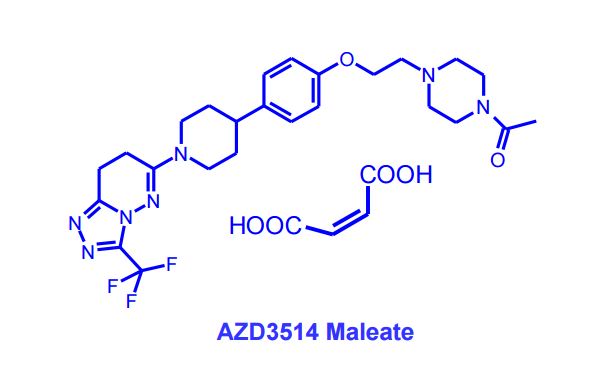
AZD3514; AZD 3514; AZD-3514.
CAS 1240299-33-5
Chemical Formula: C25H32F3N7O2
Exact Mass: 519.25696
Chemical Formula: C25H32F3N7O2
Exact Mass: 519.25696
1-(4-(2-(4-(1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl)piperidin-4-yl)phenoxy)ethyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethanone
Ethanone, 1-[4-[2-[4-[1-[7,8-dihydro-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]-4-piperidinyl]phenoxy]ethyl]-1-piperazinyl]
6-f4-{4-[2-f4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxylphenyl}piperidin-l-yl)-3-( trifluoromethyr)-7,8-dihvdro [ 1 ,2,41 triazolo [4,3-bl pyridazine
6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l- vDethoxyl phenyllpiperidin- l-vD-3-f trifluoromethyl)-7.,8-(iihv(iro [ 1 ,2,41 triazolo [4,3- blpyridazine
- 1-[4-[2-[4-[1-[7,8-Dihydro-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]-4-piperidinyl]phenoxy]ethyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethanone
- Originator AstraZeneca
- Class Antineoplastics
- Mechanism of Action Androgen receptor antagonists
AZD-3514 is a potent androgen receptor downregulator with potential anticancer cancer activity. AZD3514 is being evaluated in a Phase I clinical trial in patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
AZD3514 is currently in Phase I trail. This trial is looking at a new drug called AZD3514 for men who have prostate cancer that has spread to other parts of the body and is no longer responding to hormone therapy. Doctors often use hormone therapy to treat prostate cancer. This may keep it under control for long periods of time. But researchers are looking for treatments that will help men who have prostate cancer that stops responding to hormone therapy. Prostate cancer needs the hormone testosterone to grow. The testosterone locks into receptors on the cancer cells. AZD3514 works by breaking down these receptors so that testosterone canÂ’t tell the prostate cancer cells to grow.
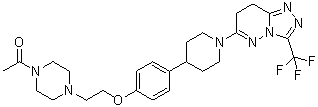
6-(4-{4-[2-(4-Acetylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-ihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine
as a white, free flowing solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.62 (2H, m), 1.88 (2H, m), 2.02 (3H, s), 2.49 (4H, m), 2.65 - 2.78 (5H, m), 2.94 (2H, m), 3.15 (2H, t), 3.42 (2H, m), 3.57 (2H, m), 4.03 (2H, t), 4.24 (2H, m), 6.80 (2H, d), 7.06 (2H, d);
m/z = 520 [M+H]+. RT = 0.87: 99% purity.
HRMS found 520.26373,
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of death from cancer among men in developed countries, and was projected to account for 25% of newly-diagnosed cases and 9% of deaths due to cancer in the USA in 2010. The androgen receptor (AR), a ligand binding transcription factor in the nuclear hormone receptor super family, is a key molecular target in the etiology and progression of prostate cancer.Binding of the endogenous AR ligand dihydrotestosterone stabilizes and protects the AR from rapid proteolytic degradation. The early stages of prostate cancer tumor growth are androgen dependent and respond well to androgen ablation, either via surgical castration or by chemical castration with a luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist in combination with an AR antagonist, such as bicalutamide.
Although introduction of androgen deprivation therapy represented a major advance in prostate cancer treatment, recurrence within 1–2 years typically marks transition to the so-called castrate-resistant state, in which the tumor continues to grow in the presence of low circulating endogenous ligand and is no longer responsive to classical AR antagonists. Castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is a largely unmet medical need with a 5-year survival rate of less than 15%. Antimitotic agents docetaxel and cabazitaxel, testosterone biosynthesis inhibitor abiraterone acetate and second generation AR antagonist enzalutamide (MDV3100) are the currently approved small-molecule drugs that have been shown to provide survival benefit.
Recent evidence from both pre-clinical and clinical studies is consistent with the importance of re-activation of AR signaling in a majority of castrate-resistant prostate tumors. It is also well established that the functional AR in castrate-resistant tumors is frequently mutated or amplified, and that over-expression can convert hormone-responsive cell lines to hormone refractory. Recent second-generation AR antagonists have been designed that retain antagonism in over-expressing cell lines, and among these agents enzalutamide has recently successfully met efficacy criteria in a large Phase III clinical trial.
By analogy with fulvestrant, an estrogen receptor (ER) downregulator approved by the FDA in 2002 for treatment of advanced breast cancer and initially characterized as a pure ER antagonist, a ligand which downregulates the AR represents one of a number of potential approaches to treatment of CRPC via a sustained reduction in tumor AR content. We recently described derivation from a novel 3-(trifluoromethyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine ligand of AR inhibitor 1 The compound also causes AR downregulation15 and high plasma levels following oral administration in pre-clinical models compensate for moderate cellular potency
Figure 1.

Structures of lead AR downregulator 1 and chemotype 2.
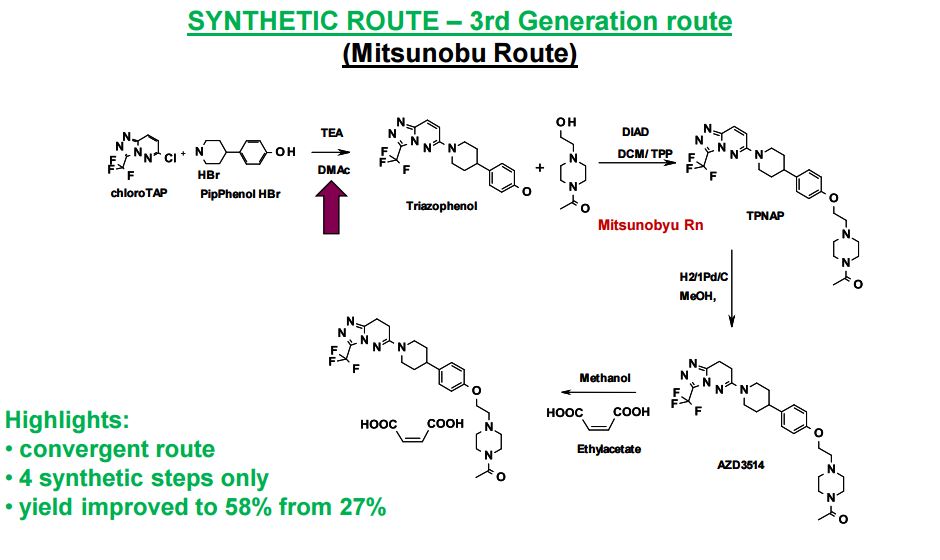
Scheme 3.

Synthesis of compounds 10, 11a–b, 12. Reagents and conditions: (a) 2-(1-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)ethanol,27 Ph3P, diisopropyl azodicarboxylate, THF, 20 °C; (b) 2-(4-acetylpiperazine-1-yl)ethanol,28 Ph3P, diisopropyl azodicarboxylate, THF, 20 °C; (c) H2, 10% Pd-C, MeOH, 50 °C.
PATENT
| Robert Hugh Bradbury, Gregory Richard Carr,Alfred Arthur Rabow, Korupoju Srinivasa Rao,Harikrishna Tumma, | |
| Applicant | Astrazeneca Ab, Astrazeneca Uk Limited |
Preparation of 6-f4-{4-[2-f4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxylphenyl}piperidin-l-yl)-3-
( trifluoromethyr)-7,8-dihvdro [ 1 ,2,41 triazolo [4,3-bl pyridazine
A solution of acetyl chloride (0.027 mL, 0.38 mmol) in DCM (0.5 mL) was added dropwise to 6-[4- [4- [2-(piperazin- 1 -yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin- 1 -yl] -3 -(trifluoromethyl)- 7,8-dihydro-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (150 mg, 0.31 mmol) and triethylamine (0.088 mL, 0.63 mmol) in DCM (1 mL) cooled to 00C under nitrogen. The resulting solution was stirred at 00C for 5 minutes then allowed to warm to room temperature and stirred for 15 minutes. The reaction mixture was diluted with water (2 mL), passed through a phase separating cartridge and then the organic layer was evaporated to afford crude product. The crude product was purified by preparative HPLC (Waters XBridge Prep Cl 8 OBD column, 5μ silica, 19 mm diameter, 100 mm length), using decreasingly polar mixtures of water (containing 1% ammonia) and MeCN as eluents. Fractions containing the desired compound were evaporated to dryness to give 6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l- yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-l-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3- b]pyridazine (80 mg, 49%) as a gum.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, CDC13) δ 1.69 (2H, m), 1.95 (2H, m), 2.08 (3H, s), 2.56 (4H, m), 2.71 - 2.84 (5H, m), 3.00 (2H, m), 3.22 (2H, t), 3.48 (2H, m), 3.63 (2H, m), 4.10 (2H, t), 4.31 (2H, m), 6.86 (2H, d), 7.12 (2H, d); m/z = 520 [M+H]+.
The 6-[4-[4-[2-(piperazin- 1 -yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin- 1 -yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8- dihydro-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine used as starting material was prepared as follows :-
Preparation of tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-(l-(benzyloxycarbonyl)-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4- yl)phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l-carboxylate DIAD (12.60 mL, 64.00 mmol) was added dropwise to benzyl 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5,6- dihydropyridine-l(2H)-carboxylate (obtained as described in Example 4.1, preparation of starting materials) (16.5 g, 53.34 mmol), tert-butyl 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-l- carboxylate (CAS 77279-24-4) (14.74 g, 64.00 mmol) and triphenylphosphine (16.79 g, 64.00 mmol) in THF (150 mL) under nitrogen. The resulting solution was stirred at ambient temperature for 16 hours. The reaction mixture was evaporated to dryness then the residue was stirred in ether (200 mL) for 10 minutes at room temperature. The resulting precipitate was removed by filtration and discarded. The ether filtrate was washed with water (100 mL) followed by saturated brine (100 mL), then dried over MgSO4, filtered and evaporated to give crude product. The crude product was purified by flash silica chromatography, elution gradient 20 to 60% EtOAc in isohexane. Fractions containing the desired product were evaporated to dryness to afford tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-(l- (benzyloxycarbonyl)- 1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl)phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l- carboxylate (34.6 g, 82%) as a gum which was contaminated with 34% by weight triphenylphosphine oxide.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.40 (9H, s), 2.42 - 2.47 (6H, m), 2.71 (2H, m), 3.32 (4H, m), 3.62 (2H, m), 4.03 - 4.10 (4H, m), 5.12 (2H, s), 6.06 (IH, m), 6.92 (2H, d), 7.31 - 7.40 (7H, m); m/z = 522 [M+H]+.
Preparation of tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l- carboxylate tert-Butyl 4-[2-[4-(l-(benzyloxycarbonyl)-l,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4- yl)phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l-carboxylate (66% pure by weight) (34.62 g, 43.80 mmol) and 5% palladium on carbon (50% wet) (4.47 g, 1.05 mmol) in MeOH (250 mL) were stirred under an atmosphere of hydrogen at 5 bar and 600C for 4 hours. The catalyst was removed by filtration and the solvents evaporated to give crude product. The crude product was purified by flash silica chromatography, eluting with 60% EtOAc in isohexane then 15% 2M ammonia/MeOH in DCM. Pure fractions were evaporated to dryness to afford tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l-carboxylate (15.42 g, 90%) as a solid. IH NMR (399.9 MHz, CDC13) δ 1.46 (9H, s), 1.62 (2H, m), 1.81 (2H, m), 2.50 - 2.59 (5H, m), 2.73 (2H, m), 2.80 (2H, t), 3.18 (2H, m), 3.44 (4H, m), 4.09 (2H, t), 6.85 (2H, d), 7.13 (2H, d); m/z = 390 [M+H]+.
Preparation of tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-[l-(3-(trifluoromethyl)-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3- b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl]phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l-carboxylate
DIPEA (2.348 mL, 13.48 mmol) was added to 6-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)- [l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (obtained as described in Monatsh. Chem. 1972, 103, 1591) (2 g, 8.99 mmol) and tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l- carboxylate (3.68 g, 9.44 mmol) in DMF (30 mL). The resulting solution was stirred at 800C for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and the solvents evaporated to dryness. The resulting solid was triturated with water then collected by filtration, washed with ether and dried to afford tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-[l-(3-(trifluoromethyl)- [l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl]phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l -carboxylate (5.02 g, 97%) as a solid.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, CDC13) δ 1.46 (9H, s), 1.76 (2H, m), 2.00 (2H, m), 2.54 (4H, m), 2.75 - 2.86 (3H, m), 3.11 (2H, m), 3.46 (4H, m), 4.11 (2H, m), 4.37 (2H, m), 6.87 (2H, d), 7.13 (3H, m), 7.92 (IH, d); m/z = 576 [M+H]+.
Preparation of tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-[l-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro-
[1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazin-6-yl)piperidin-4-yl] phenoxy] ethyl] piperazine- 1- carboxylate
10% Palladium on carbon (0.924 g, 0.87 mmol) was added to tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-[l-(3- (trifluoromethyl)-[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4- yl]phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l -carboxylate (2.5 g, 4.34 mmol) and ammonium formate (2.74 g, 43.43 mmol) in ethanol (100 mL). The resulting mixture was stirred at 78°C, with further portions of ammonium formate being added every 5 hours until the reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and the catalyst was removed by filtration. The filtrate was evaporated to dryness, redissolved in DCM (100 mL) and the solution was washed with water (100 mL) followed by brine (50 mL), then the solvents were evaporated to afford tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-[l-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro- [l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyπdazin-6-yl)pipeπdin-4-yl]phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l-carboxylate (2.02O g, 81%) as a solid.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, CDC13) δ 1.46 (9H, s), 1.69 (2H, m), 1.95 (2H, m), 2.52 (4H, m), 2.71 - 2.82 (5H, m), 3.00 (2H, m), 3.22 (2H, t), 3.45 (4H, m), 4.09 (2H, m), 4.31 (2H, m), 6.86 (2H, d), 7.12 (2H, d); m/z = 578 [M+H]+.
Preparation of 6- [4-[4- [2-(piperazin-l-yl)ethoxy] phenyl] piperidin-1-yl] -3- (trifluor omethyl)-7,8-dihydr o- [ 1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazine
TFA (10 mL) was added to tert-butyl 4-[2-[4-[l-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro- [l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyπdazin-6-yl)pipeπdin-4-yl]phenoxy]ethyl]piperazine-l-carboxylate (2.02 g, 3.50 mmol) in DCM (10 mL). The resulting solution was stirred at ambient temperature for 1 hour then added to an SCX column. The desired product was eluted from the column using 2M ammonia/MeOH and the solvents were evaporated to afford 6-[4-[4- [2-(piperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin-l-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro- [l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (1.660 g, 99%) as a solid.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, CDC13) δ 1.68 (2H, m), 1.95 (2H, m), 2.55 (4H, m), 2.70 - 2.80 (5H, m), 2.91 (4H, m), 3.00 (2H, m), 3.22 (2H, t), 4.09 (2H, t), 4.30 (2H, m), 6.87 (2H, d), 7.11 (2H, d); m/z = 478 [M+H]+.
Example 5.2
Larger scale preparation of 6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l- vDethoxyl phenyllpiperidin- l-vD-3-f trifluoromethyl)-7.,8-dihvdro [ 1 ,2,41 triazolo [4,3- blpyridazine
Ammonium formate (99 g, 1568.94 mmol) was added to 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l- yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin- 1 -yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)[ 1 ,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (81.2 g, 156.89 mmol) and 10% palladium on carbon (8.35 g, 7.84 mmol) in EtOH (810 mL) under nitrogen. The resulting mixture was stirred at 700C for 6 hours, then ammonium formate (50 g) was added. The mixture was stirred at 700C for 2 hours then further portions of 10% palladium on carbon (8.35 g, 7.84 mmol) and ammonium formate (50 g) were added and stirring continued at 700C for a further 10 hours. Ammonium formate (50 g) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at 700C for 24 hours then cooled to room temperature. The catalyst was removed by filtration and the reaction charged with further 10% palladium on carbon (8.35 g, 7.84 mmol) and stirred at 700C for 16 hours. Further ammonium formate (50 g) was added and the stirring continued for 5 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and a further portion of 10% palladium on carbon (8.35 g, 7.84 mmol) was added. The mixture was heated to 700C for a 30 hours, cooled to room temperature and the catalyst removed by filtration and washed with EtOH. The solvent was evaporated and the residue dissolved in DCM (500 mL) and the solution washed with water (500 mL). The aqueous layer was re-extracted with DCM (500 mL), then EtOAc (500 mL x 2). The combined extracts were dried over MgSO4, filtered and evaporated to give crude product. The crude product was purified by flash silica chromatography, elution gradient 0 to 5% MeOH in DCM. Pure fractions were evaporated to dryness to afford a gum, which was slurried with ether (300 mL) and re-evaporated. Methyl tert-butyl ether (250 mL) was added and the mixture was stirred vigorously for 3 days. The solid was collected by filtration and dried to afford 6-(4-{4-[2-(4- acetylpiperazin- 1 -yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin- 1 -yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8- dihydro[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (60.8 g, 75%) as a solid.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, CDC13) δ 1.62 (2H, m), 1.88 (2H, m), 2.02 (3H, s), 2.49 (4H, m), 2.65 - 2.78 (5H, m), 2.94 (2H, m), 3.15 (2H, t), 3.42 (2H, m), 3.57 (2H, m), 4.03 (2H, t), 4.24 (2H, m), 6.80 (2H, d), 7.06 (2H, d); m/z = 520 [M+H]+.
The 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin-l-yl]-3-
(trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine used as starting material was prepared as follows :-
Preparation of 4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenol Benzyl 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridine-l(2H)-carboxylate (obtained as described in Example 4.1, preparation of starting materials) (37.7 g, 121.86 mmol) and 5% palladium on carbon (7.6 g, 3.57 mmol) in methanol (380 mL) were stirred under an atmosphere of hydrogen at 5 bar and 25°C for 2 hours. The catalyst was removed by filtration, washed with MeOH and the solvents evaporated. The crude material was triturated with diethyl ether, then the desired product collected by filtration and dried under vacuum to afford 4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenol (20.36 g, 94%) as a solid. IH NMR (399.9 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.46 (2H, m), 1.65 (2H, m), 2.45 (IH, m), 2.58 (2H, m), 3.02 (2H, m), 6.68 (2H, d), 7.00 (2H, d), 9.15 (IH, s); m/z = 178 [M+H]+.
Preparation of 4- { 1- [3-(trifluor omethyl) [1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazin-6-yl] piperidin- 4-yl}phenol
DIPEA (48.2 mL, 276.86 mmol) was added to 6-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)- [l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (obtained as described in Monatsh. Chem. 1972, 103, 1591) (24.65 g, 110.74 mmol) and 4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenol (20.61 g, 116.28 mmol) in DMF (200 mL). The resulting solution was stirred at 800C for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, then evaporated to dryness and re-dissolved in DCM (1 L) and washed with water (2 x 1 L). The organic layer was washed with saturated brine (500 mL), then dried over MgSO4, filtered and evaporated to afford crude product. The crude product was triturated with ether to afford 4-{l-[3- (trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl}phenol (36.6 g, 91%) as a solid.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.64 (2H, m), 1.87 (2H, m), 2.75 (IH, m), 3.09 (2H, m), 4.40 (2H, m), 6.69 (2H, d), 7.05 (2H, d), 7.65 (IH, d), 8.24 (IH, d), 9.15 (IH, s); m/z = 364 [M+H]+.
Preparation of 2-(4-{l-[3-(trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6- yl]piperidin-4-yl}phenoxy)ethanol
A solution of ethylene carbonate (121 g, 1376.13 mmol) in DMF (200 mL) was added dropwise to a stirred suspension of 4-{l-[3-(trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3- b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl}phenol (100 g, 275.23 mmol) and potassium carbonate (76 g, 550.45 mmol) in DMF (200 mL) at 800C over a period of 15 minutes under nitrogen.
The resulting mixture was stirred at 800C for 20 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, then concentrated and diluted with DCM (2 L), and washed sequentially with water (1 L) and saturated brine (500 mL). The organic layer was dried over MgSO4, filtered and evaporated to afford crude product. The crude product was purified by flash silica chromatography, elution gradient 70 to 100% EtOAc in isohexane. Fractions containing the desired product were evaporated to dryness then triturated with EtOAc (150 mL). The resulting solid was washed with further EtOAc (50 mL) and ether then dried to give 2-(4- { 1 -[3-(trifluoromethyl)[ 1 ,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4- yl}phenoxy)ethanol. The filtrate was evaporated and further purified by flash silica chromatography, elution gradient 70 to 100% EtOAc in isohexane. Fractions containing the desired product were evaporated to dryness then triturated with ether, dried and combined with the material previously collected to afford 2-(4- { 1 -[3-
(trifluoromethyl)[ 1 ,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl}phenoxy)ethanol (89 g, 79%) as a solid.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.66 (2H, m), 1.88 (2H, m), 2.80 (IH, m), 3.10 (2H, m), 3.70 (2H, m), 3.95 (2H, t), 4.41 (2H, m), 4.85 (IH, t), 6.87 (2H, d), 7.18 (2H, d), 7.67 (IH, d), 8.25 (IH, d); m/z = 408 [M+H]+.
Preparation of 2-(4-{ 1- [3-(trifluoromethyl) [ 1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazin-6- yl] piperidin-4-yl}phenoxy)ethyl methanesulfonate
A solution of methanesulfonyl chloride (20.37 mL, 262.16 mmol) in DCM (300 mL) was added to 2-(4- { 1 -[3-(trifluoromethyl)[ 1 ,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4- yl}phenoxy)ethanol (89 g, 218.46 mmol) and triethylamine (60.9 mL, 436.93 mmol) in DCM (900 mL) at 00C over a period of 30 minutes under nitrogen. The resulting solution was stirred at 00C for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was diluted with DCM (1 L), and washed with water (2 L). The organic layer was dried over MgSO4, filtered and evaporated to afford 2-(4- { 1 -[3-(trifluoromethyl)[ 1 ,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4- yl}phenoxy)ethyl methanesulfonate (104 g, 98%) as a solid.
IH NMR (399.9 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 1.67 (2H, m), 1.89 (2H, m), 2.83 (IH, m), 3.11 (2H, m), 3.23 (3H, s), 4.23 (2H, t), 4.41 (2H, m), 4.52 (2H, t), 6.91 (2H, d), 7.21 (2H, d), 7.66 (IH, d), 8.24 (IH, d); m/z = 486 [M+H]+. Preparation of 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin-l-yl]-3- (trifluor omethyl) [ 1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazine DIPEA (107 mL, 613.00 mmol) was added to 2-(4-{l-[3-
(trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl}phenoxy)ethyl methanesulfonate (99 g, 204.33 mmol) and N-acetylpiperazine (28.8 g, 224.77 mmol) in DMA (500 mL). The resulting solution was stirred at 1100C for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and the solvents were evaporated. The residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate (1 L) and the solution was washed with water (1 L). The aqueous was re-extracted with ethyl acetate (1 L) and the combined organics were washed with brine (1 L), dried over MgSO4, filtered and evaporated to give crude product. The aqueous layer was basifϊed to pH 12 with 2M NaOH, then extracted with ethyl acetate (1 L), washed with brine (IL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and evaporated to give further crude product. The crude product was purified by flash silica chromatography, elution gradient 0 to 3% MeOH in DCM then 5% MeOH in DCM. Pure fractions were evaporated to give 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin-l-yl]-3- (trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (81 g, 77%) as a solid. IH NMR (399.9 MHz, DMS0-d6) δ 1.59-1.73 (2H, m), 1.87 (2H, d), 1.99 (3H, s), 2.42 (2H, t), 2.71 (2H, t), 2.76-2.86 (IH, t), 3.08 (2H, t), 3.38-3.47 (4H, m), 4.08 (2H, t), 4.41 (2H, d), 6.88 (2H, d), 7.18 (2H, d), 7.62 (IH, d), 8.26 (IH, d); m/z = 518 [M+H]+.
Example 5.5
Alternative route for the preparation of 6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l- vDethoxyl phenyllpiperidin- l-vD-3-f trifluoromethyl)-7.,8-(iihv(iro [ 1 ,2,41 triazolo [4,3- blpyridazine Form A
Methanol (375.0 mL) was added to 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l- yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin-l-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)[ 1,2,4] triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (25.0 g, 48 m mol) in a 2.0 L autoclave reactor and to this was added 10% Pd/C (12.5 g, 50% w/w) paste at 22-25°C under nitrogen gas atmosphere. The reaction was performed under hydrogen pressure (5.0 bar) at 500C temperature for 10.0 h. The reaction mass was cooled to room temperature and the catalyst removed by filtration. Filtered cake was washed with methanol. The solvent was evaporated and the residue was azeotropically distilled by ethylacetate (2 x 125.0 mL) at 400C under reduced pressure to 3.0 rel vol (75.0 mL). Drop wise addition of tert-butylmethylether (MTBE, 375.0 mL) to the reaction mass resulted in solid material, which was collected by filtration and washed with MTBE (50.0 mL). The material was dried under reduced pressure with nitrogen gas bleed at 500C to afford the desired product 6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-l-yl)-3- (trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro[l,2,4]triazolo [4,3-b]pyridazine (22.3 g, 88%) as a white color free flowing solid. The isolated material was confirmed by XRPD as Form A. IH NMR (400.13 MHz, CDC13): δ 1.62 (2H, m), 1.88 (2H, m), 2.02 (3H, s), 2.49 (4H, m), 2.65 - 2.78 (5H, m), 2.94 (2H, m), 3.15 (2H, t), 3.42 (2H, m), 3.57 (2H, m), 4.03 (2H, t), 4.24 (2H, m), 6.80 (2H, d), 7.06 (2H, d); m/z = 520 [M+H]+.
The 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin-l-yl]-3- (trifluoromethyl)[ 1,2,4] triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine used as starting material was prepared as follows :-
Preparation of 4- { 1- [3-(trifluor omethyl) [1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazin-6-yl] piperidin- 4-yl}phenol: Dimethylacetamide (250.0 mL) was added to 6-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)- [l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine [CAS: 40971-95-7] (50.0 g, 225 m mol) at 22-25°C in a suitable round bottom flask followed by 4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenol [CAS: 62614-84-0] (60.9 g, 236 m mol) at 22-25°C. The reaction mass was stirred to obtain a clear solution. Triethylamine (79.1 mL, 561 m mol) was slowly added to the reaction mass by drop wise addition over a period of 60 min at 25-300C. Temperature was raised to 400C and the reaction mass stirred for 1.0 h. After completion of reaction, water (500.0 mL) was added to the reaction mass by drop wise addition over a period of 30 min at 40-430C. The slurry mass was stirred for 30 min at 400C and then filtered under reduced pressure. The wet material was slurry washed using water (500.0 mL) for 30 min at 400C. The solid was collected by filtration and the material washed with water (125.0 mL). The material was dried under reduced pressure with nitrogen gas bleed at 500C to afford the desired product 4-{l-[3-(trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl]piperidin-4-yl}phenol (75.1 g, 89.9%) as a free flowing solid. IH NMR (400.13 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 1.64 (2H, m), 1.87 (2H, m), 2.75 (IH, m), 3.09 (2H, m), 4.40 (2H, m), 6.69 (2H, d), 7.05 (2H, d), 7.65 (IH, d), 8.24 (IH, d), 9.15 (IH, s); m/z = 364 [M+H]+.
Preparation of 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin-l-yl]-3- (trifluor omethyl) [ 1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazine:
Dichloromethane (225.0 mL) and 4-{l-[3-(trifluoromethyl)[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin- 6-yl]piperidin-4-yl} phenol (50.0 g, 138 m mol) were charged to a suitable round bottom flask at 22-25°C. Triphenylphosphine (72.2 g, 275 m mol) and l-[4-(2-hydroxy- ethyl)piperazin-l-yl]ethanone [CAS: 83502-55-0] (47.4 g, 275 m mol) were added successively to the reaction mass and stirred for 10 min at 22-25°C. Di-isopropyl azodicarboxylate (55.65 g, 275 m mol) in dichloromethane (75.0 mL) was added to the reaction mass slowly drop wise at 25-300C over a period of 60-90 min. The resulting reaction mass was stirred for 1.0 h at 25-300C to complete the reaction. n-Heptane (600.0 mL) was introduced to the reaction mass by drop wise addition over a period of 15-30 min at 22-25°C and stirred for 30 min at the same temperature. Thus precipitated solid was filtered and washed with n-heptane (150.0 mL). The material was then suck dried for 30 min under reduced pressure. The crude material was purified by slurry washing in methanol (325.0 mL) at 22-25°C. The solid was then collected by filtration and washed with methanol (50.0 mL). The material was dired under reduced pressure with nitrogen gas bleed at 500C to afford the desired product 6-[4-[4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l- yl)ethoxy]phenyl]piperidin- 1 -yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)[ 1 ,2,4] triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (61.2 g, 84%) as a free flowing solid.
IH NMR (400.13 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 1.59-1.73 (2H, m), 1.87 (2H, d), 1.99 (3H, s), 2.42 (2H, t), 2.71 (2H, t), 2.76-2.86 (IH, t), 3.08 (2H, t), 3.38-3.47 (4H, m), 4.08 (2H, t), 4.41 (2H, d), 6.88 (2H, d), 7.18 (2H, d), 7.62 (IH, d), 8.26 (IH, d); m/z = 518 [M+H]+.
Example 5.8
Preparation of 6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-l-yl)-3-(trifluor omethyl)-7,8-dihydr 0 [1 ,2,4] triazolo [4,3-b] pyridazine maleate
A clear solution of maleic acid (0.445 g, 3.84 m mol) in methanol (1.0 mL) was added to a clear solution of 6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-l-yl)-3- (trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine, obtained as described in Example 5.5, (2.0 g, 3.84 m mol) in methanol (2.0 mL) at 22-25°C and the resulting clear solution heated to 500C for 30 min. The reaction mass was cooled to 22-25°C and ethylacetate (16.0 mL) added drop wise to the reaction mass at 22-25°C. The reaction mass was then stirred for 60 min at 22-25°C. The resulting white color material was collected by filtration and washed with ethylacetate (5.0 mL). The material was dried under reduced pressure with nitrogen gas bleed at 500C to afford the desired product 6-(4- {4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-l-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-l-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8- dihydro[l,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine maleate (2.21 g, 90.0%) as free flowing white color material.
IH NMR (400.13 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 1.62 (2H, m), 1.77 (2H, m), 2.02 (3H, s), 2.75 (IH, m), 2.77 (2H, m), 2.80 (2H, m), 2.95 (4H, m), 3.16 (2H, t), 3.36 (6H, m), 4.22 (4H, m), 6.08 (2H, s), 6.91 (2H, d), 7.17 (2H, d).
PAPER
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Apr 1;23(7):1945-8
Volume 23, Issue 7, 1 April 2013, Pages 1945–1948
Discovery of AZD3514, a small-molecule androgen receptor downregulator for treatment of advanced prostate cancer
- Oncology iMed, AstraZeneca, Mereside, Alderley Park, Macclesfield SK10 4TG, UK
Removal of the basic piperazine nitrogen atom, introduction of a solubilising end group and partial reduction of the triazolopyridazine moiety in the previously-described lead androgen receptor downregulator 6-[4-(4-cyanobenzyl)piperazin-1-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (1) addressed hERG and physical property issues, and led to clinical candidate 6-(4-{4-[2-(4-acetylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine (12), designated AZD3514, that is being evaluated in a Phase I clinical trial in patients with castrate-resistant prostate cancer.

SYNTHESIS
6-(4-{4-[2-(4-Acetylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}piperidin-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-7,8-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine AZD 3514
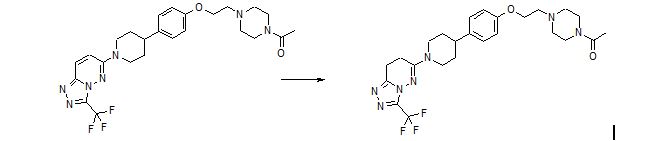
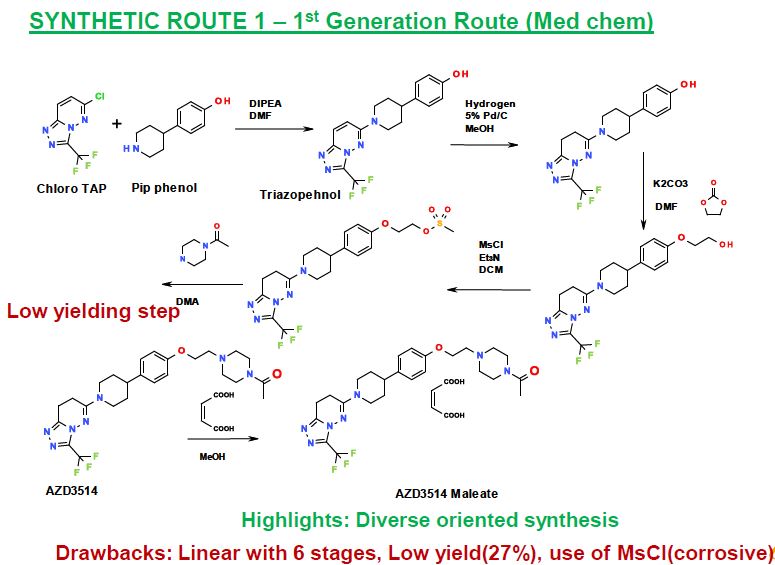
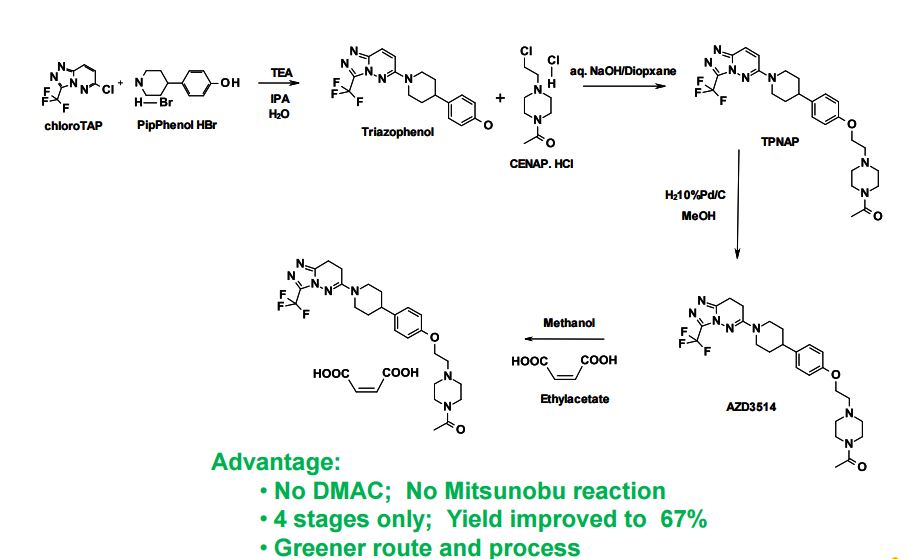
SYNTHETIC ROUTE 2ND GENERATION
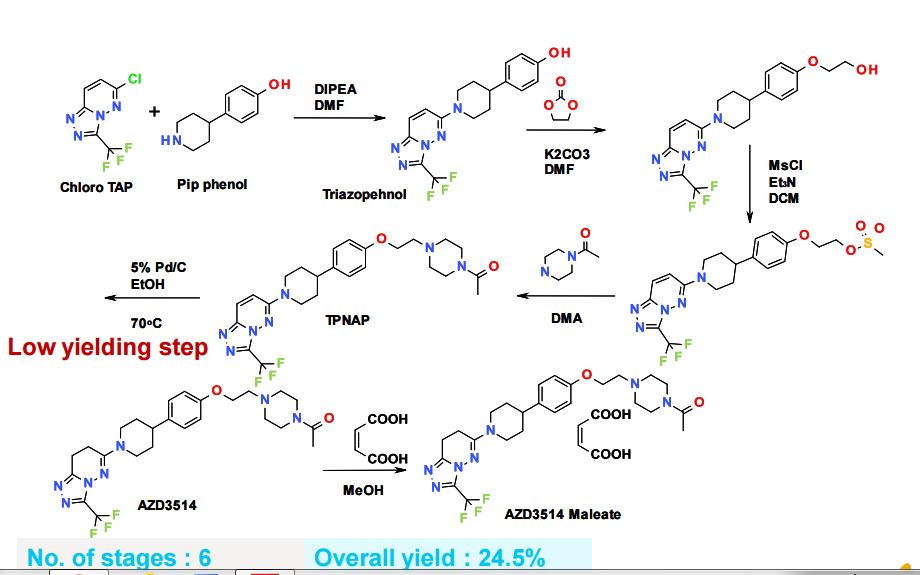
SYNTHETIC ROUTE 4TH GENERATION
REFERENCES
1: Bradbury RH, Acton DG, Broadbent NL, Brooks AN, Carr GR, Hatter G, Hayter BR, Hill KJ, Howe NJ, Jones RD, Jude D, Lamont SG, Loddick SA, McFarland HL, Parveen Z, Rabow AA, Sharma-Singh G, Stratton NC, Thomason AG, Trueman D, Walker GE, Wells SL, Wilson J, Wood JM. Discovery of AZD3514, a small-molecule androgen receptor downregulator for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Apr 1;23(7):1945-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.02.056. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PubMed PMID: 23466225.














Some pics, Team at Astrazeneca , Bangalore, INDIA

Vijaykumar Sengodan Chellappan

Jagannath V, PMP®

Associate Research Scientist II at AstraZeneca India Pvt Ltd

Rifahath Mon
Associate Research Scientist at AstraZeneca

Route Scouting, Process Design, Technology Transfer, Trouble shooting, QbD, Green Chemistry

Srinivasa Rao Korupoju

Harikrishna Tumma Ph. D.

Rashmi HV

Anandan Muthusamy

Partha Pratim Bishi,


Its party time — with Anandan Muthusamy, Santosh Kumar, Rifahath Mon NP, Vidya Nandialath andPartha Pratim Bishi.


ASTAZENECA BANGALORE
2010-Away day — with Andiappan Murugan, Shilpa C Patil, Jyoti Solapure, Jnaneshwara G K Kindel,Sidda Lingesha, Mahesh Dange, Avipsa Ghosh,Vidya Nandialath, Ranga Nc, Jayan Rappai andPartha Pratim Bishi.
///////////////AZD 3514 MALEATE, AZD 3514 , AZD-3514, Prostate cancer, Androgen receptor downregulator, AZD3514, 1240299-33-5