirez reported 24-week results from part 1 of the study, which will continue for a total of 96 weeks. In this part, participants were randomly allocated into five equal-sized arms receiving doravirine at doses of 25, 50, 100 or 200mg once daily, or else efavirenz once daily, all in combination with tenofovir/FTC.
At 24 weeks, 76.4% of participants taking doravirine had viral load below 40 copies/ml compared with 64.3% of people taking efavirenz. Response rates were similar across doravirine doses (25mg: 80.0%; 50mg: 76.2%; 100mg: 71.4%; 200mg: 78.0%). More than 80% of participants in all treatment arms reached the less stringent virological response threshold of <200 copies/ml.
Both doravirine and efavirenz worked better for people with lower pre-treatment viral load in an ad hoc analysis. For people with <100,000 copies/ml at baseline, response rates (<40 copies/ml) ranged from 83 to 89% with doravirine compared with 74% with efavirenz. For those with >100,000 copies/ml, response rates ranged from 50 to 91% with doravirine vs 54% with efavirenz.
Median CD4 cell gains were 137 cells/mm3 for all doravirine arms combined and 121 cells/mm3 for the efavirenz arm.
Doravirine was generally safe and well tolerated. People taking doravirine were less than half as likely as people taking efavirenz to experience serious adverse events (3.0% across all doravirine arms vs 7.1% with efavirenz) or to stop treatment for this reason (2.4 vs 4.8%). Four people taking doravirine and two people taking efavirenz discontinued due to adverse events considered to be drug-related.
The most common side-effects were dizziness (3.6% with doravirine vs 23.8% with efavirenz), abnormal dreams (9.0 vs 7.1%), diarrhoea (4.8 vs 9.5%), nausea (7.8 vs 2.4%) and fatigue (6.6 vs 4.8%). Other central nervous system (CNS) adverse events of interest included insomnia (5.4 vs 7.1%), nightmares (1.2 vs 9.5%) and hallucinations (0.6 vs 2.4%). Overall, 20.5% of people taking doravirine reported at least one CNS side-effect, compared with 33.3% of people taking efavirenz.
People taking doravirine had more favourable lipid profiles and less frequent liver enzyme (ALT and AST) elevations compared with people taking efavirenz.
The researchers concluded that doravirine demonstrated potent antiretroviral activity in treatment-naive patients, a favourable safety and tolerability profile, and fewer drug-related adverse events compared with efavirenz.
Based on these findings, the 100mg once-daily dose was selected for future development and will be used in part 2 of this study, a dose-confirmation analysis that will enrol an additional 120 participants.
In the discussion following the presentation, Daniel Kuritzkes from Harvard Medical School noted that sometimes it takes longer for viral load to go down in people who start with a high level, so with further follow-up past 24 weeks doravirine may no longer look less effective in such individuals.
Reference
Morales-Ramirez J et al. Safety and antiviral effect of MK-1439, a novel NNRTI (+FTC/TDF) in ART-naive HIV-infected patients. 21st Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, Boston, abstract 92LB, 2014.
Merck Moves Doravirine Into Phase 3 Clinical Trials
Wednesday Mar 19 | Posted by: roboblogger | Full story: EDGE
Earlier this month, at the 21st Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections , Merck indicated plans to initiate a Phase 3 clinical trial program for doravirine in combination with ARV therapy in the second half of 2014.
PAPER
A Robust Kilo-Scale Synthesis of Doravirine
† Process Research and Development, Merck Research Laboratories, 126 E. Lincoln Ave., Rahway, New Jersey 07065,United States
‡ Process Research and Development, Merck Frosst Center for Therapeutic Research, 16711 Trans Canada Highway, Kirkland, Quebec H9H 3L1, Canada
∥ WuXi AppTec Co., Ltd., No. 1 Building, No. 288 FuTe ZhongLu, WaiGaoQiao Free Trade Zone, Shanghai 200131, China
Org. Process Res. Dev., Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00163, http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00163
*E-mail: louis-charles_campeau@merck.com.

Doravirine is non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) currently in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of HIV infection. Herein we describe a robust kilo-scale synthesis for its manufacture. The structure and origin of major impurities were determined and their downstream fate-and-purge studied. This resulted in a redesign of the route to introduce the key nitrile functionality via a copper mediated cyanation which allowed all impurities to be controlled to an acceptable level. The improved synthesis was scaled to prepare ∼100 kg batches of doravirine to supply all preclinical and clinical studies up to phase III. The synthesis affords high-quality material in a longest linear sequence of six steps and 37% overall yield.
PAPER
Highly Efficient Synthesis of HIV NNRTI Doravirine
Department of Process Chemistry, Merck & Co., Inc., P.O. Box 2000, Rahway, New Jersey 07065, United States
Org. Lett., 2015, 17 (6), pp 1353–1356
DOI: 10.1021/ol503625z
Publication Date (Web): March 09, 2015
Copyright © 2015 American Chemical Society
*E-mail: donald_gauthier@merck.com., *E-mail: benjamin_sherry@merck.com.
Gauthier, D. R., Jr.; Sherry, B. D.; Cao, Y.; Journet, M.; Humphrey, G.; Itoh, T.; Mangion, I.; Tschaen, D. M.Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1353, DOI: 10.1021/ol503625z...........http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/ol503625z

The development of an efficient and robust process for the production of HIV NNRTI doravirine is described. The synthesis features a continuous aldol reaction as part of a de novo synthesis of the key pyridone fragment. Conditions for the continuous flow aldol reaction were derived using microbatch snapshots of the flow process.
Doravirine (1). A 75 L flask was charged a 9.63 wt% solution of 16 in NMP (11.6kg, 7.55 mol). Charged 10(2.00 kg, 6.29 mol), NMP
(3.8 L) and 2-methyl-2-butanol (6.0 L). To theresulting suspension was slowly added N,N-diisopropylethylamine (4.38 L, 25.2 mol) over 4 h. The reaction was aged for 18 h at ambient temperature. The tan solution was quenched with acetic acid (1.26 L, 22.0 mol) and aged at ambient temperature overnight. The tan solution was warmed to 70 °C. Water (2.52 L) was added and the batch was seeded with crystalline 1 (134 g) to induce crystallization. The thin suspension was aged 1 h at 70 °C. Additional water (14.3 L)
was added over 7 h. The slurry was aged for 2 h at 70 °C and slowly cooled to 20 °C over 5 h. The slurry was filtered and washed with 2:1 NMP/water (6 L), followed by water (6 L x 2). The filter cake was dried under nitrogen to give 2.53 kg (85% yield) of 1 as a white solid.
(3.8 L) and 2-methyl-2-butanol (6.0 L). To theresulting suspension was slowly added N,N-diisopropylethylamine (4.38 L, 25.2 mol) over 4 h. The reaction was aged for 18 h at ambient temperature. The tan solution was quenched with acetic acid (1.26 L, 22.0 mol) and aged at ambient temperature overnight. The tan solution was warmed to 70 °C. Water (2.52 L) was added and the batch was seeded with crystalline 1 (134 g) to induce crystallization. The thin suspension was aged 1 h at 70 °C. Additional water (14.3 L)
was added over 7 h. The slurry was aged for 2 h at 70 °C and slowly cooled to 20 °C over 5 h. The slurry was filtered and washed with 2:1 NMP/water (6 L), followed by water (6 L x 2). The filter cake was dried under nitrogen to give 2.53 kg (85% yield) of 1 as a white solid.
Characterization Data : 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 500 MHz): δ 3.11 (s,3H), 5.17 (s, 2H), 6.66 (d, 1H, J = 7.4 Hz), 7.52 (m, 1H), 7.61 (dd, 1H, J = 2.4, 1.3 Hz), 7.74 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 1.4Hz), 7.89 (d, 1H, J = 7.4 Hz), 11.68 (s, 1H) ppm.
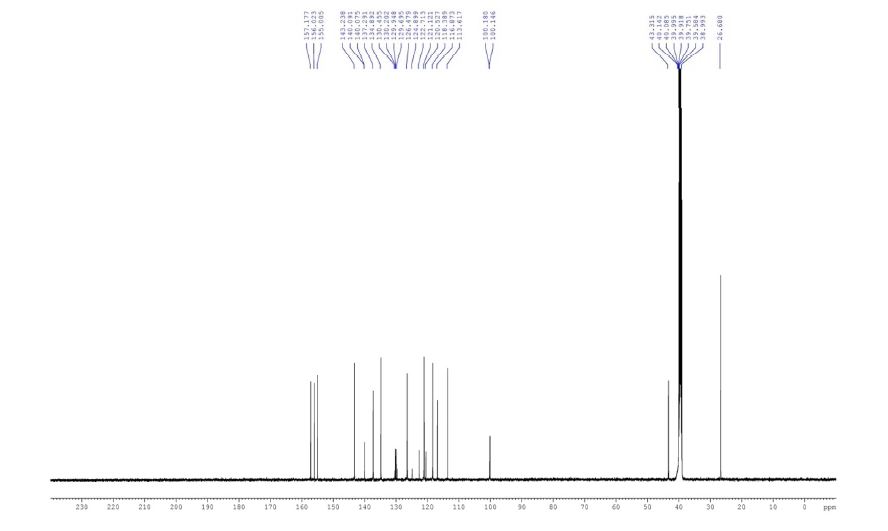
13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 125.7 MHz): δ 26.7, 43.3, 100.2, 113.6,116.8, 118.4, 121.1, 121.6, 126.5, 129.9, 134.9, 137.3, 140.1, 143.2, 155.0, 156.0, 157.2 ppm.
19F NMR (DMSO-d6,470.5 MHz): δ -62.3 ppm.
HMRS (ESI) calcd for C17H12N5O3F3Cl [M+H]+ 426.0581, found 426.0588.
13C NMR
1H NMR
| US20100034813 * | 8 Nov 2007 | 11 Feb 2010 | Yi Xia | Substituted pyrazole and triazole compounds as ksp inhibitors |
| US20100256181 * | 14 Nov 2008 | 7 Oct 2010 | Tucker Thomas J | Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors |
| US20110245296 * | 6 Oct 2011 | Jason Burch | Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors |
| Reference | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | * | COWDEN ET AL.: "A new synthesis of 1,2,4-triazolin-5-ones: application to the convergent synthesis of an NK1 antagonist.", TETRAHEDRON LETTERS, vol. 41, no. 44, 2000, pages 8661 - 8664, XP004236142 |
| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2015329521 | 2015-11-19 | PROCESS FOR MAKING REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE INHIBITORS |
| US9150539 | 2015-10-06 | Crystalline form of a reverse transcriptase inhibitor |
| US2015232447 | 2015-08-20 | CRYSTALLINE FORM OF A REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE INHIBITOR |
| US2013296382 | 2013-11-07 | NON-NUCLEOSIDE REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE INHIBITORS |
| US2011245296 | 2011-10-06 | NON-NUCLEOSIDE REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE INHIBITORS |
References
- Collins, Simon; Horn, Tim. "The Antiretroviral Pipeline." (PDF). Pipeline Report. p. 10. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- Safety and Antiviral Activity of MK-1439, a Novel NNRTI, in Treatment-naïve HIV+ Patients. Gathe, Joseph et al. 20th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections. 3–6 March 2013. Abstract 100.
- CROI 2013: MK-1439, a Novel HIV NNRTI, Shows Promise in Early Clinical Trials. Highleyman, Liz. HIVandHepatitis.com. 6 March 2013.
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| 3-Chloro-5-({1-[(4-methyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]-2-oxo-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-dihydro-3-pyridinyl}oxy)benzonitrile | |
| Clinical data | |
| Routes of administration | Oral[1] |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 1338225-97-0 |
| ATC code | none |
| PubChem | CID 58460047 |
| ChemSpider | 28424197 |
| UNII | 913P6LK81M |
| KEGG | D10624 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2364608 |
| Synonyms | MK-1439 |
| PDB ligand ID | 2KW (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C17H11ClF3N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 425.75 g/mol |
//////////Doravirine, MK-1439, 1338225-97-0 , Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, Reverse transcriptase inhibitor, ANTIVIRAL, Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase, HIV, Triazolinone, Pyridone, Inhibitor,
AND
Cn1c(n[nH]c1=O)Cn2ccc(c(c2=O)Oc3cc(cc(c3)Cl)C#N)C(F)(F)F